The United States
1. The Senate on Thursday failed to clear a procedural vote on a crucial government funding package, with a shutdown set to begin on Saturday at 12:01 ET.

Source: CNBC
2. Initial jobless claims remained low at 209k, slightly above consensus.
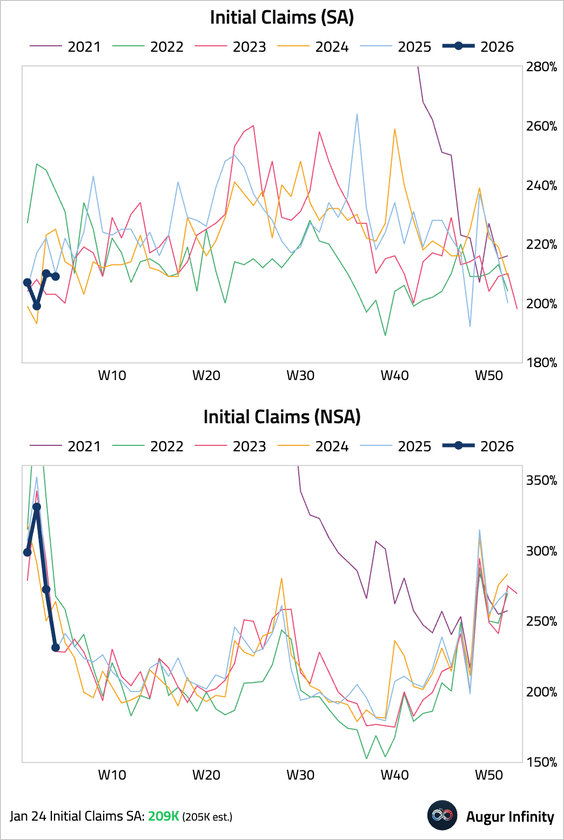
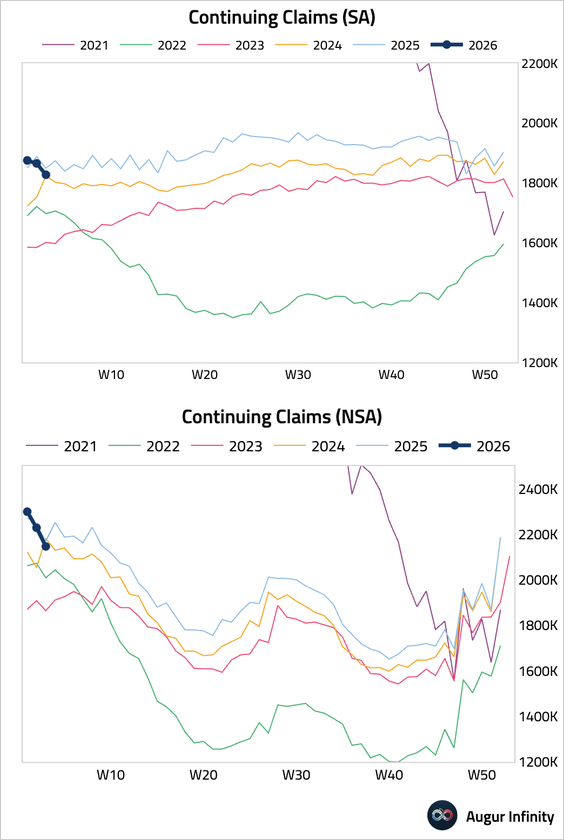
• Continuing claims fell to 1.827 million, suggesting the unemployed are finding work quickly. The data may reflect weak seasonal hiring in Q4, which has resulted in fewer post-holiday layoffs.
3. Factory orders rebounded, well ahead of consensus.
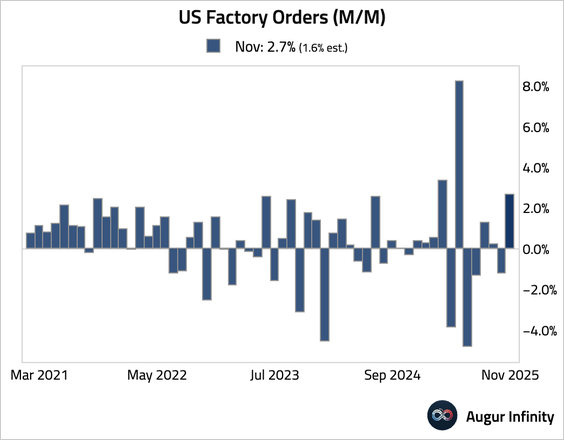
• The headline strength, however, was driven by the volatile transportation sector. Excluding transportation, orders improved by a meager 0.2%.
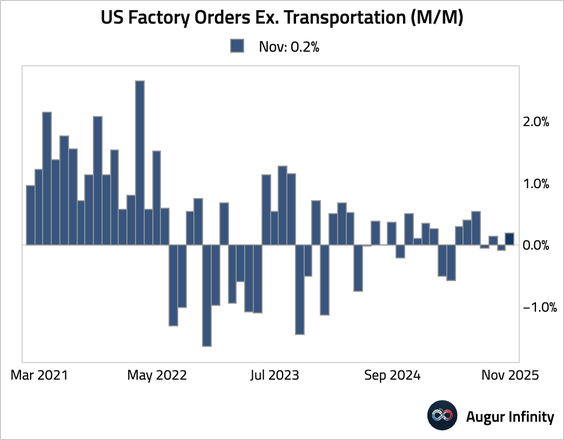
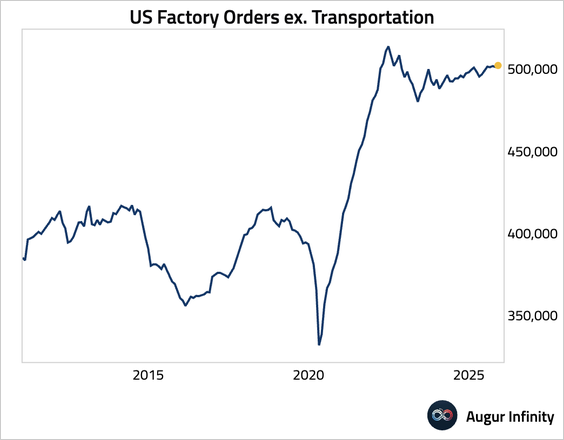
– In level terms, factory orders excluding transportation have been stagnant over the past three years.
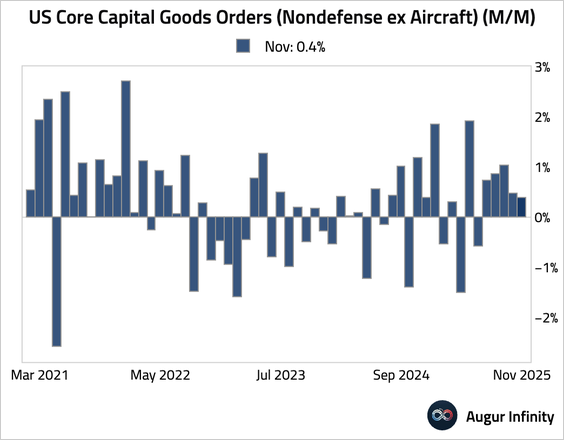
• Growth in core capital goods orders was revised down by 0.3 percentage points to 0.4%.
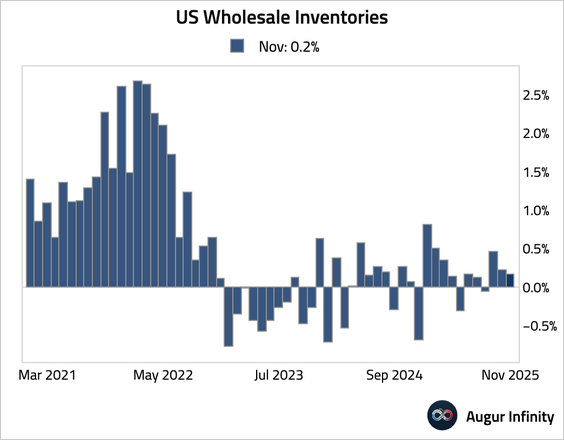
4. Wholesale inventories increased modestly.
5. The trade deficit widened significantly more than expected, driven by a sharp drop in exports and a surge in imports, reversing the prior two months of narrowing …
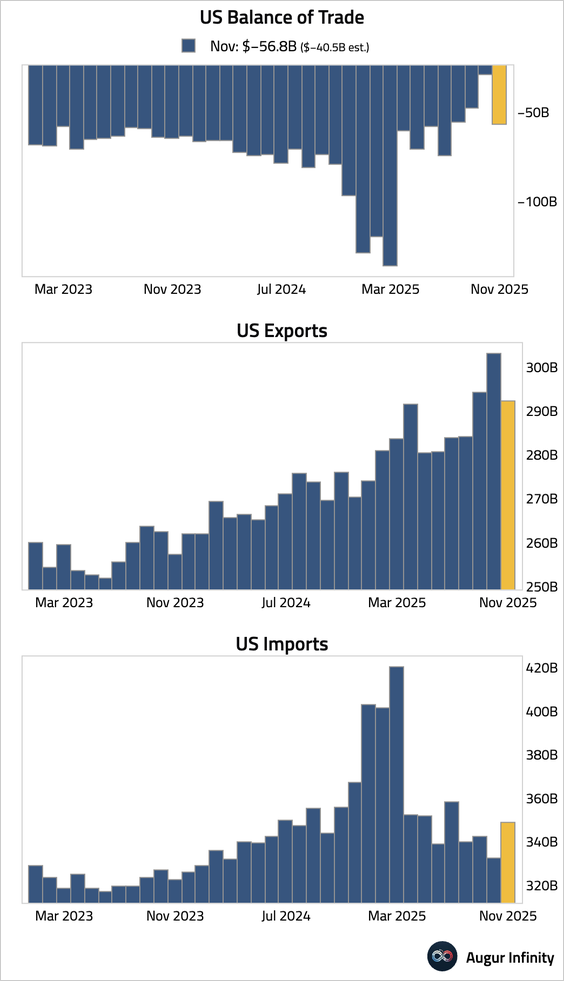
… amid some payback in gold-related exports and large moves in pharmaceuticals.
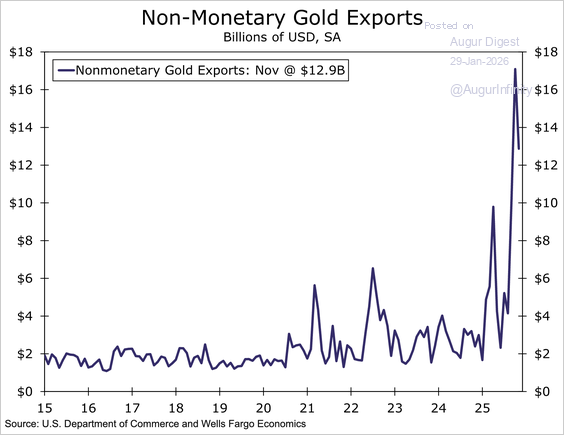
Source: Wells Fargo
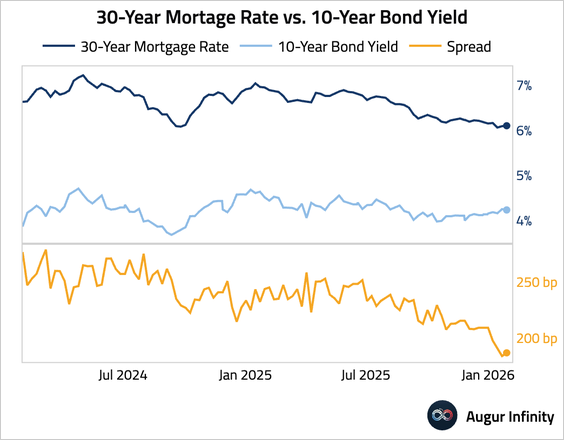
6. Mortgage rates ticked higher, with the average 30-year fixed rate rising to 6.1%.
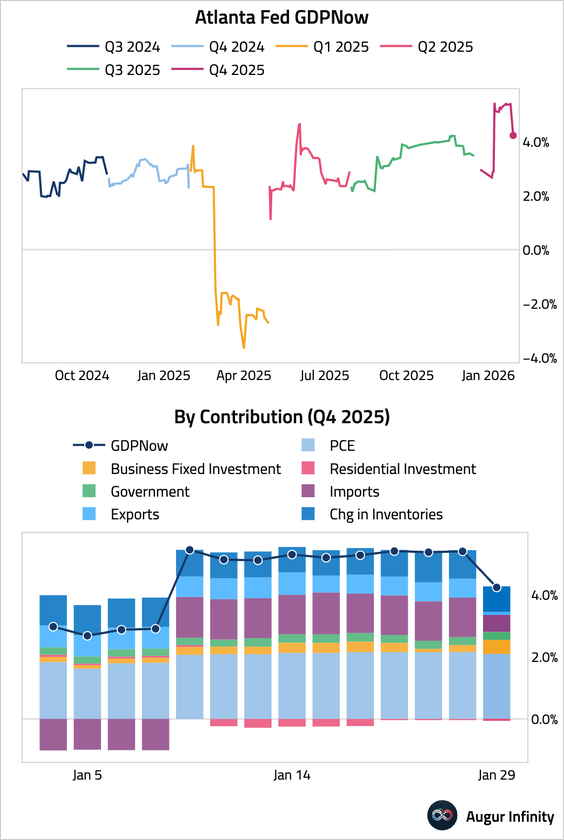
7. The Atlanta Fed's GDPNow model is now tracking Q4 GDP at 4.2%, down from 5.4% on January 26.
8. Population growth slowed to 0.5% in 2025, driven primarily by a sharp pullback in immigration, while growth remained concentrated in the South and Mountain West.
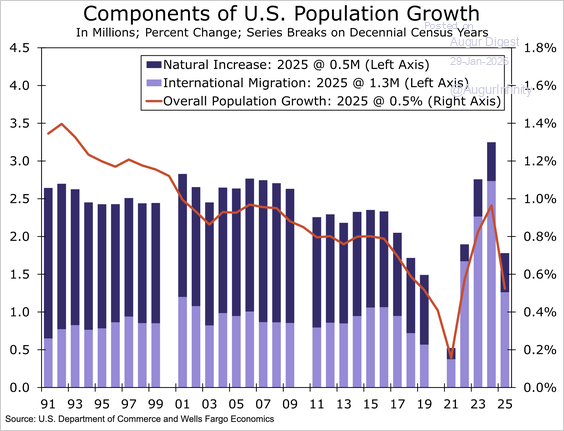
Source: Wells Fargo
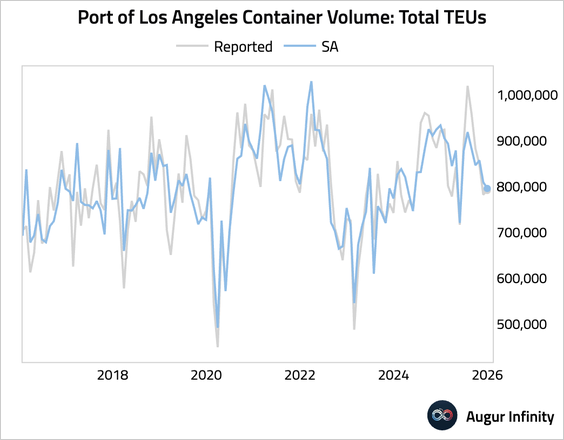
9. Container volume at the Port of Los Angeles fell further in December on a seasonally adjusted basis.
10. The share of bachelor’s graduates starting a job in their graduation year has fallen to about 36.6% for the 2025 cohort, extending a decline that began in 2023 as post-pandemic hiring cooled. The share of graduates finding a job in their field of study also inched down.
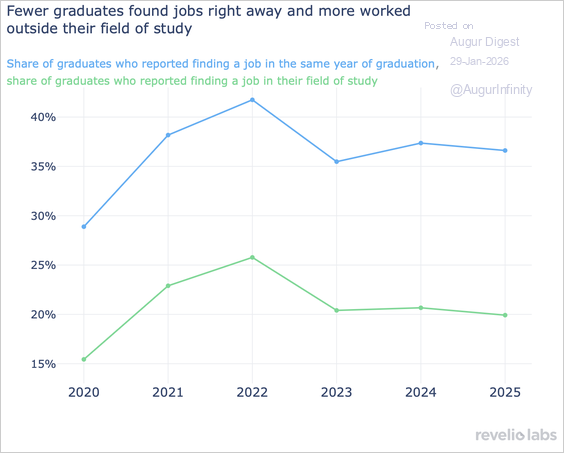
Source: Revelio Labs Read full article
Canada
1. The trade deficit widened unexpectedly as exports fell while imports remained little changed.
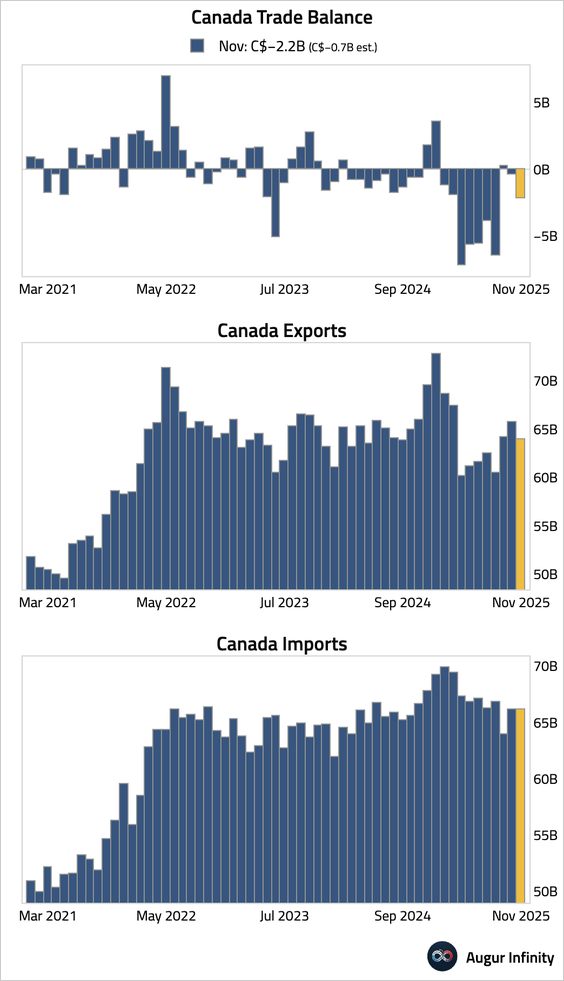
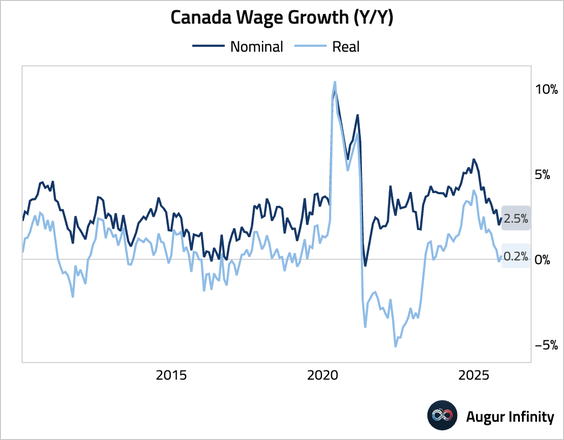
2. Average weekly earnings growth accelerated.
The United Kingdom
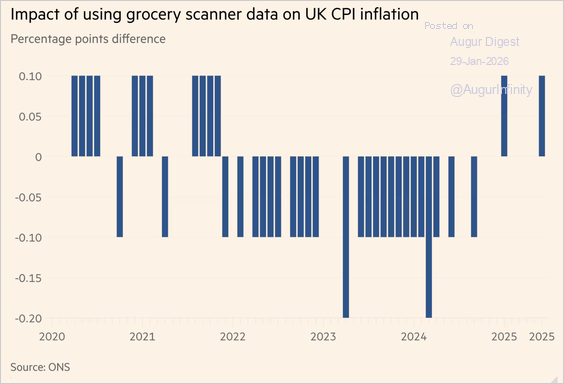
1. The ONS will revamp CPI measurement starting next month by incorporating over a billion supermarket scanner and online sales data and expanding hotel price sampling. A historical analysis showed only modest impacts on the headline rate.
Source: @financialtimes Read full article
The Eurozone
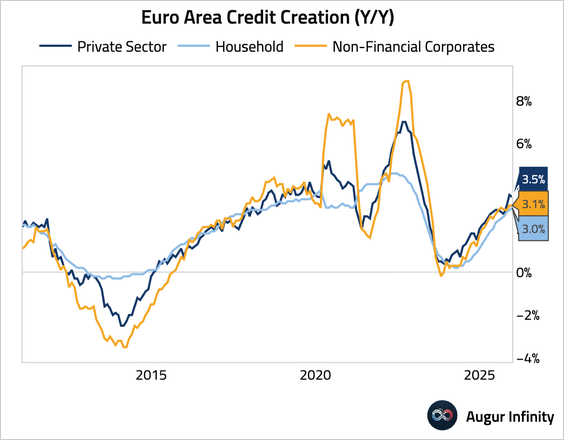
1. Euro area credit growth remained resilient. Household credit creation accelerated slightly, while growth in lending to non-financial corporates eased.
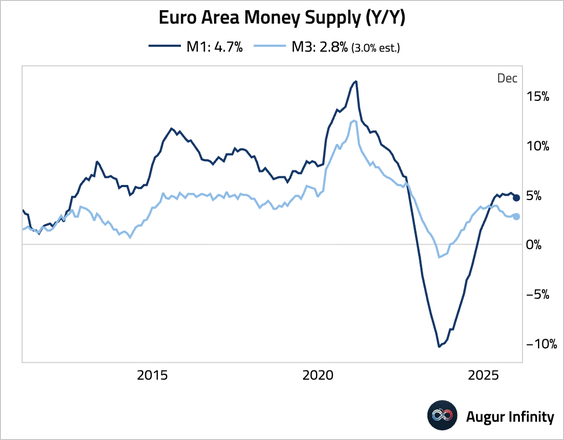
– Money growth slowed modestly.
• Euro area economic sentiment rose to 99.4, well above expectations and its highest level in three years.
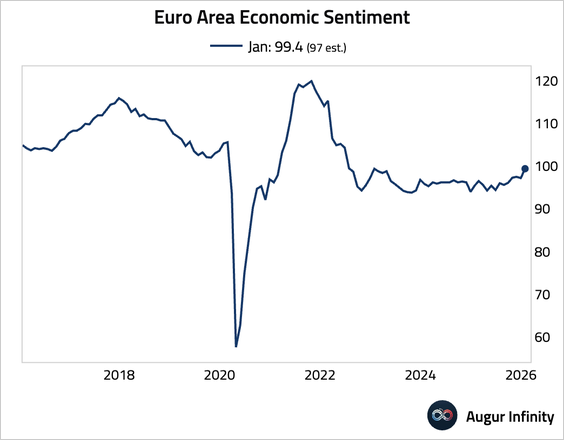
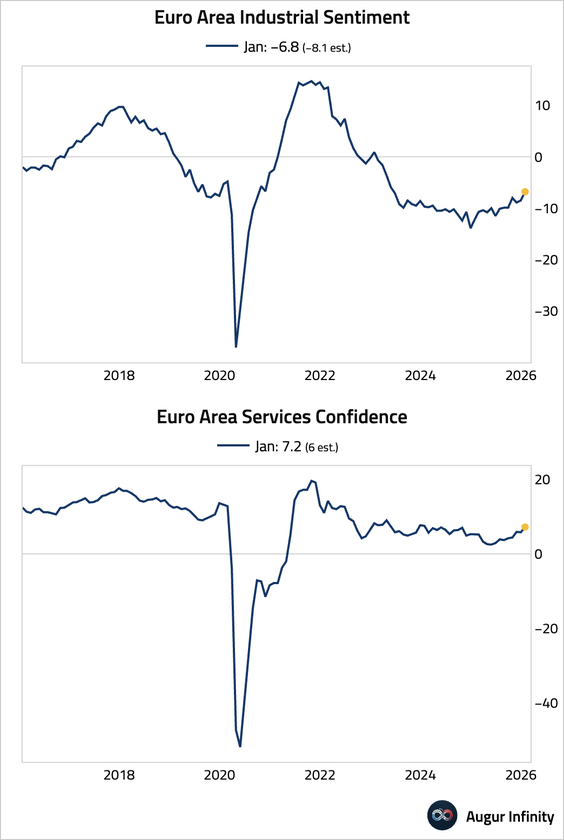
– The improvement was broad-based across both industrial and services sectors, led by a surge in employment expectations.
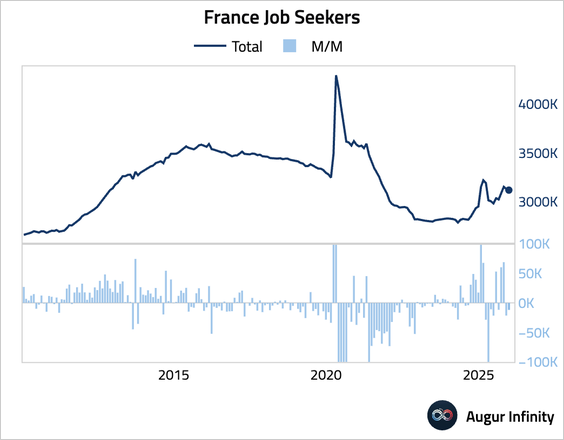
2. The number of jobseekers in France continued to decline, though at a slower pace than in the prior month.
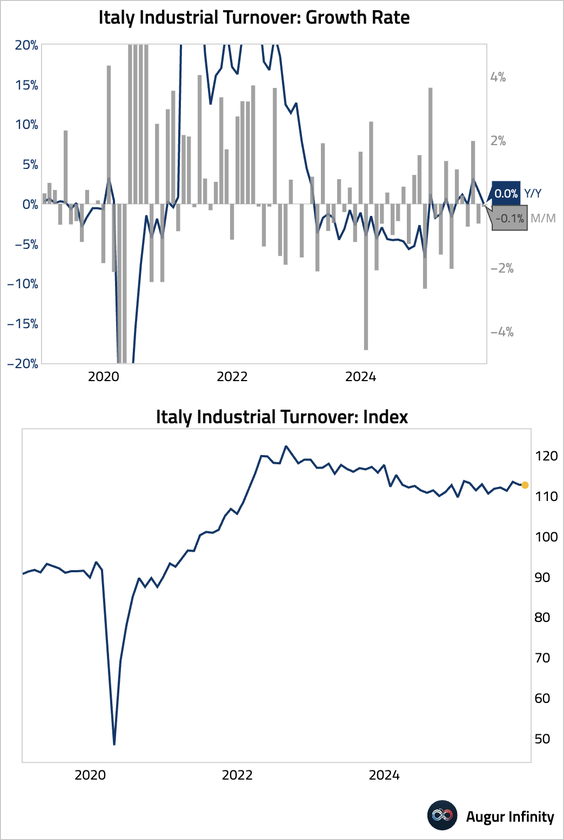
3. Italian industrial sales contracted for a second consecutive month, and year-over-year growth stalled.
4. Spanish retail sales saw broad-based declines, as consumers tightened spending over the holidays.
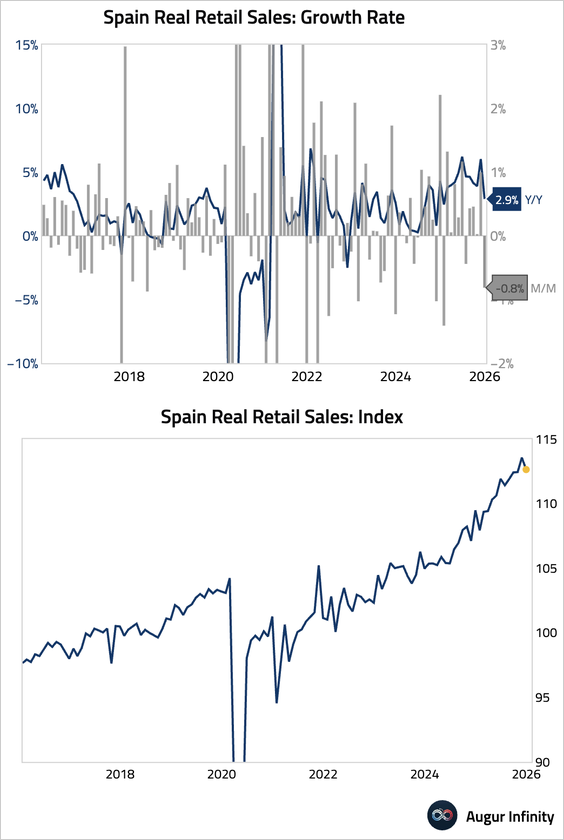
• Daily VAT data suggest a plunge in spending at the start of Q1, signaling continued weakness ahead.
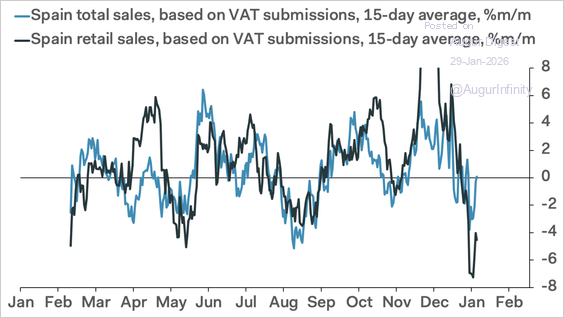
Source: Pantheon Macroeconomics
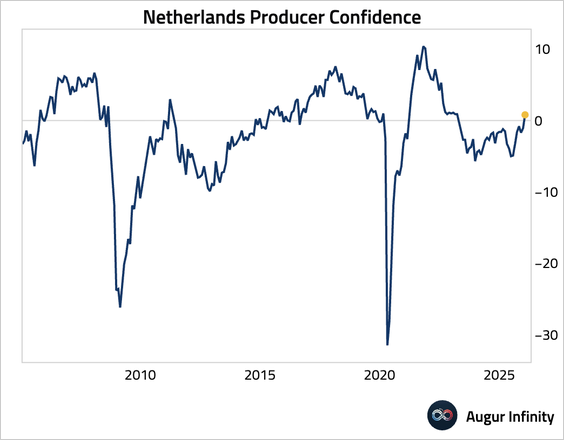
5. Dutch business confidence returned to positive territory for the first time since March 2023.
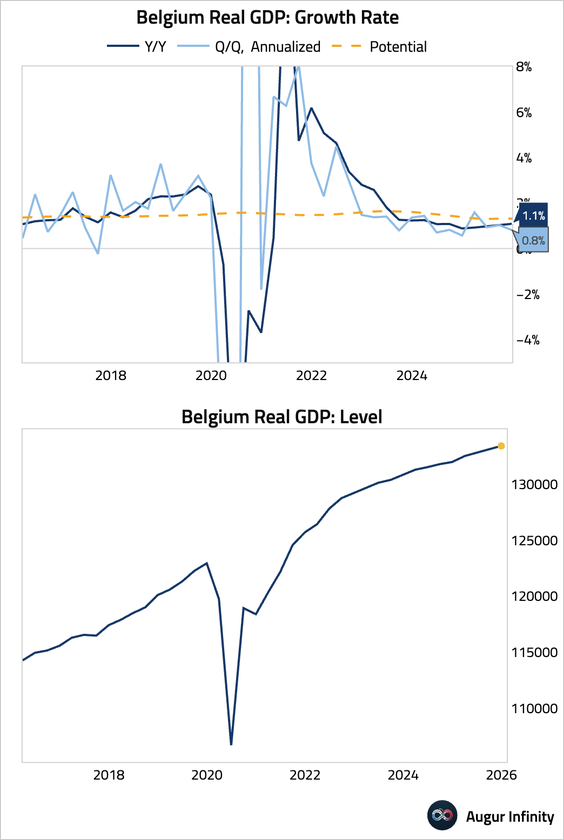
6. Belgium's GDP growth slowed in Q4.
7. Portuguese retail sales fell sharply toward year-end.
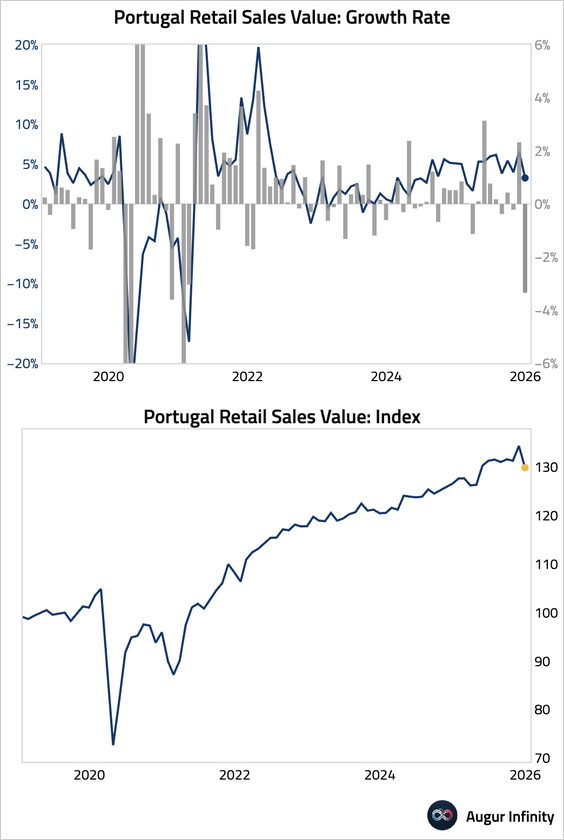
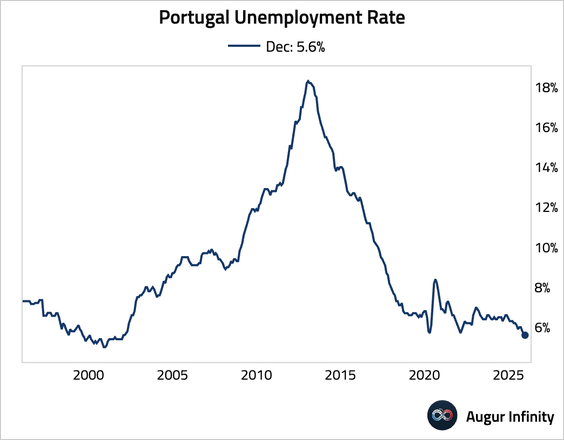
• Unemployment rate edged down to 5.6%, reaching its lowest point since December 2001.
8. Greek retail sales have been stable.
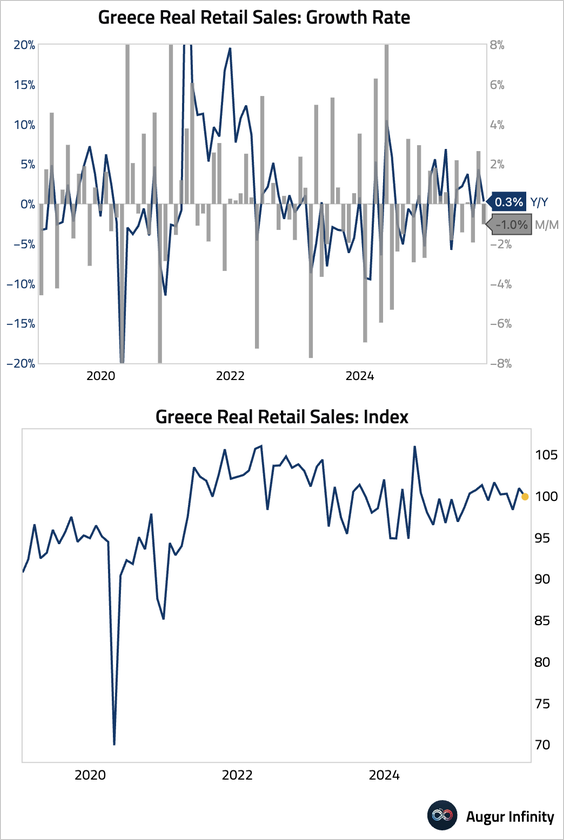
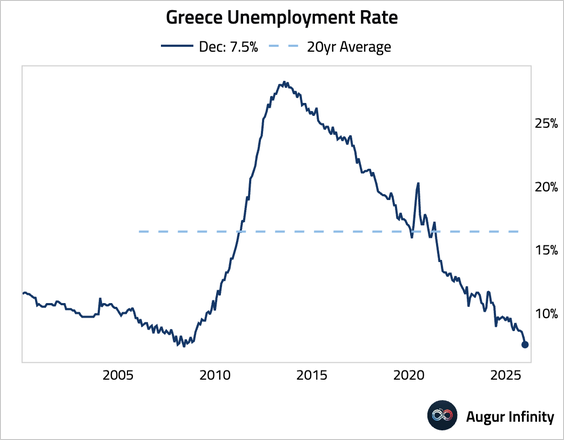
• Unemployment rate fell to its lowest level since May 2008.
Europe
1. Sweden’s Riksbank held its policy rate at 1.75%, in line with expectations.
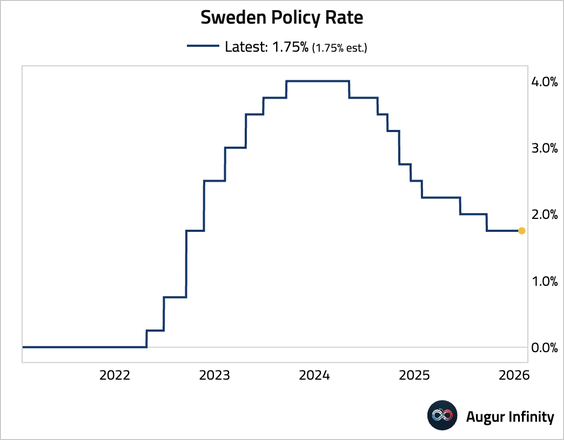
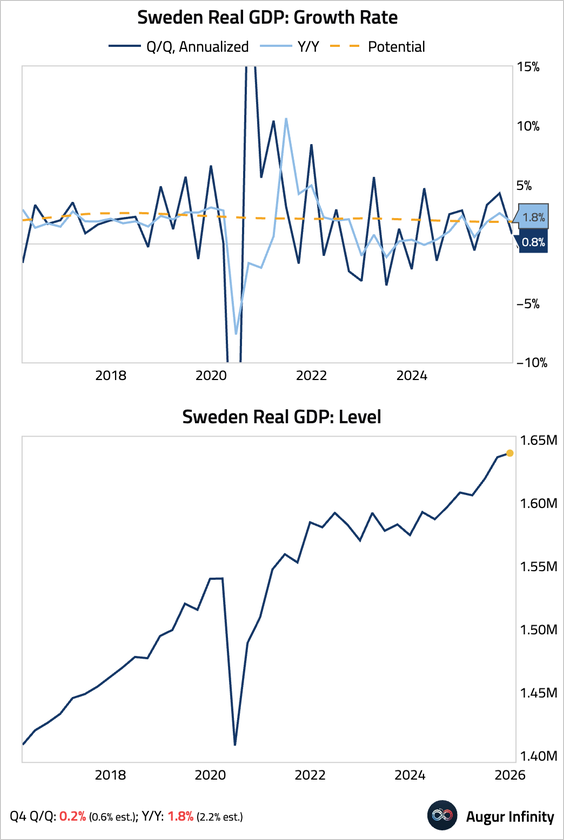
• The economy slowed in Q4, with GDP growth rates missing consensus estimates.
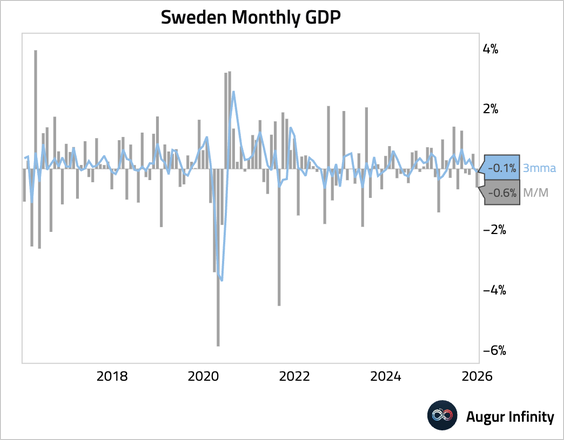
• Monthly GDP contracted in December, and the three-month moving average dipped below zero as well.
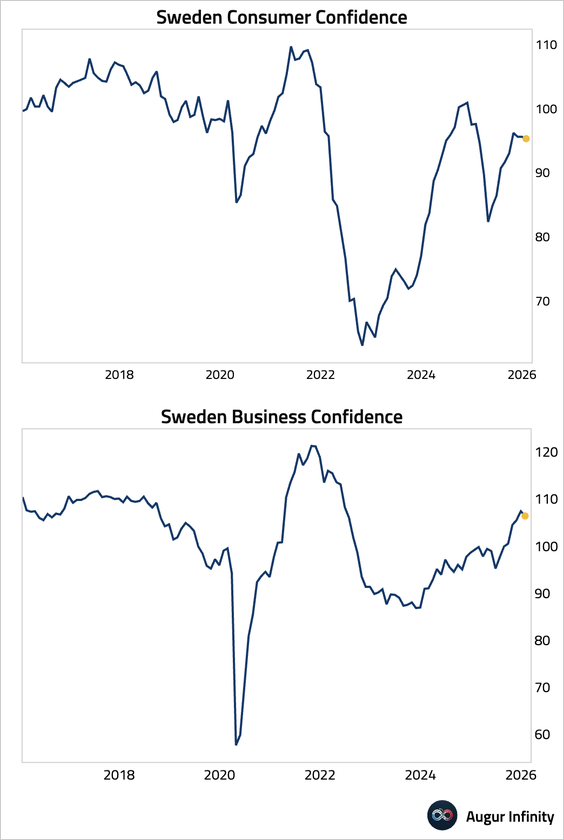
• Business and consumer confidence in Sweden eased slightly in January.
• Average consumer inflation expectations for the year ahead declined.
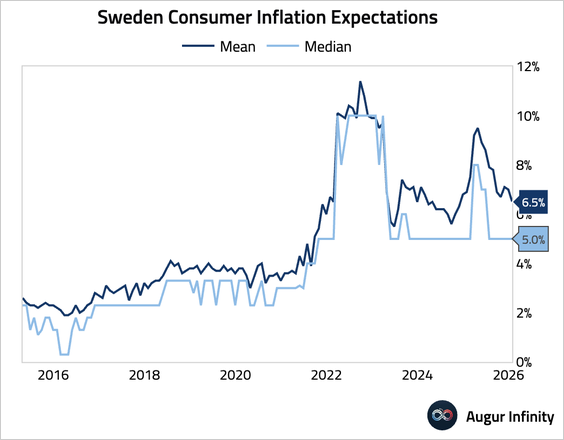
• Credit creation remained resilient, with loan growth for both households and non-financial corporations edging up.
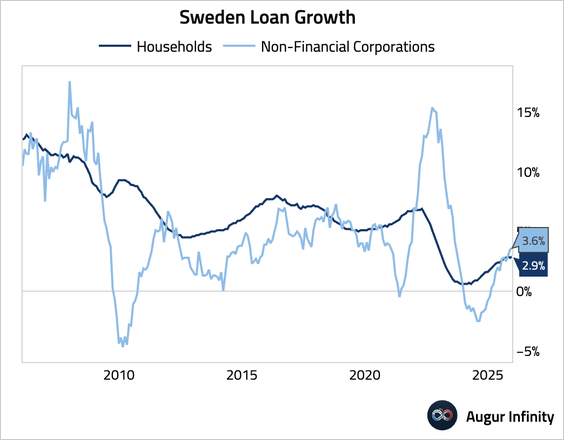
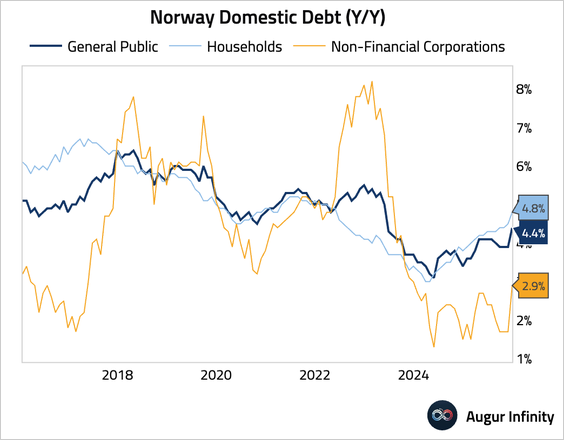
2. Norway’s domestic loan growth accelerated in December.
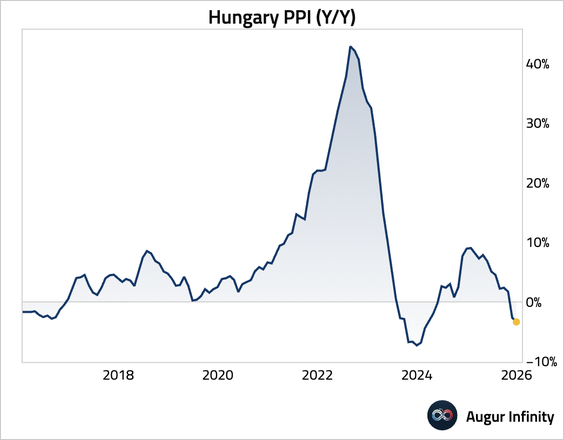
3. Hungary’s trade surplus widened.
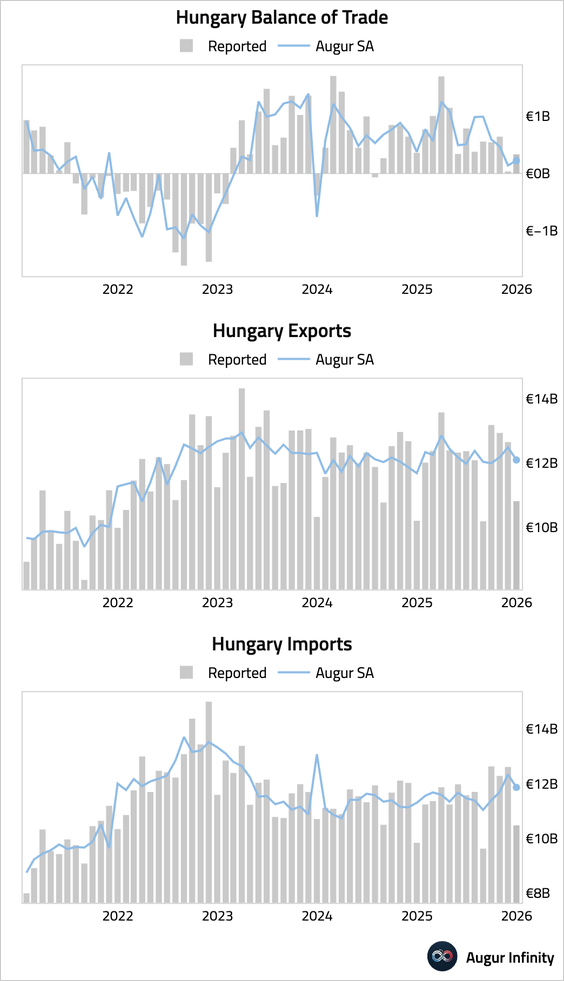
• Producer price deflation deepened.
4. Europe’s rental affordability has deteriorated sharply, with average earners unable to afford a one-bedroom apartment in all but eight major cities as rent growth has outpaced wages.
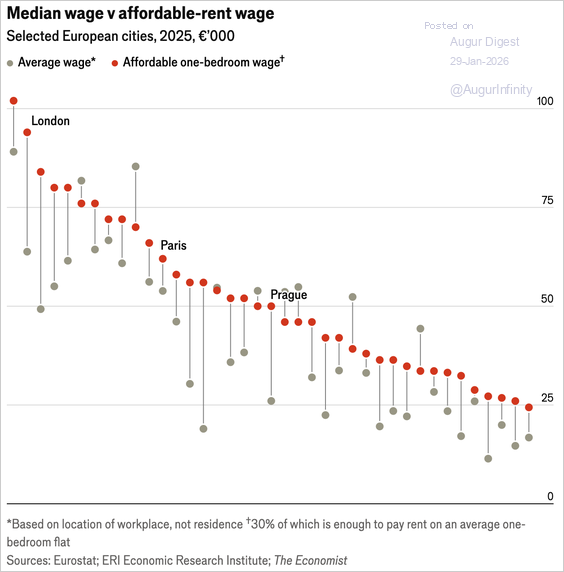
Source: The Economist Read full article
Japan
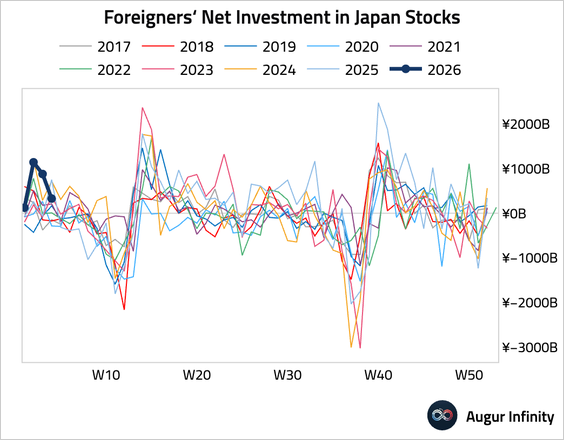
1. Japanese investors turned net sellers of foreign stocks, …
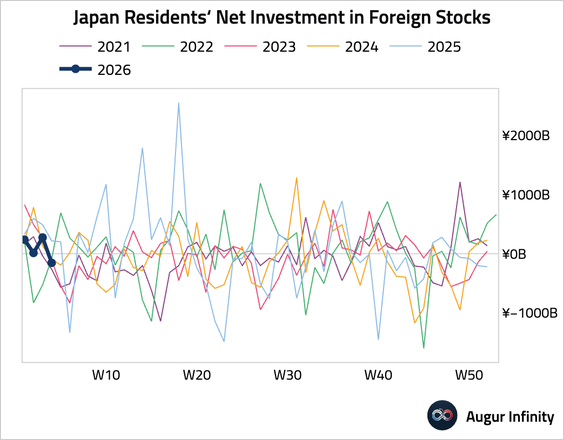
… but resumed buying foreign bonds.
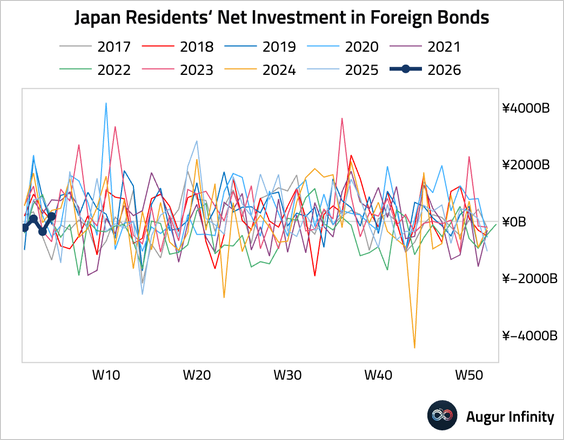
• Foreign investors continued to purchase Japanese stocks, albeit at a much slower pace.
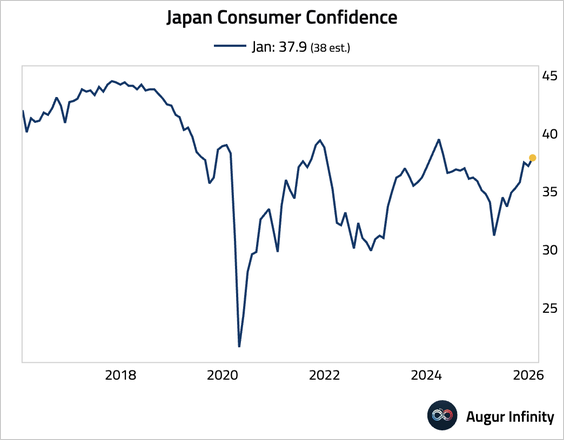
2. Consumer confidence rose to its highest level since April 2024, driven by improved outlooks for livelihood, employment, and income growth. The survey’s base date of January 15 does not capture the prime minister’s remarks on a potential consumption tax cut made later in the month.
3. The yen fell sharply against the dollar after Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said the US is “absolutely not” intervening in Japan’s currency market.
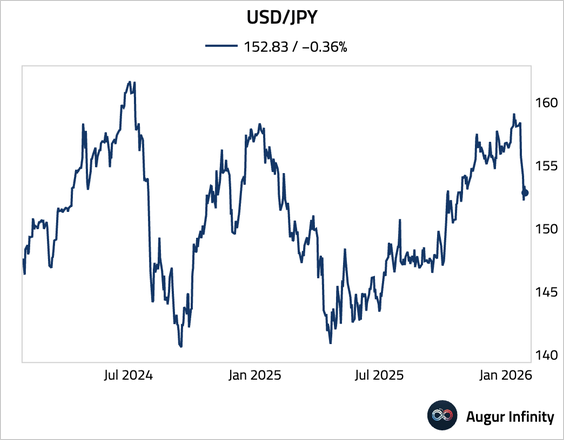

Source: @markets Read full article
4. Real yields on Japanese inflation-indexed bonds have been rising quickly and are on the verge of breaking out into positive territory. However, they are still much lower than real yields in other developed markets.
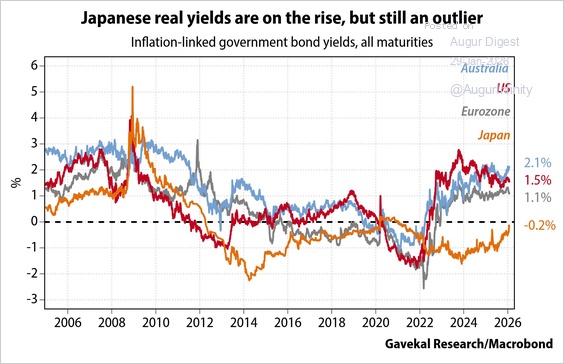
Source: Gavekal Research
Asia-Pacific
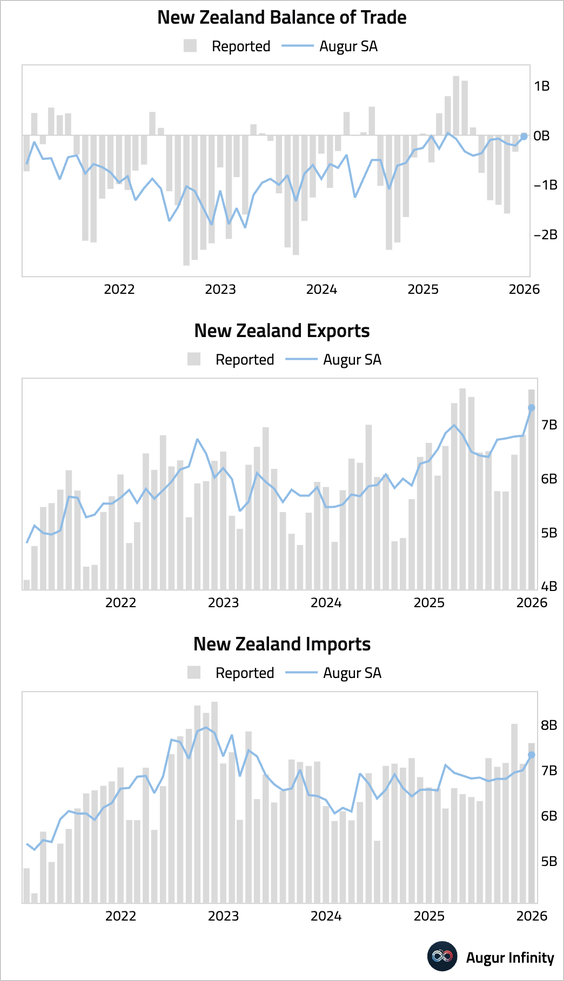
1. New Zealand’s trade balance swung to a small surplus, as exports jumped more than imports.
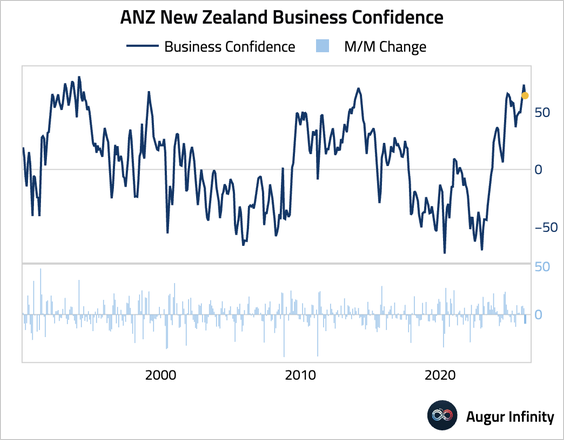
• Business confidence moderated from a 30-year high. Although this was a notable drop, the pullback was expected, and the level remains historically strong.
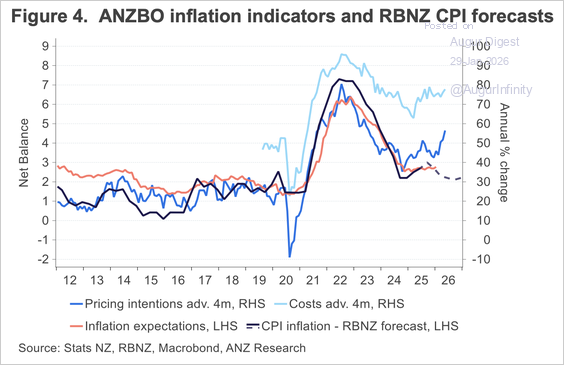
– Inflation indicators showed renewed pressure, with firms’ intentions to raise prices jumping to the highest since March 2023.
Source: @ANZ_Research
2. Australian trade prices rebounded in Q4.
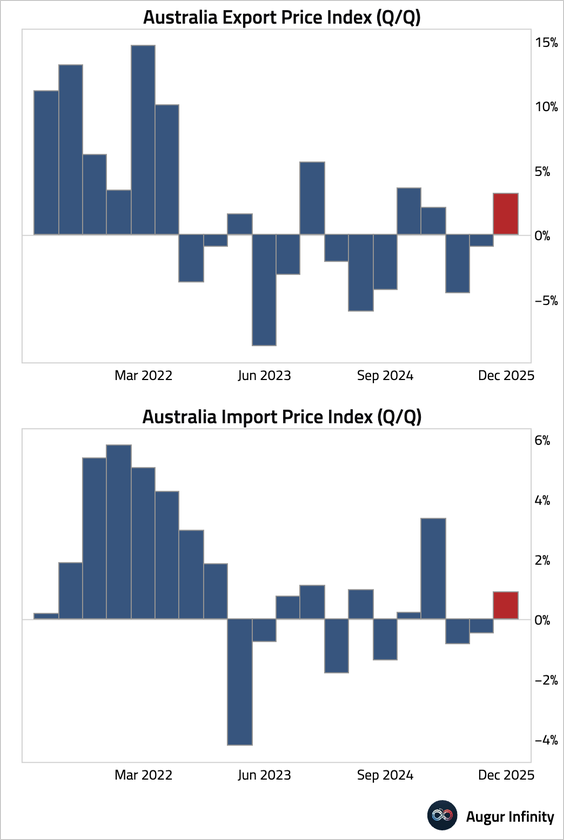
• Australian dollar bond issuance hit a January record of A$50.7 billion as investors and global issuers are drawn by Australia’s AAA ratings, low default rates, and relatively stable credit market amid heightened FX volatility.
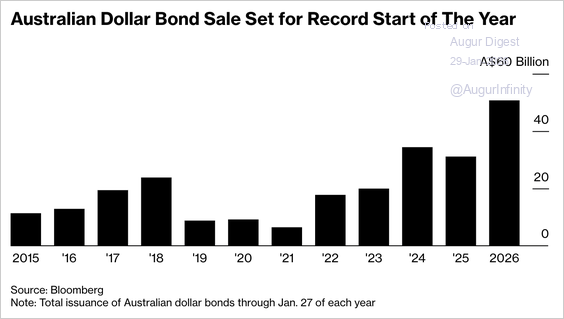
Source: @markets Read full article
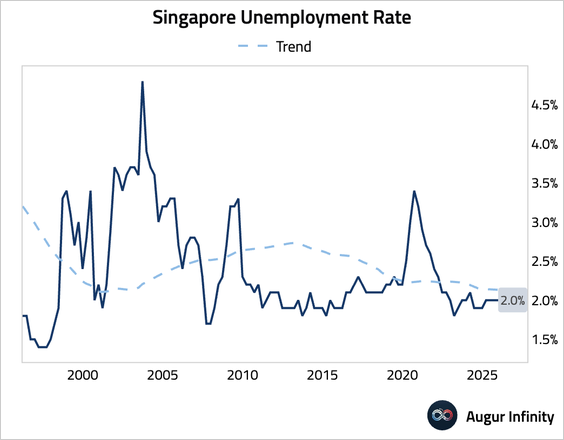
3. Singapore’s Q4 unemployment rate held steady at 2.0%.
China
1. Chinese property stocks surged after reports that regulators have stopped requiring developers to submit the “three red lines” debt metrics, signaling a meaningful easing of property-sector controls aimed at stabilizing the prolonged housing slump.
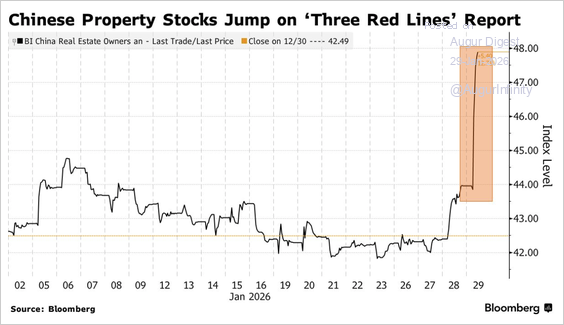
Source: @markets Read full article
2. China has added more power capacity over the past four years than the entire US grid.
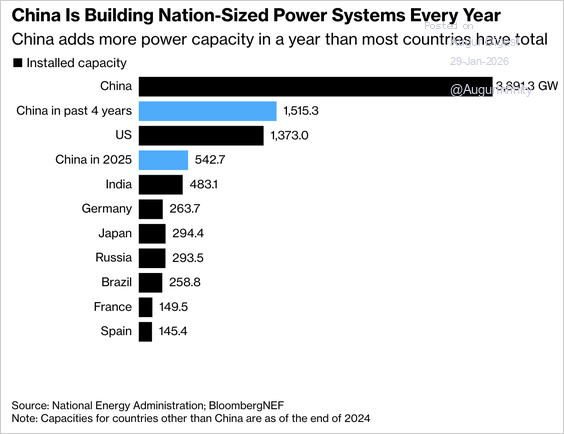
Source: Bloomberg Read full article
India
1. Implied volatility on Nifty 50 is low relative to global peers.
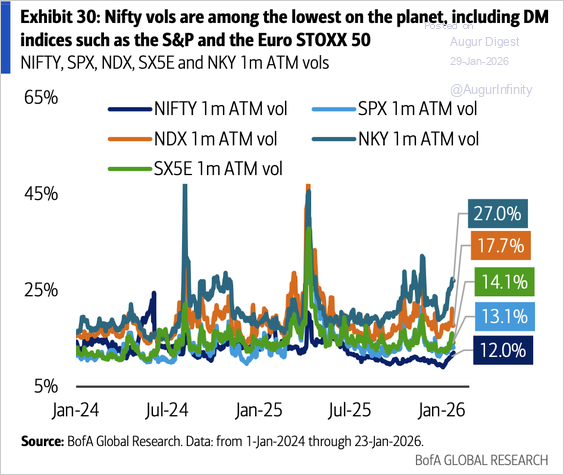
Source: BofA Global Research
Emerging Markets
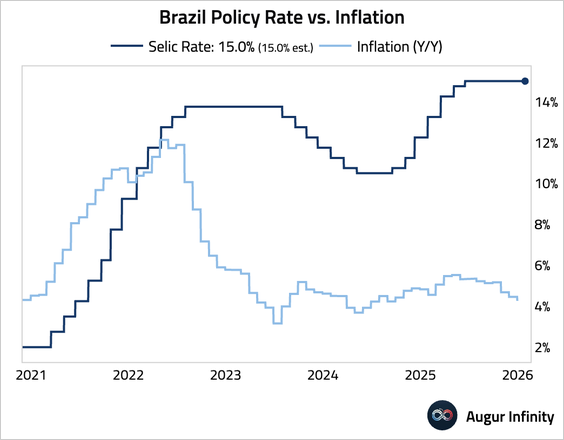
1. Brazil’s Copom held the Selic rate at 15% but delivered explicitly dovish forward guidance, signaling that rate cuts are likely to begin as soon as March—most likely with a 50 bps move.
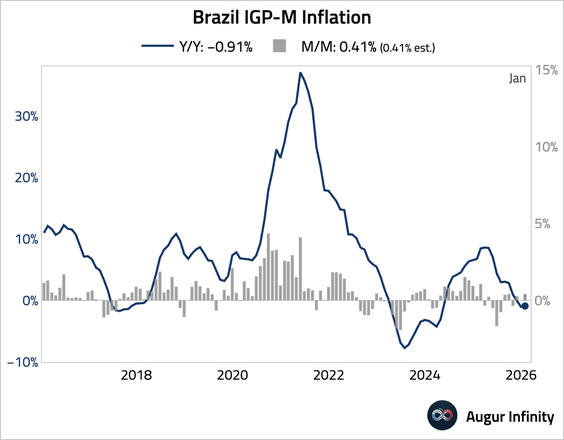
• The IGP-M inflation index rose 0.41% M/M, in line with expectations.
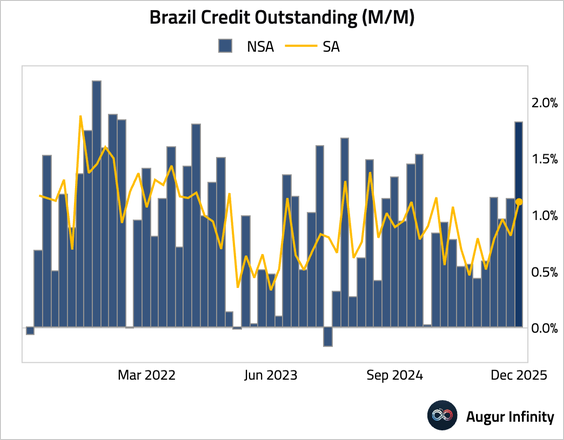
2. Bank lending accelerated in December, driven by a strong surge in corporate credit.
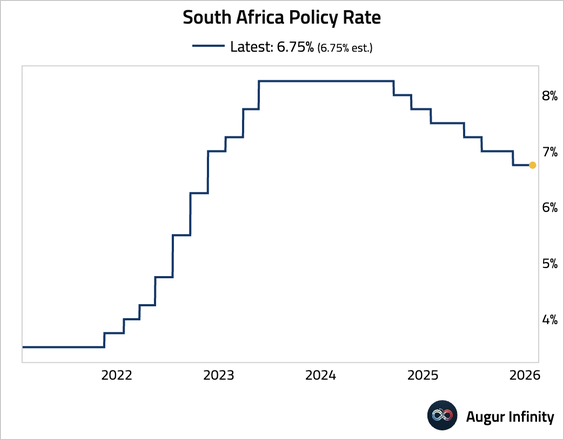
3. The South African Reserve Bank held its policy rate at 6.75%, but the decision revealed a dovish tilt. The Monetary Policy Committee was split 4-2, with two members dissenting in favor of a rate cut. The dissents, coupled with a lower inflation forecast for 2026, signal that an easing cycle is approaching.
4. Indonesian equities plunged in the prior session, after MSCI flagged fundamental investability and transparency issues—warning the country could be downgraded from emerging to frontier market status. Regulators responded by saying that they will double minimum free-float requirements to 15% and signaled potential support from the country’s sovereign wealth fund Danantara.
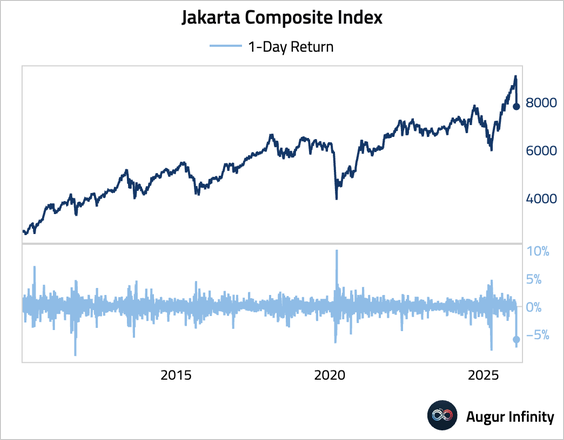

Source: @financialtimes Read full article
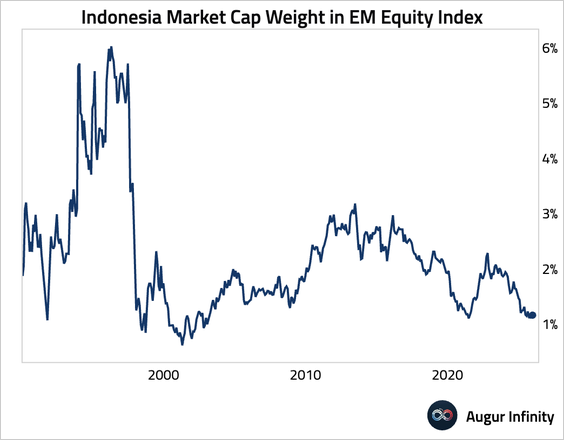
• Indonesia’s market cap weight in MSCI EM is low at around 1.2%.
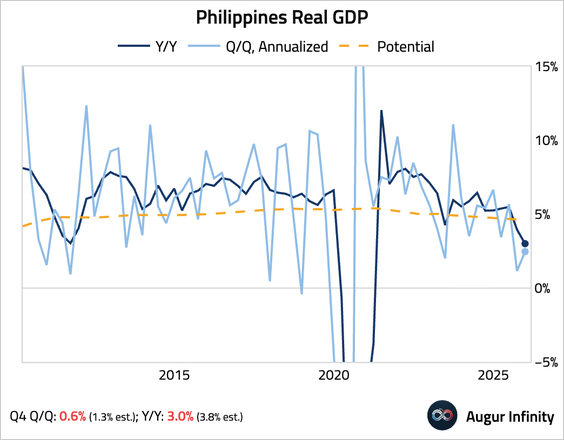
5. The Philippine economy expanded by far less than expected in Q4, with the year-over-year growth rate slowing to the weakest pace in nearly 15 years outside the pandemic, as a major corruption scandal hit investment, consumption, and government spending.
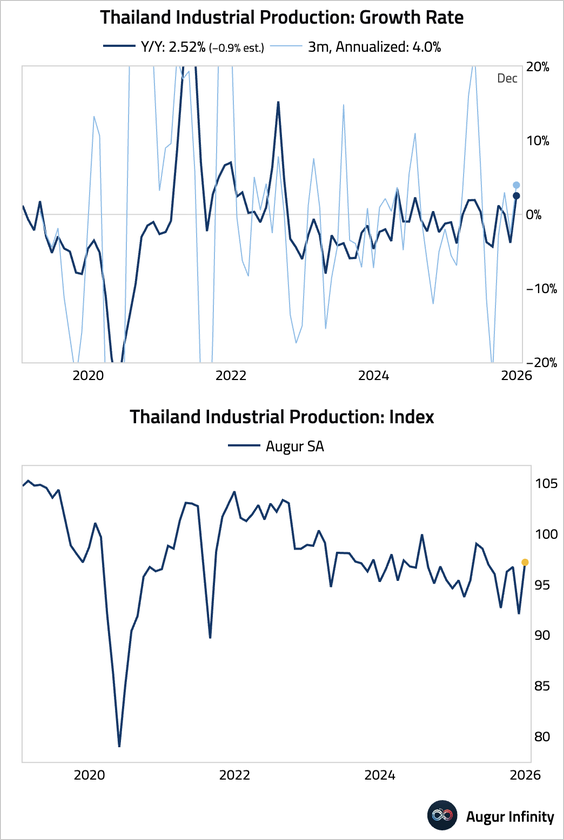
6. Thai industrial production rebounded strongly, well above consensus.
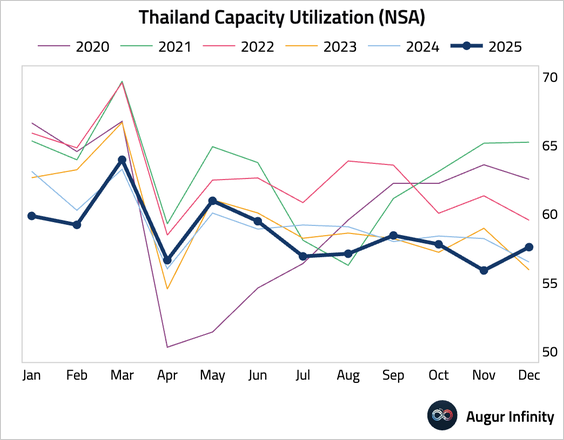
• Capacity utilization improved in a month that typically sees a seasonal decline.
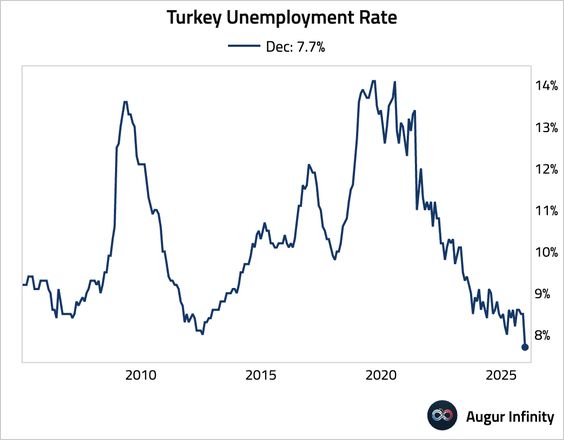
7. Turkey’s unemployment rate fell sharply to secularly low levels.
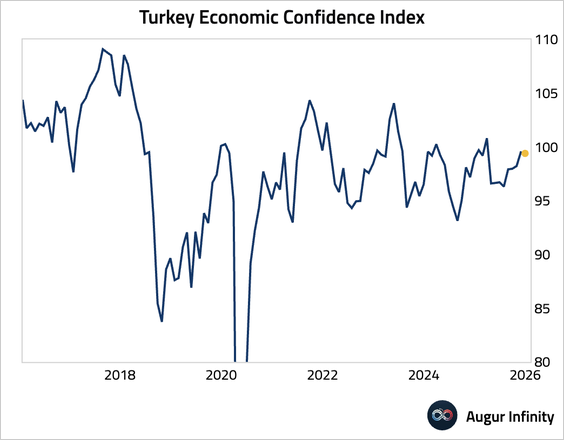
• Its economic confidence index was stable.
8. Ecuador’s successful $4 billion bond sale at its lowest borrowing costs in years has boosted investor optimism that Argentina—benefiting from easing political risk and falling spreads—could soon regain global market access.
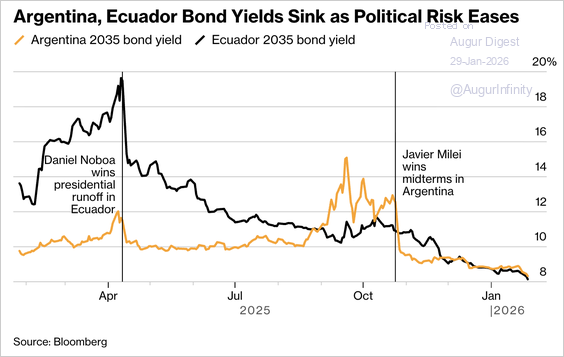
Source: @markets Read full article
Equities
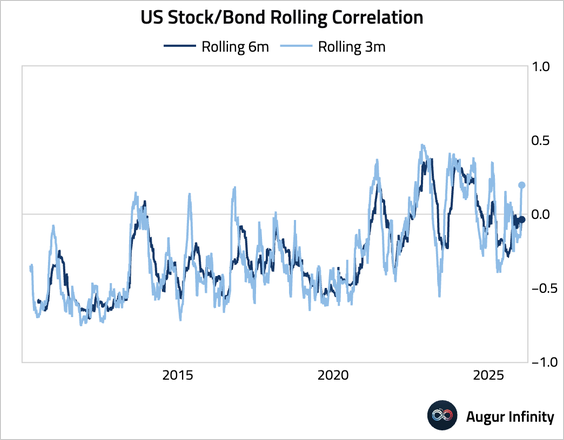
1. Stock/bond correlation has turned positive on a trailing three-month basis.
2. Citadel’s retail risk-on/risk-off indicator reached its 99th percentile, indicating “extreme risk-on” conditions.
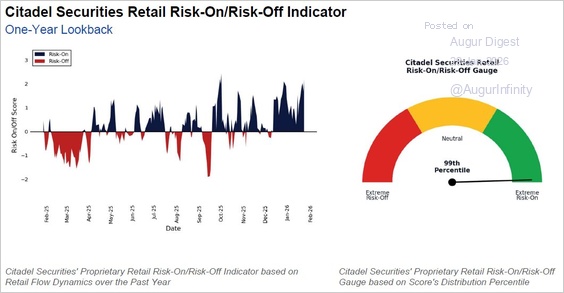
Source: Citadel via @TommyThornton
3. Post-IPO performance in 2025 was underwhelming, especially for high-growth companies that debuted with large price jumps.
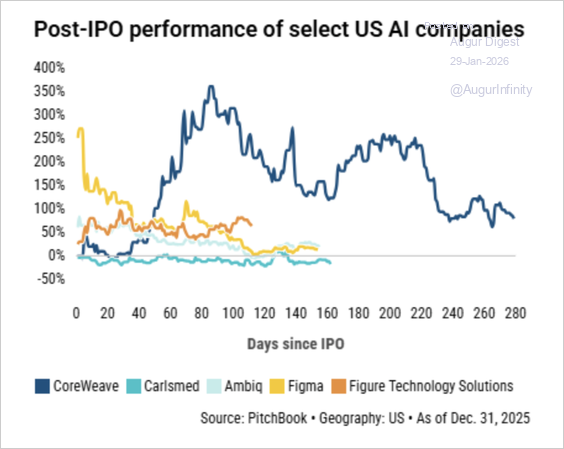
Source: PitchBook
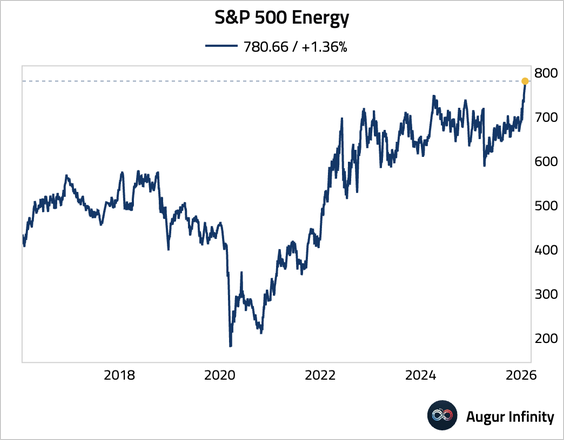
4. The energy sector continued to surge.
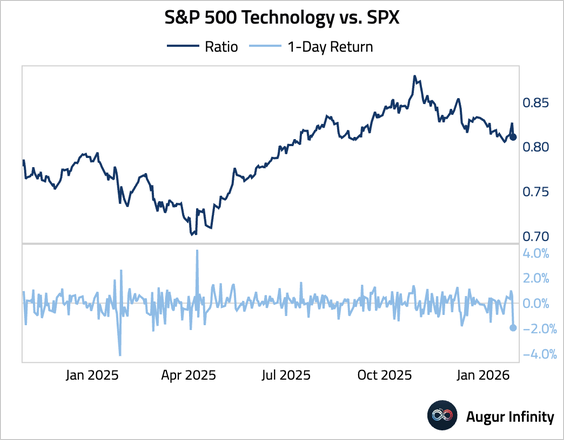
5. Tech underperformed the broader market by the most since January 2025.
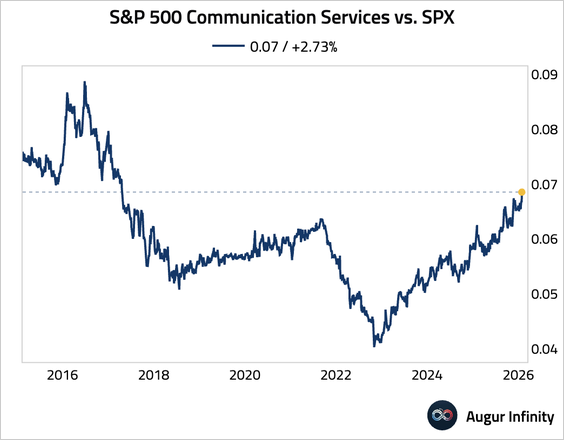
6. The ratio of the communication services sector to S&P 500 is trading at the highest level since April 2017.
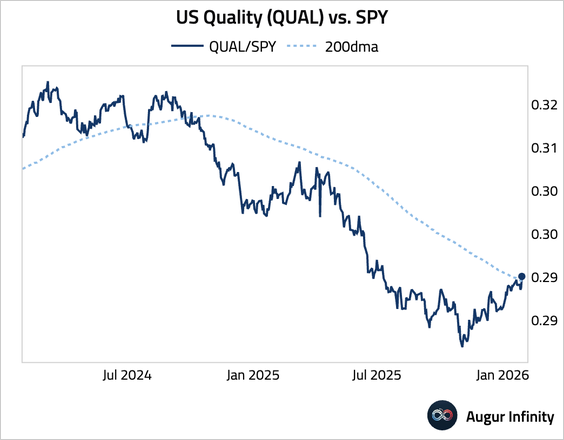
7. US Quality (QUAL) vs. SPY broke above its 200-day moving average.
Rates
US Treasury auction demand remained robust throughout 2025, with domestic investors absorbing record supply.
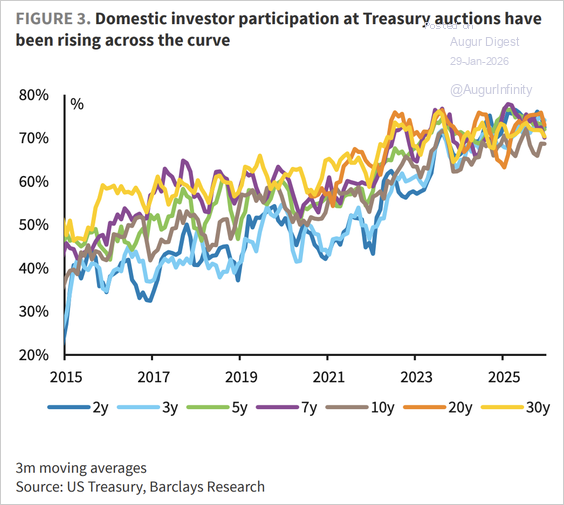
Source: Barclays Research
• Foreign participation has been low and stable, …
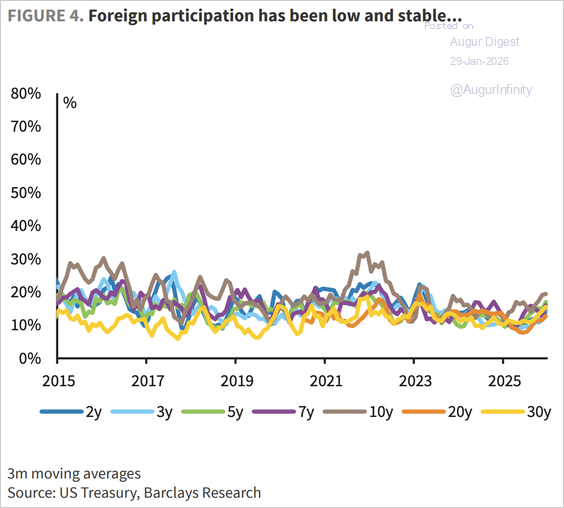
Source: Barclays Research
… but rebounded into year-end.
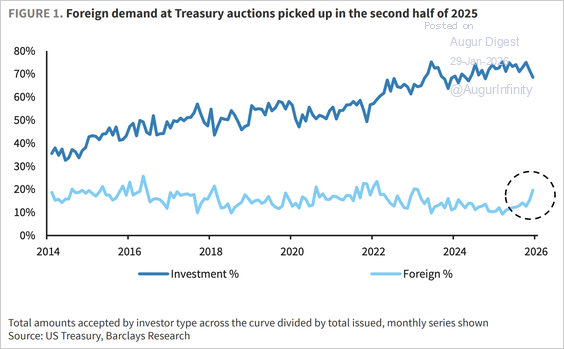
Source: Barclays Research
Energy
1. Brent crude futures hit $70 a barrel for the first time since September 2025 as increased tensions in Iran injected a geopolitical risk premium.
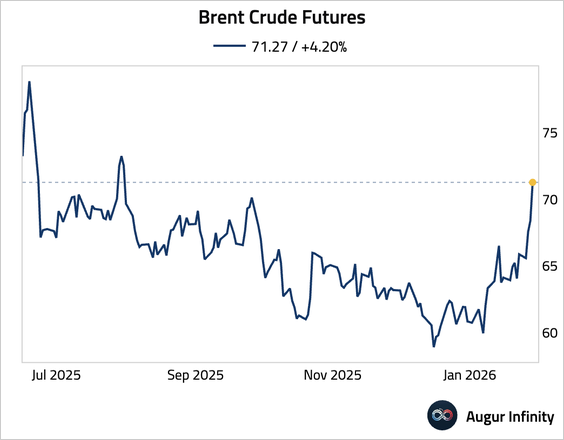
• Oil options markets have seen their longest bullish run since late 2024, with traders paying elevated premiums for call options.
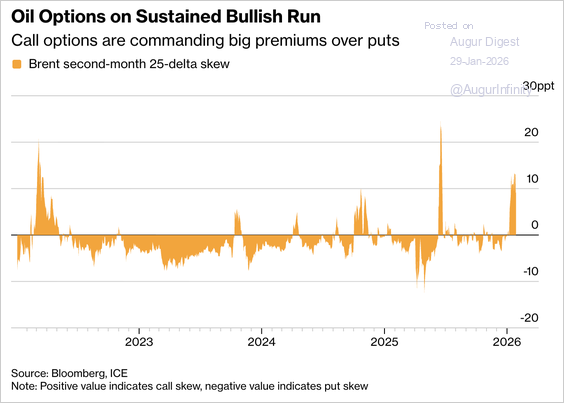
Source: @markets Read full article
2. With buyers and ports fearful of running afoul of sanctions, the volume of Russian and Iranian oil loitering at sea—much of it off the Chinese coast—is hitting records.
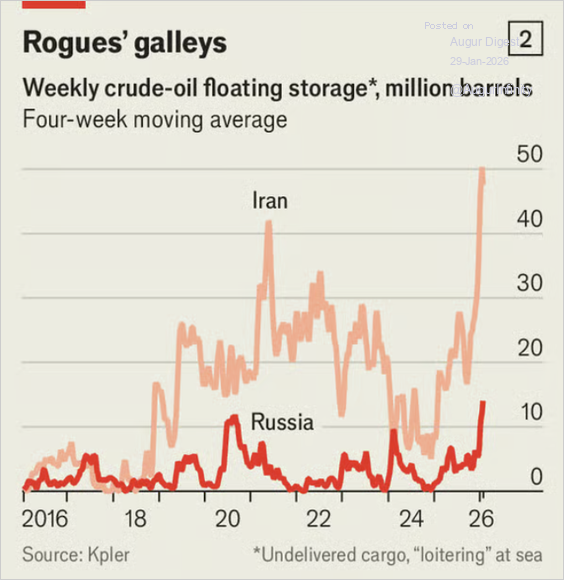
Source: The Economist Read full article
3. WTI-Brent spread continued to slump.
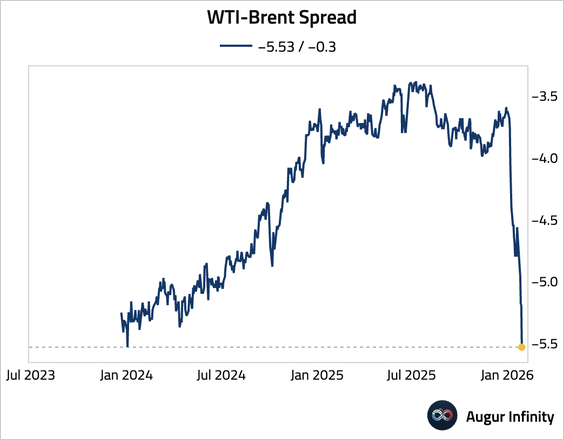
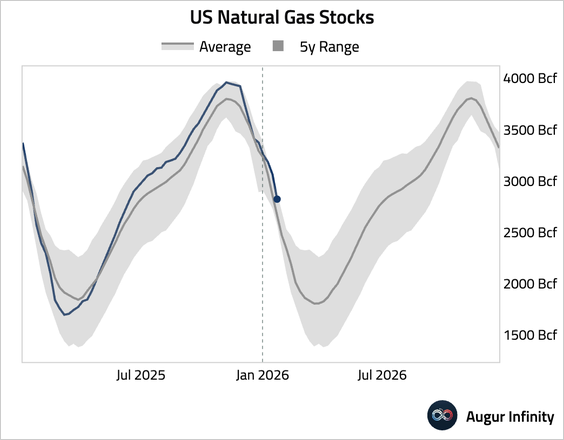
4. Natural gas inventories saw a larger-than-expected drawdown for the week.
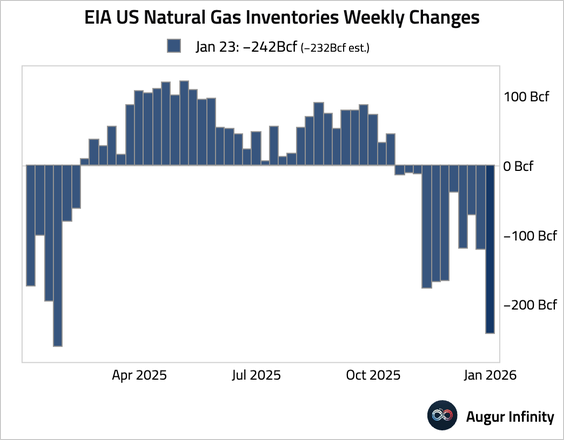
Commodities
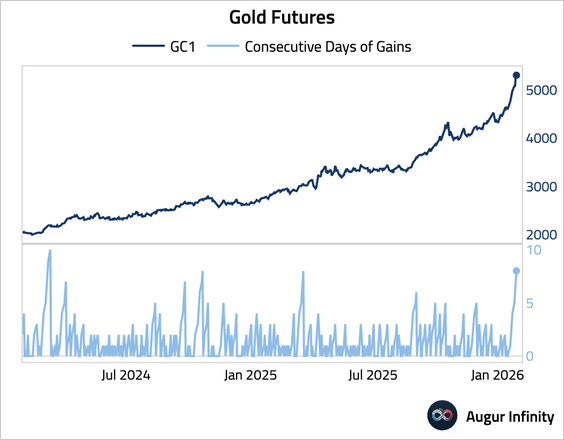
1. Gold gained for an eighth consecutive day.
2. Copper prices surged, with an intraday high above $14,000, as a wave of speculative buying—largely from Chinese investors—overwhelmed signs of weak physical demand.
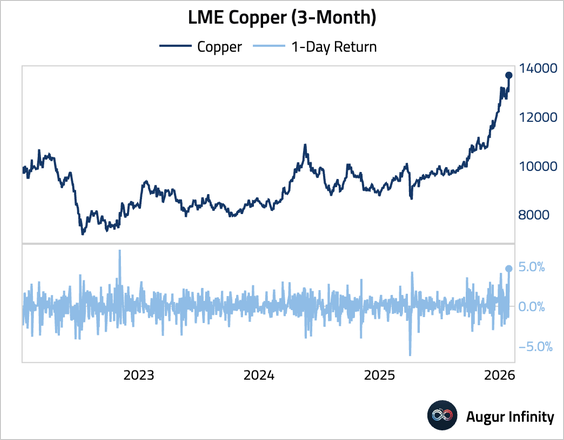

Source: @markets Read full article
3. US Midwest aluminum premiums surged above $1 per pound for the first time, more than doubling since June, as the import tariffs sharply lifted US prices relative to global benchmarks.
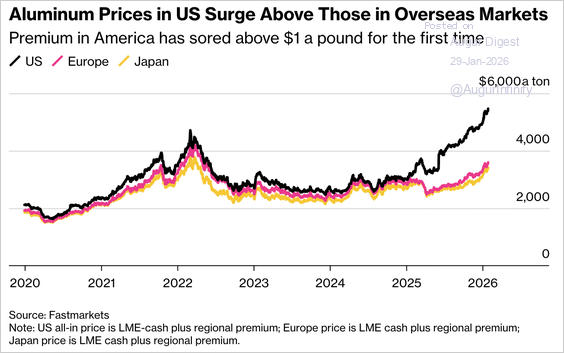
Source: @markets Read full article
Global Developments
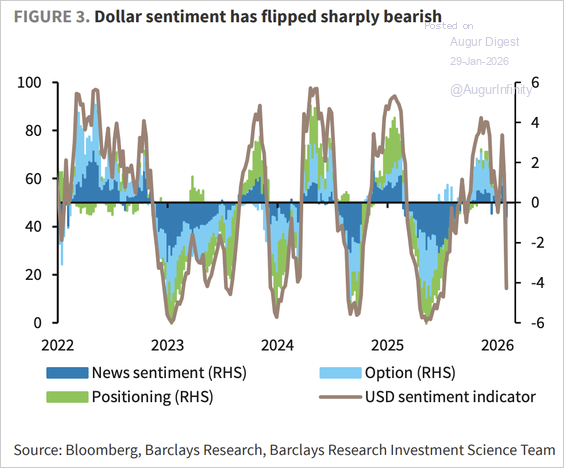
1. Barclays’s dollar sentiment index has flipped sharply into negative territory.
Cryptocurrency
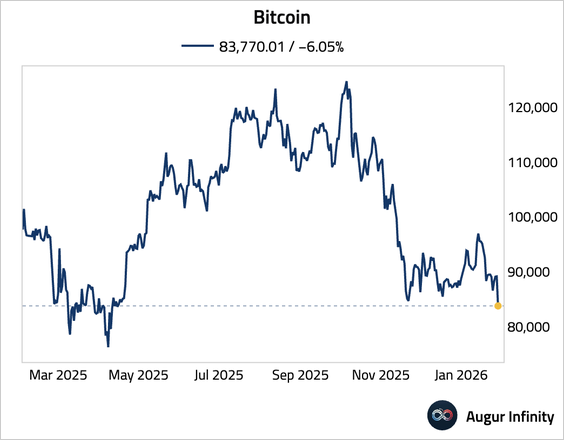
1. Bitcoin is at the lowest level since April 2025.
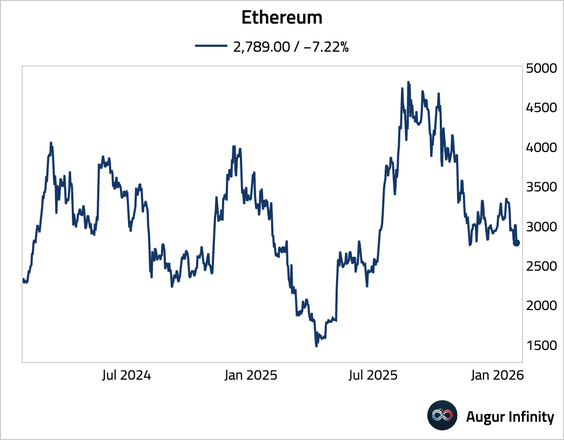
2. Ethereum 1-day return is -7.7%, a 2.2σ move.