Headlines
- The United States and the European Union finalized a trade agreement that imposes a 15 percent tariff on European imports and includes commitments for $750 billion in US energy purchases and $600 billion in US investments.
- The United States and China agreed to extend existing tariff rates for three months to provide additional time for ongoing trade negotiations.
- The US Treasury Department announced it expects to borrow $1.007 trillion in the third quarter, an increase of $453 billion from its April forecast.
Charts of the Day
- The US and EU announced a trade deal setting the US tariff on most EU goods at 15%; the EU will eliminate its tariffs on US products. The deal includes a major EU commitment to purchase $750 billion in US energy over three years, a substantial increase from the current ~$80 billion/year run-rate. The EU also made a $600 billion investment pledge.
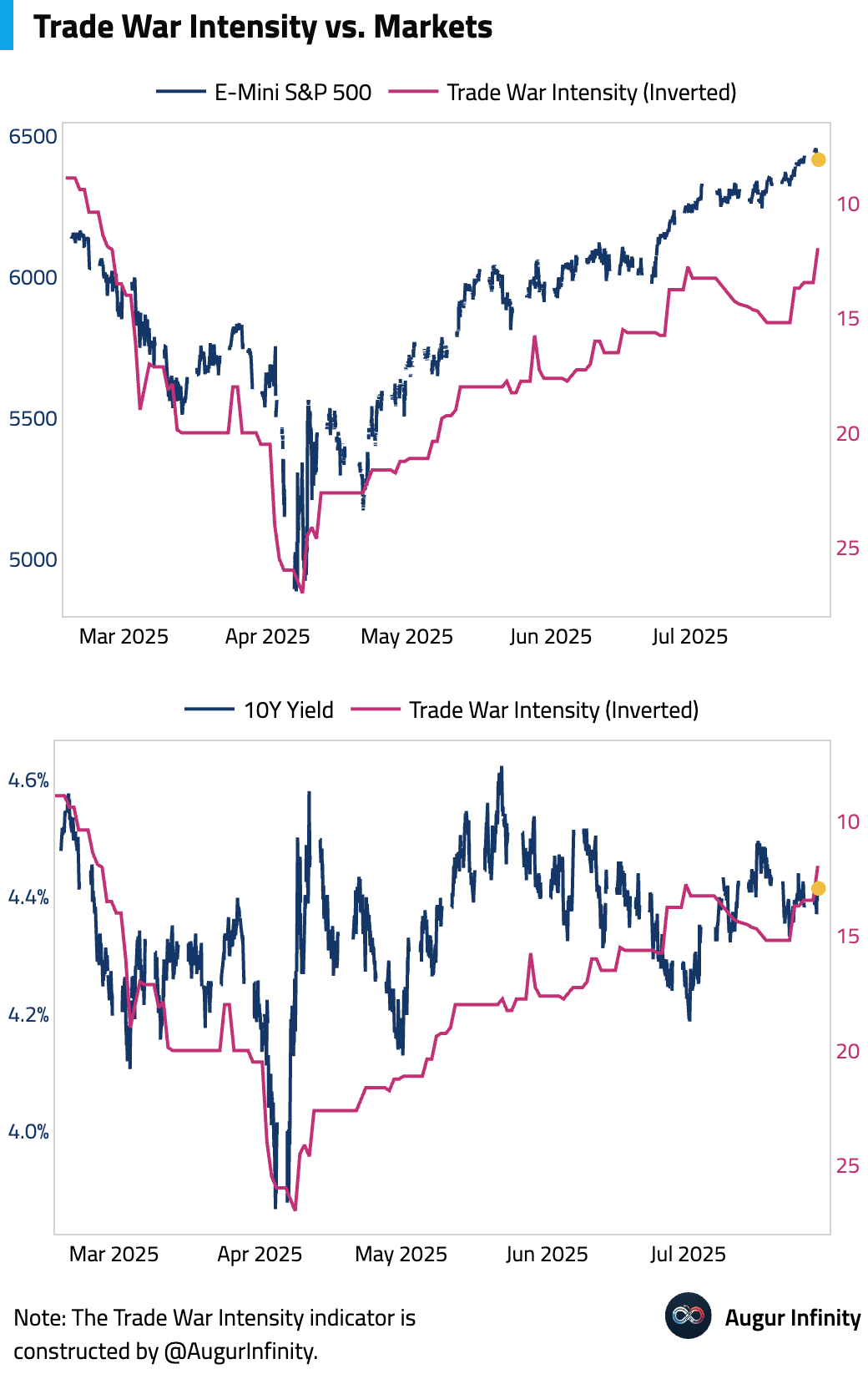
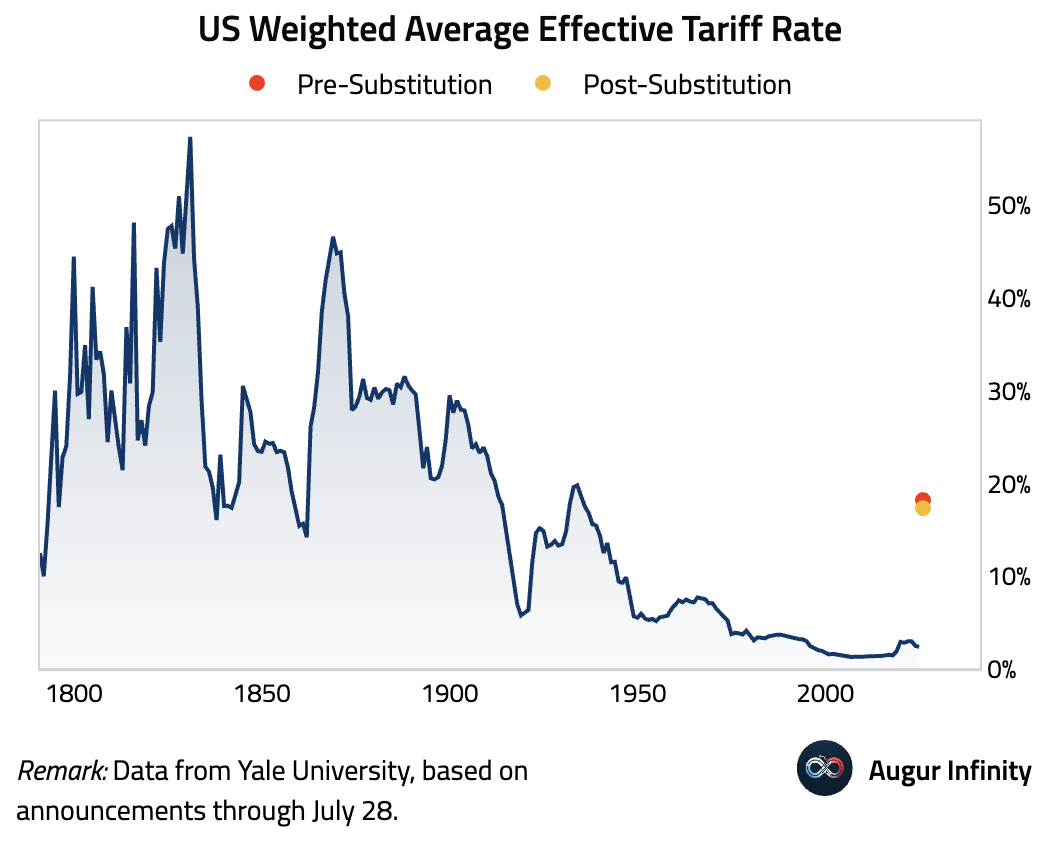
- Following the EU trade deal announcement, the Budget Labs estimates that consumers face an overall average effective tariff rate of 18.2%, the highest since 1934. After accounting for consumption shifts, the average tariff rate is estimated at 17.3%, the highest since 1935.
Global Economics
United States
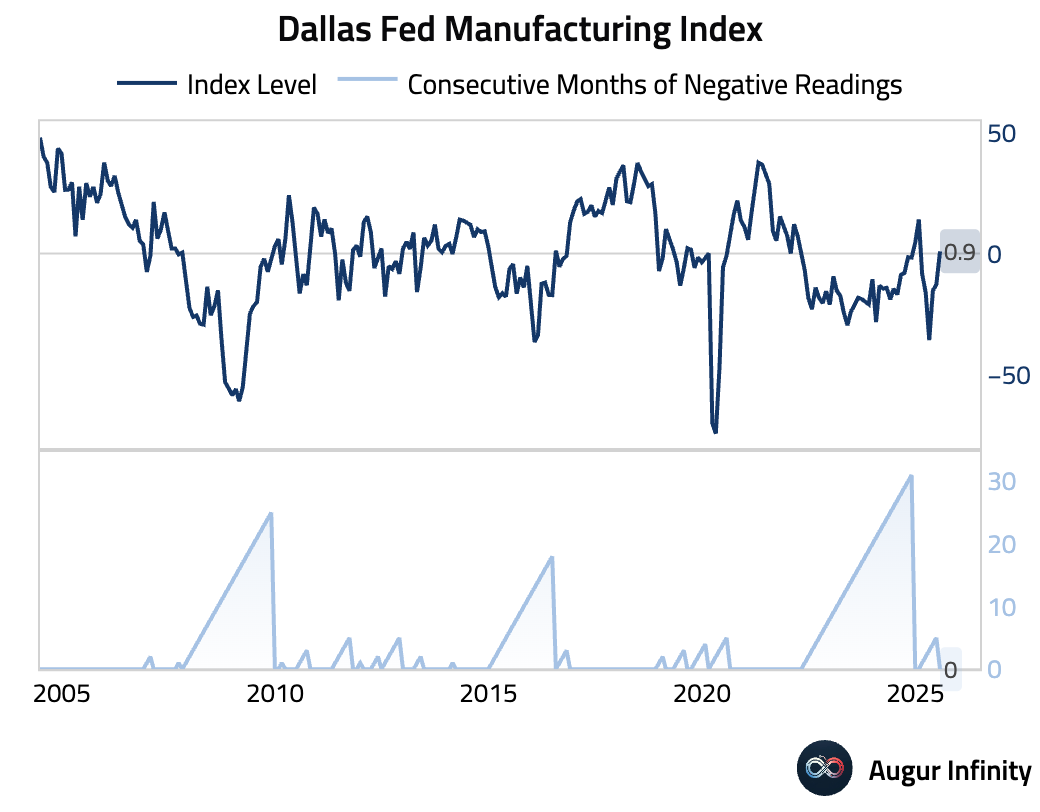
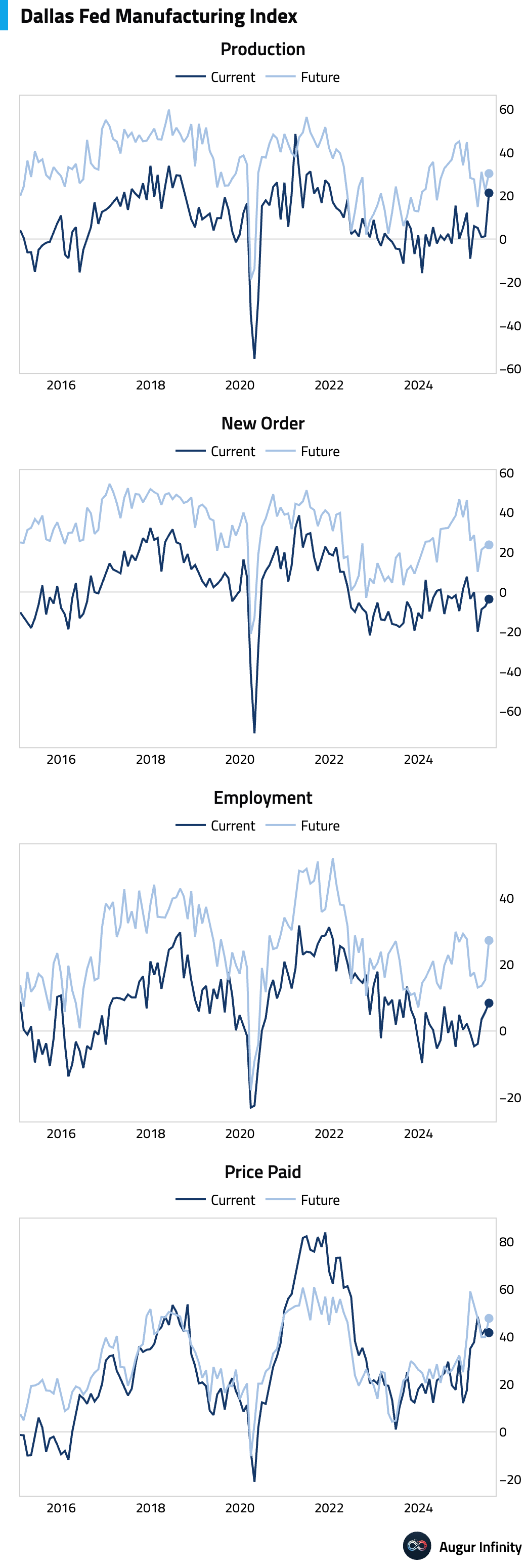
- The Dallas Fed Manufacturing Index for July jumped to 0.9 from -12.7 in June, returning to positive territory and marking its strongest reading since January 2025. The improvement was broad-based, with sub-indices for new orders, production, and employment all rising.
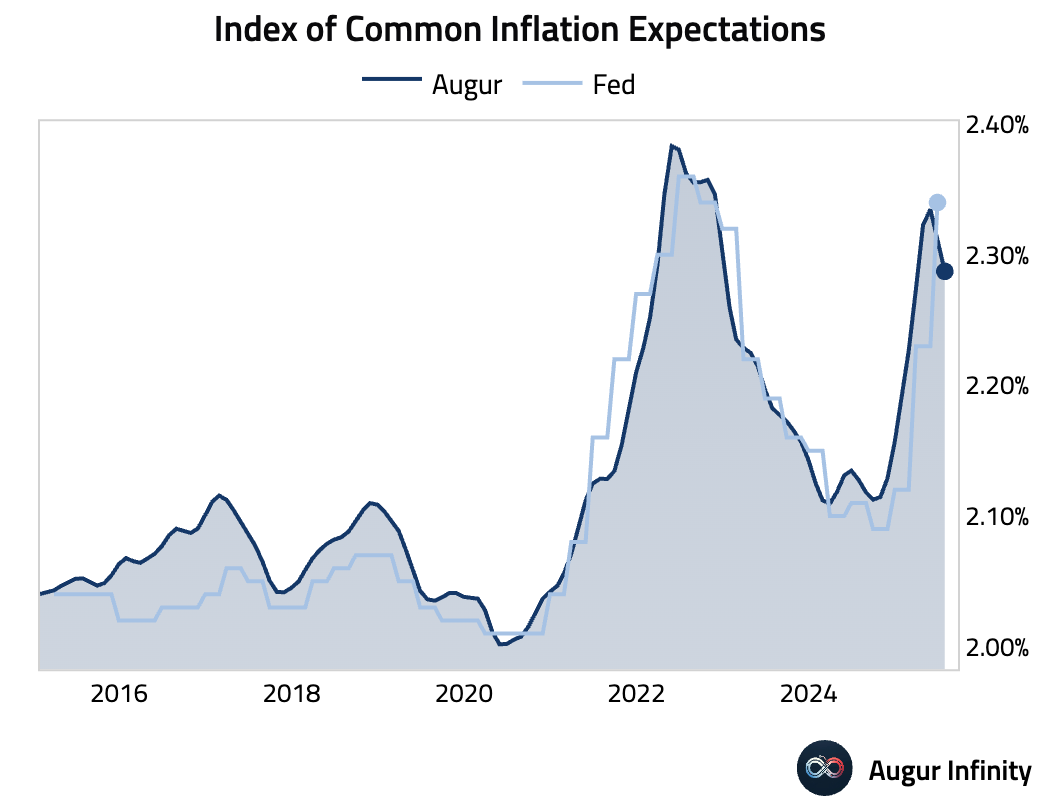
- The Fed's Index of Common Inflation Expectations (CIE) rose from 2.23% to 2.34% in the second quarter. However, our higher-frequency monthly tracking suggests the indicator has already turned down over the past two months.
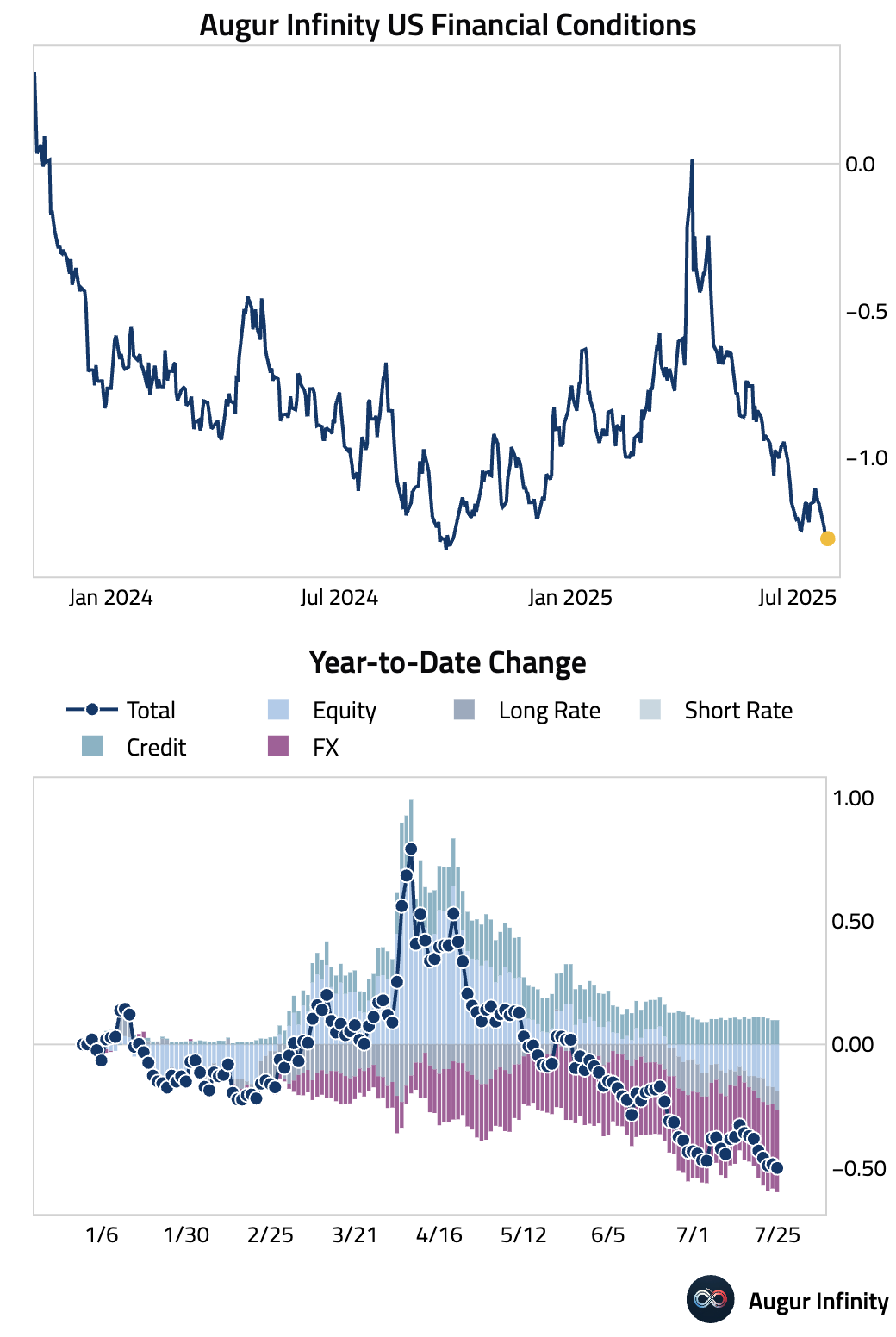
- US financial conditions have eased significantly this year, driven by the rally in equities, a weakening dollar, and a small decline in long-term bond yields. This easing provides a tailwind for economic activity despite ongoing trade negotiations.
Canada
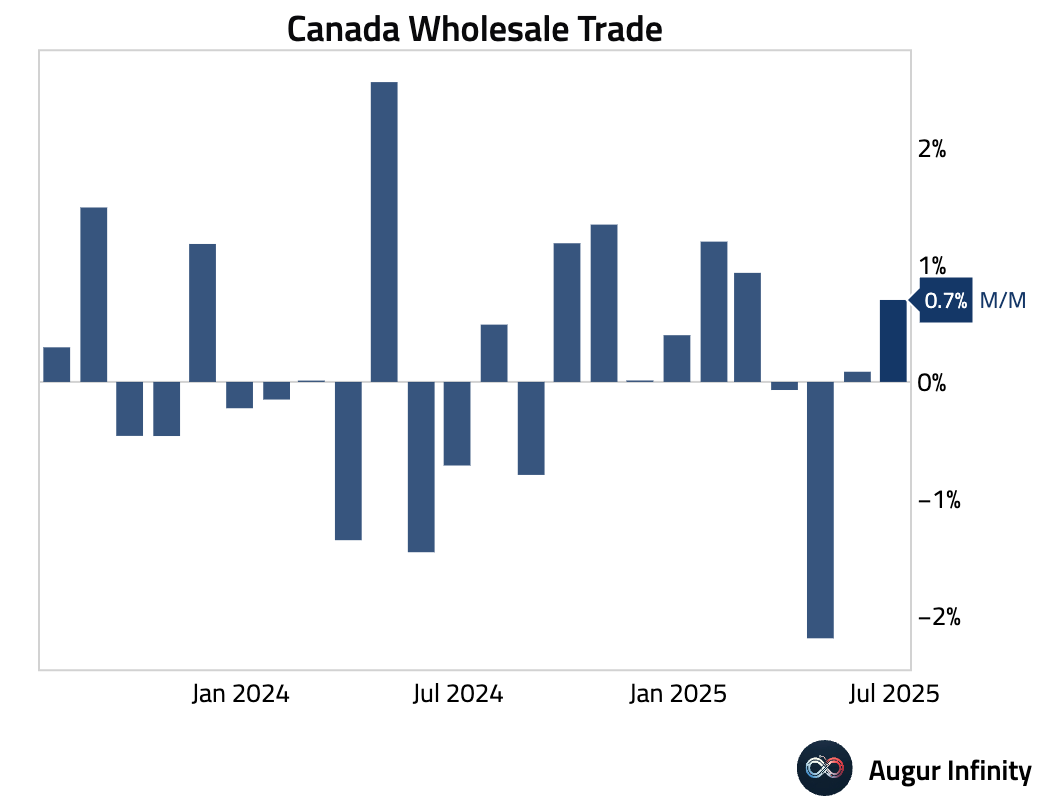
- Preliminary data for June shows Canadian wholesale sales rose 0.7% M/M, accelerating from the 0.1% increase in May and suggesting a pickup in business activity.
Europe
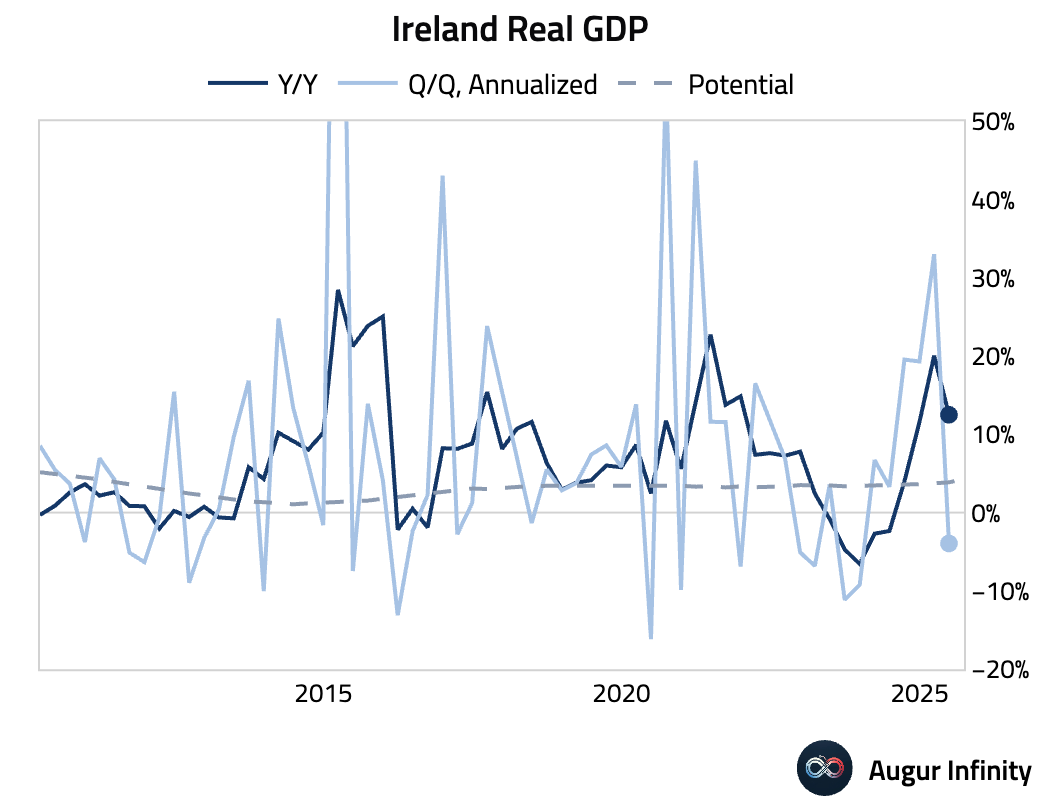
- Irish GDP contracted 1.0% Q/Q in the second quarter, a sharp reversal from the 7.4% expansion in Q1. On a Y/Y basis, growth moderated to 12.5% from 20.0%.
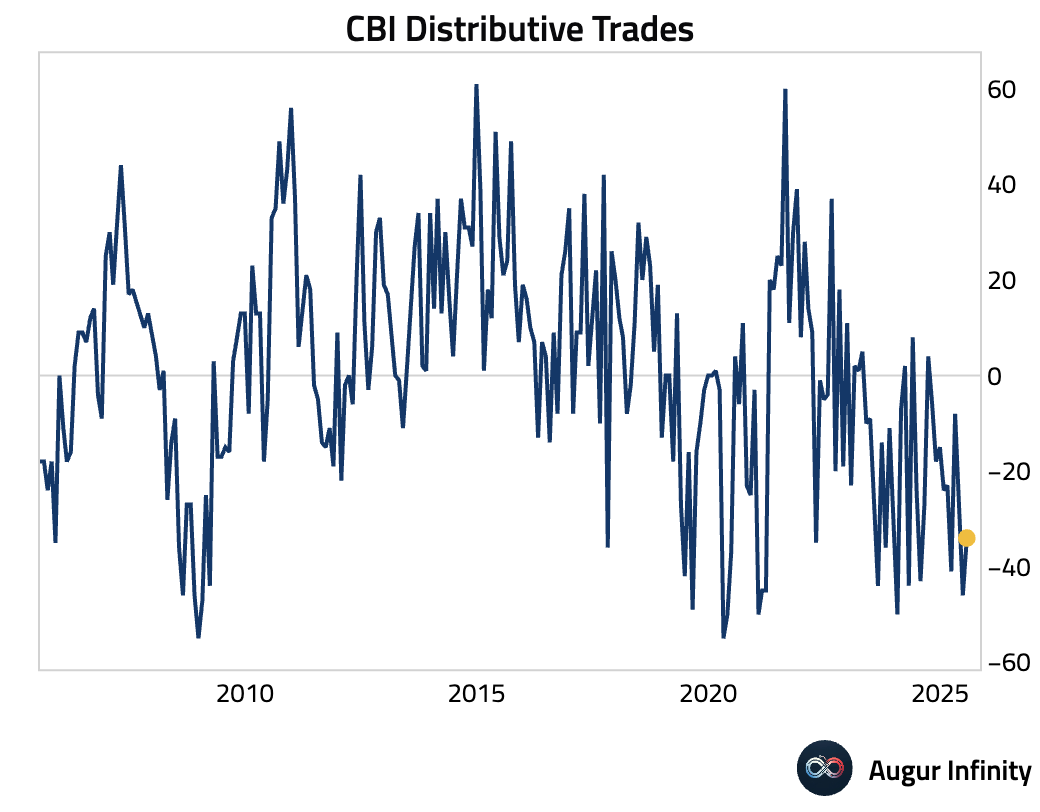
- The UK's CBI Distributive Trades balance improved to -34 in July from -46 in June, but missed the consensus estimate of -26. The reading indicates that retail sales conditions remain weak, although the pace of decline has eased.
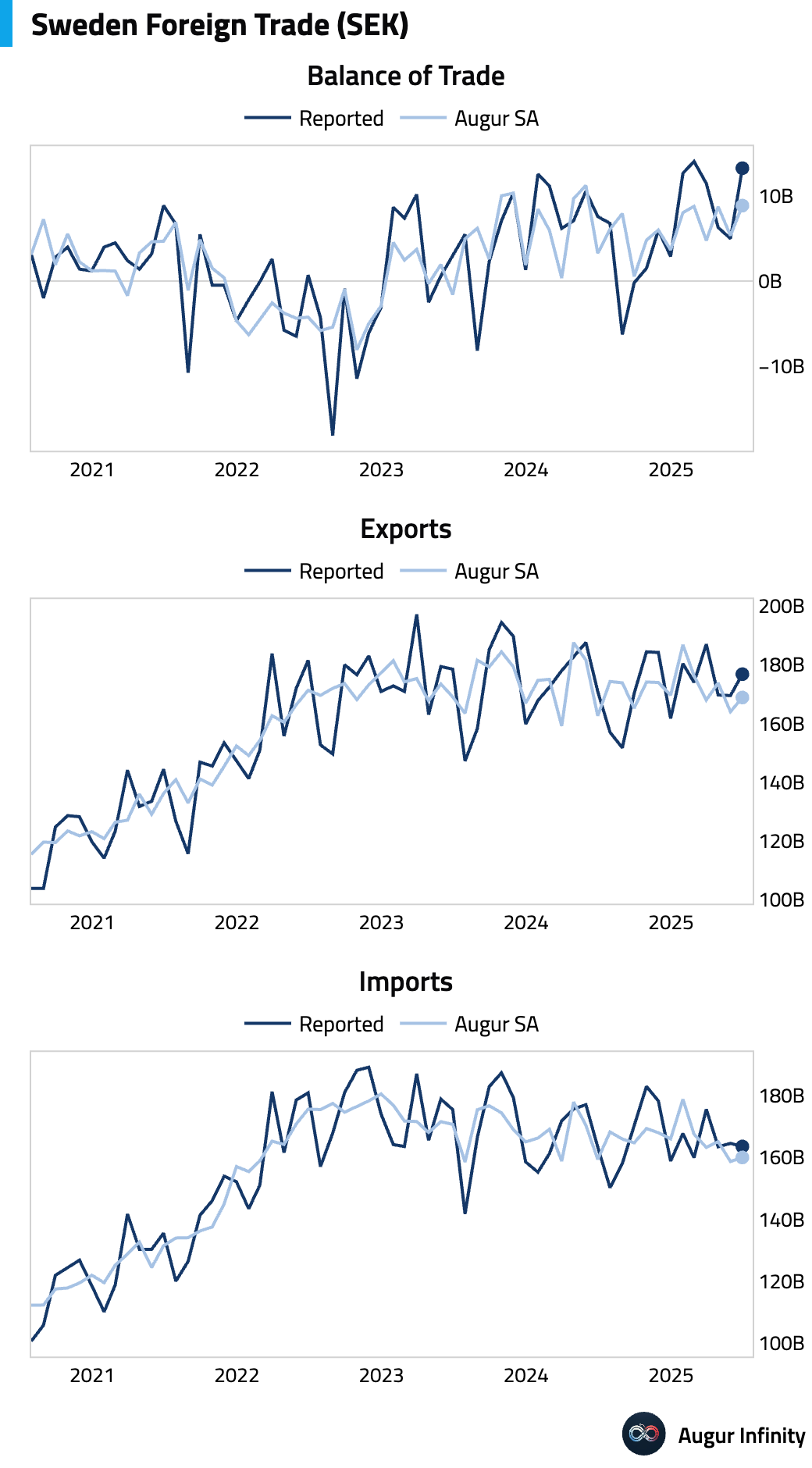
- Sweden's trade balance registered a surplus of SEK 13.3 billion in June, a substantial increase from the SEK 5.0 billion surplus recorded in May, driven by stronger export performance.
Asia-Pacific
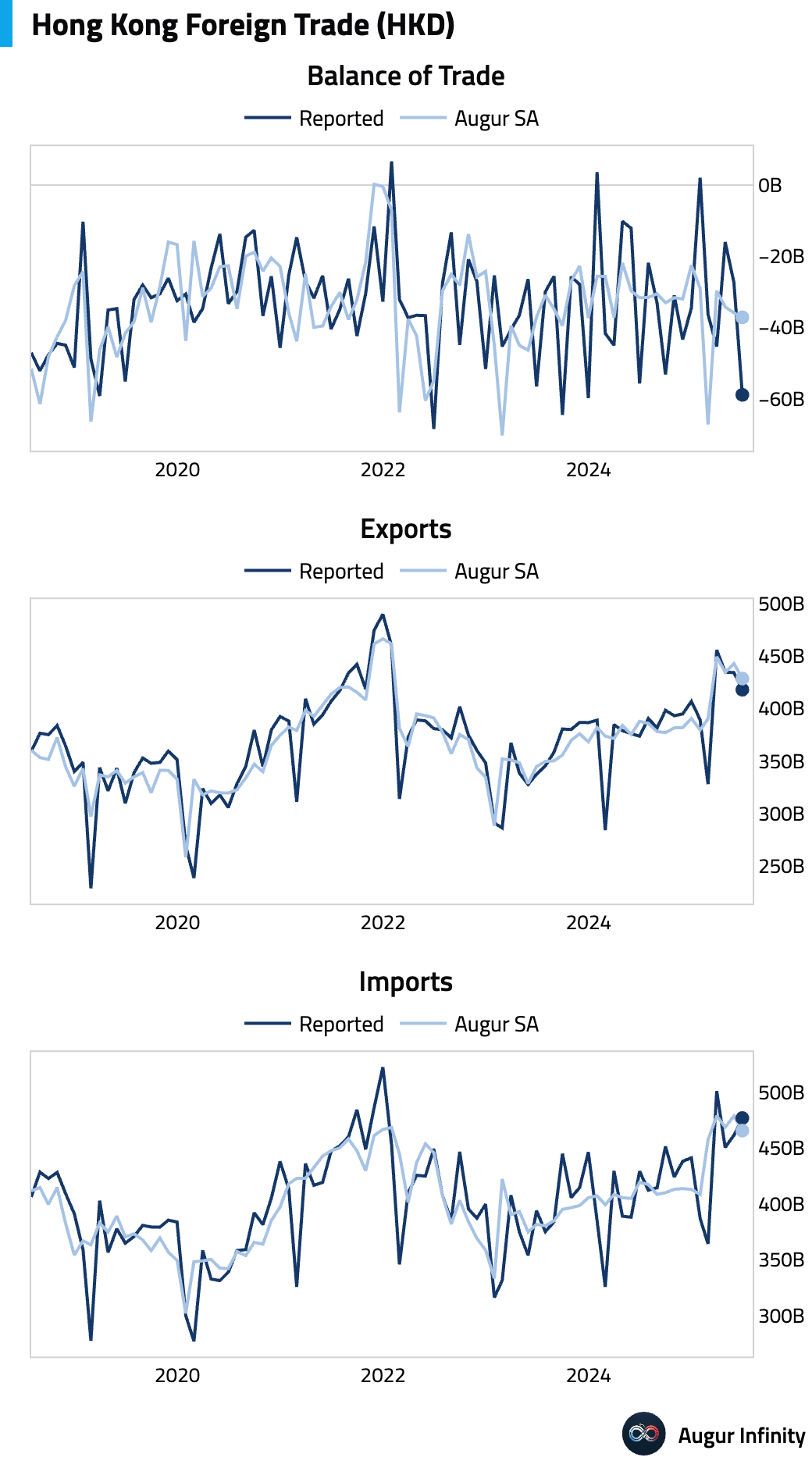
- Hong Kong's trade deficit widened significantly to H$-58.9 billion in June, its largest since December 2023, from H$-27.3 billion in May. The deterioration came as export growth slowed to 11.9% Y/Y from 15.5%, while import growth eased to 11.1% Y/Y from 18.9%.
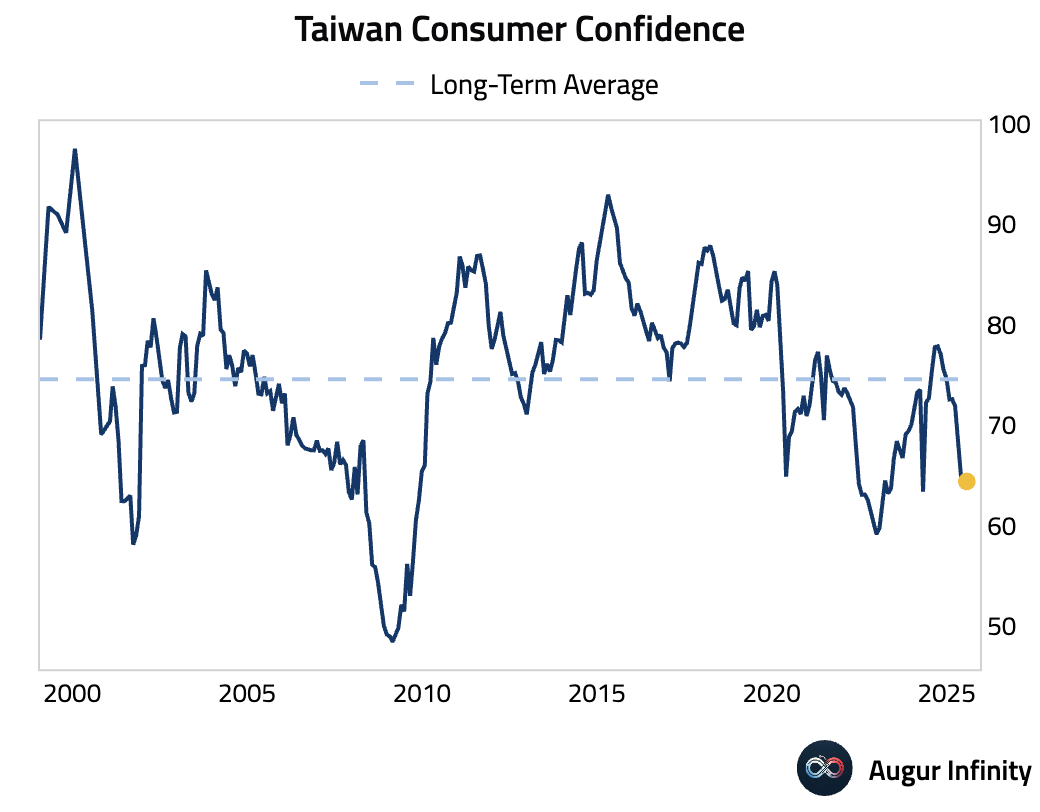
- Taiwan's consumer confidence improved for a second consecutive month, rising to 64.38 in July from 63.7 in June, suggesting a more optimistic outlook among households.
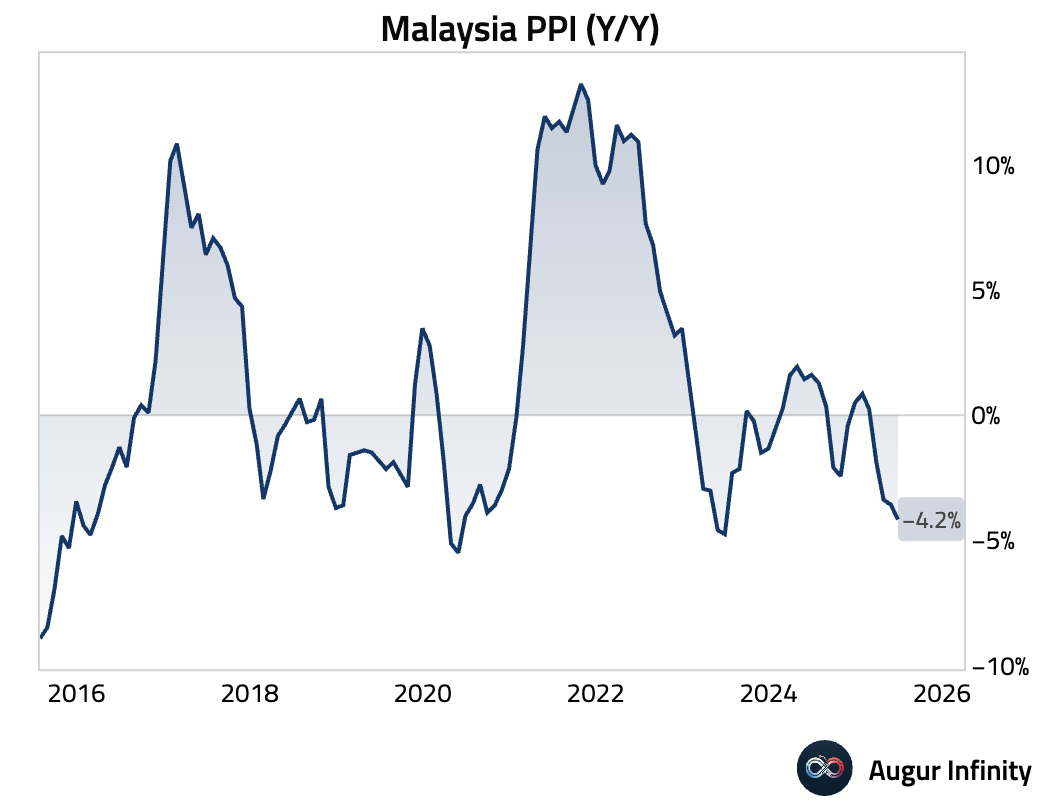
- Malaysia's Producer Price Index (PPI) declined 4.2% Y/Y in June, a sharper fall than May's 3.6% drop. This marks the weakest reading in a year and points to persistent disinflationary pressures in the production pipeline.
China
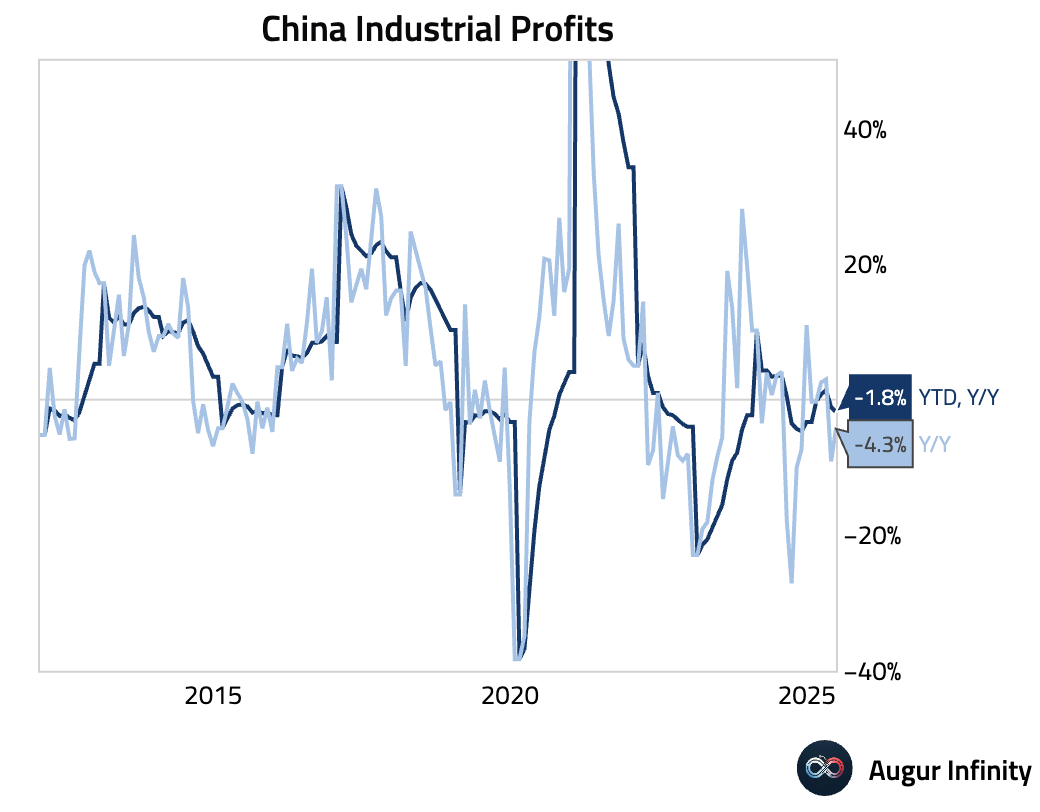
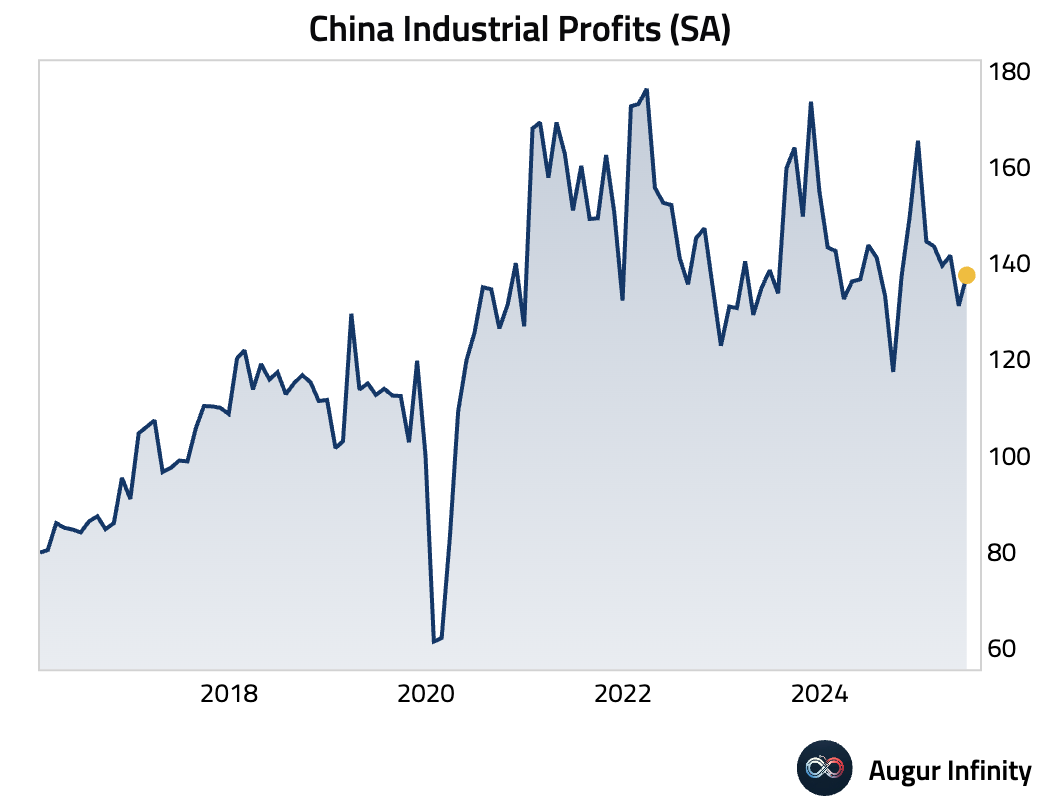
- Industrial profits year-to-date through June fell 1.8% Y/Y, a worsening from the -1.1% Y/Y pace in May. For the month of June alone, profits fell 4.4% Y/Y, though this was an improvement from May's 9.4% drop and showed a 6.2% sequential rebound. The data revealed a significant divergence, with a 96.8% Y/Y surge in auto industry profits—potentially driven by one-off factors—masking a 15.8% Y/Y decline in upstream sector profits.
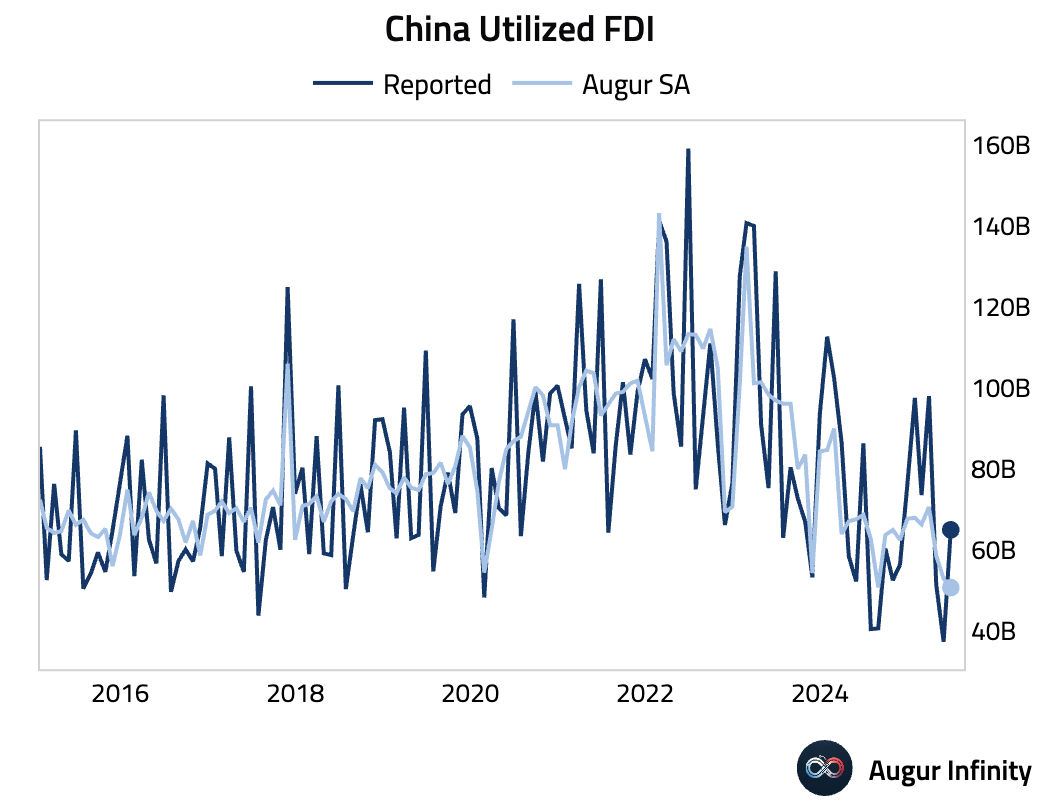
- Foreign direct investment continues to contract, with utilized FDI falling 15.2% Y/Y in June, accelerating from the 13.2% decline seen in May.
- Second-quarter PBOC surveys revealed deepening economic headwinds. Bankers' surveys showed loan demand fell to its lowest level on record, driven by weakness in small and medium-sized enterprises. Enterprise surveys pointed to plunging export orders and worsening deflationary pressures. Meanwhile, depositor surveys indicated deepening consumer caution, with a rising share of households intending to save more amid weaker employment and property price sentiment.
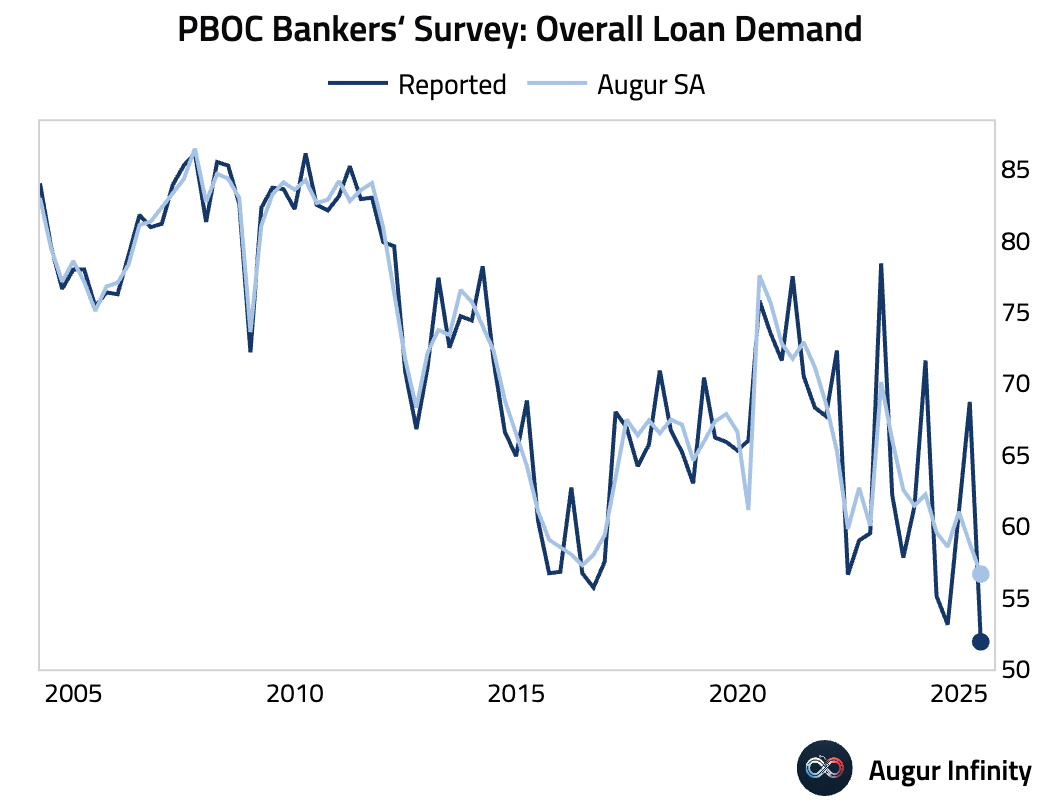
Emerging Markets ex China
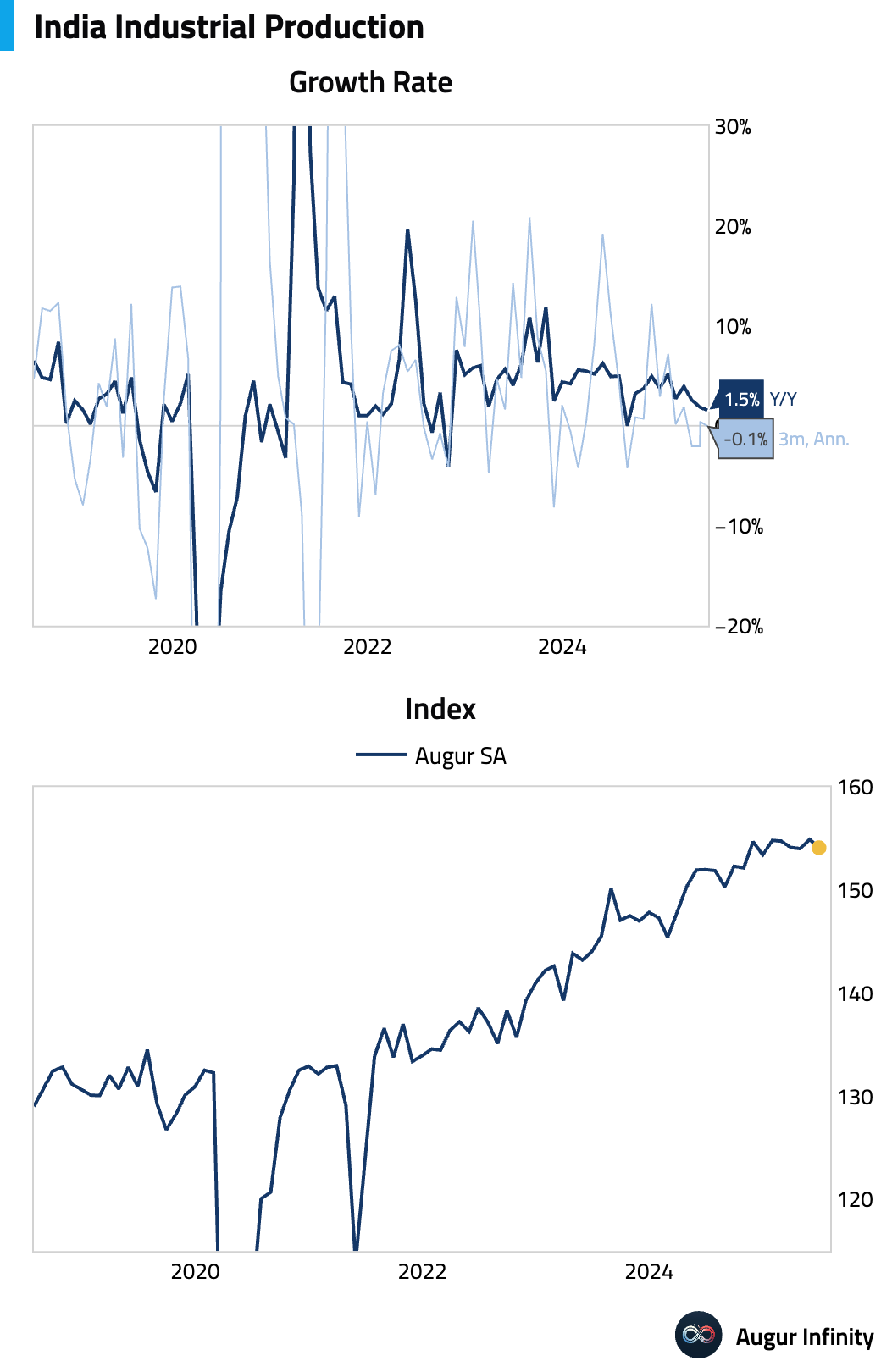
- India's industrial production growth slowed to 1.5% Y/Y in June, missing the 2.0% consensus and decelerating from May's 1.9% print. This marks the weakest annual growth since August 2024. However, manufacturing production accelerated to 3.9% Y/Y from 3.2%.
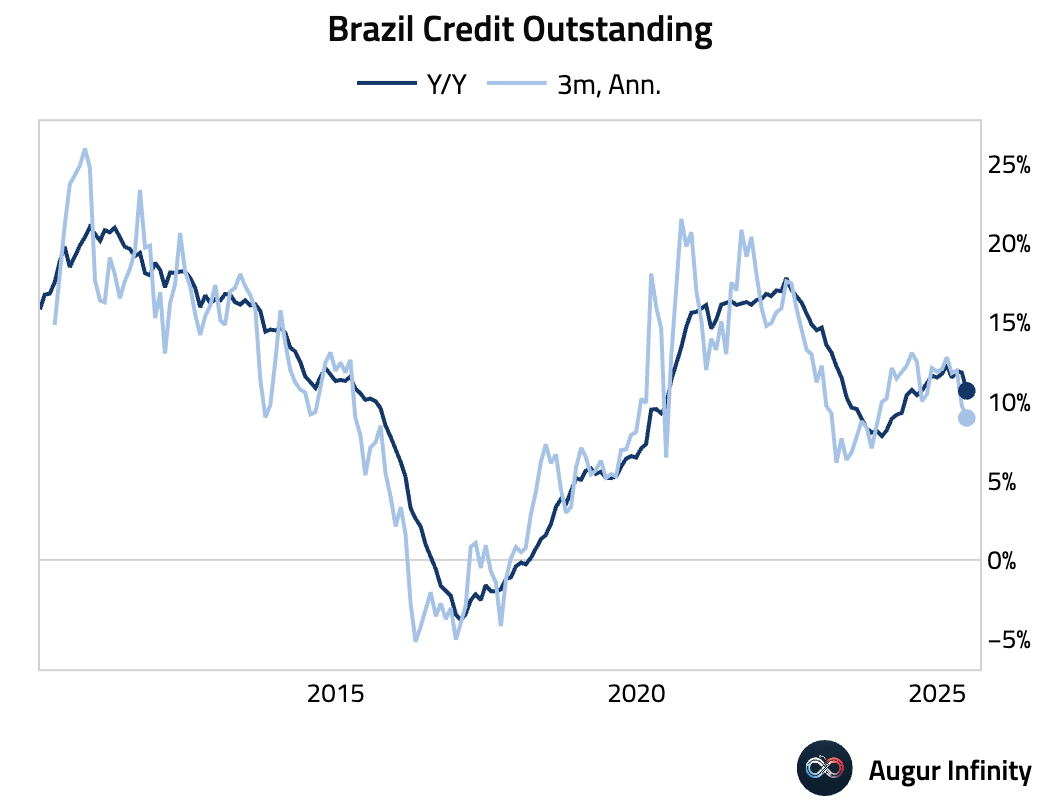
- Brazil's bank lending growth held steady at 0.5% M/M in June. However, broader credit dynamics show weakness, as a 7.5% M/M drop in corporate credit origination offset a 1.4% rise in household lending. Signs of stress are emerging, with household NPLs rising to 6.3% and indebtedness reaching 49.0% of disposable income.
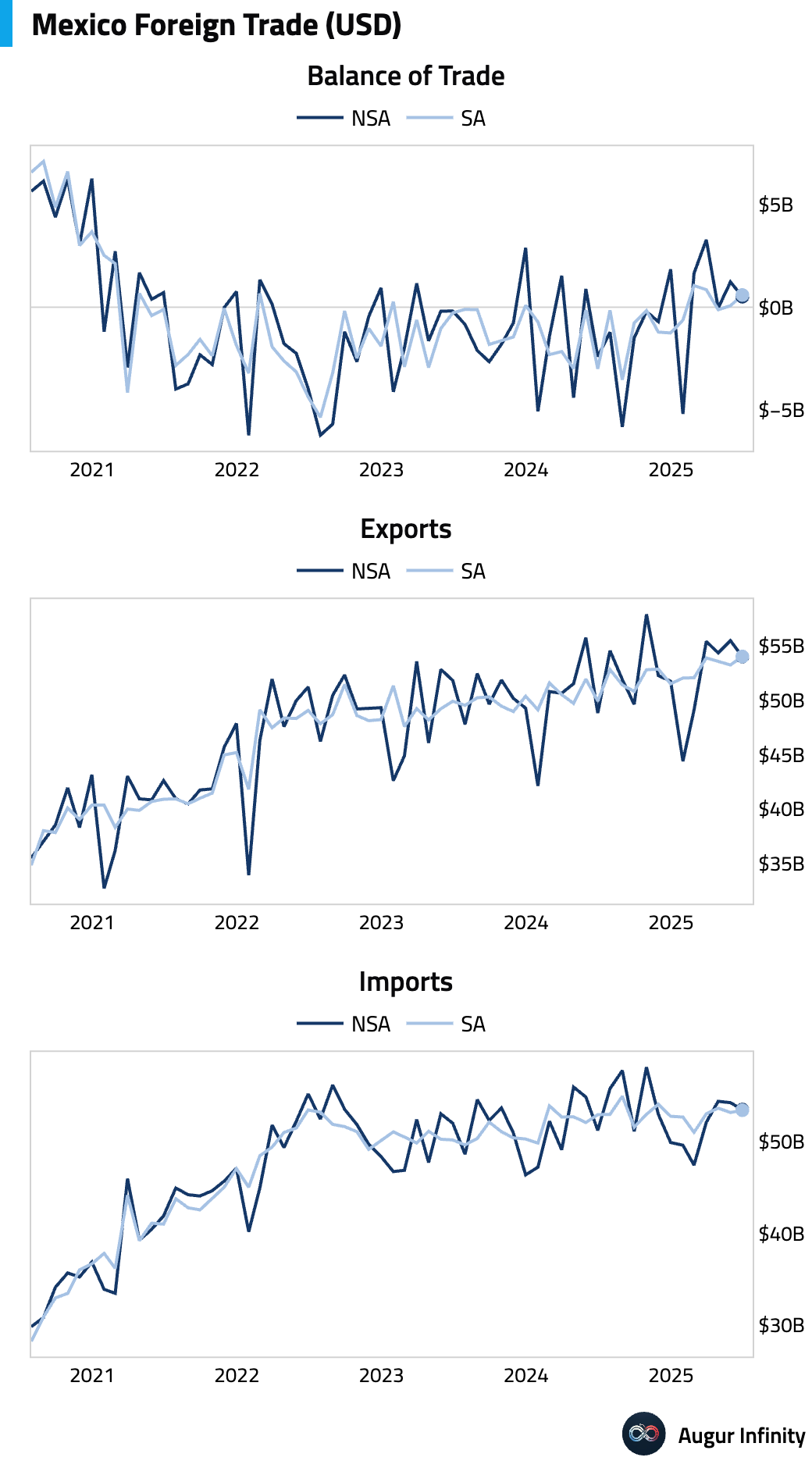
- Mexico's trade balance recorded a $514 million surplus in June, missing the $610 million consensus and narrowing from May's $1.23 billion surplus. The positive balance was driven by a robust non-oil surplus that masked a deteriorating oil deficit. Underlying data points to firm manufacturing exports but soft domestic investment, as capital goods imports fell for the seventh consecutive month.
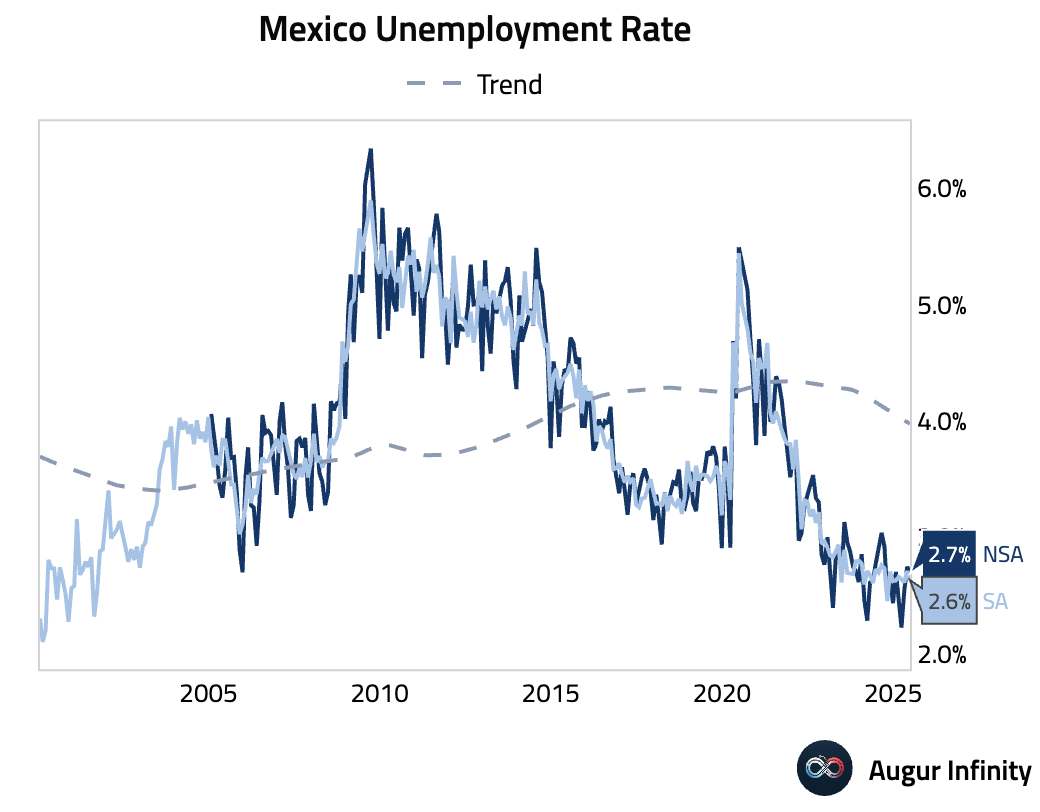
- Mexico's unemployment rate edged down to 2.7% in June, beating the 2.8% consensus and holding near multi-decade lows. However, this headline strength masks weakness in the formal sector, where employment has been largely stagnant since the third quarter of 2024.
Global Markets
Equities
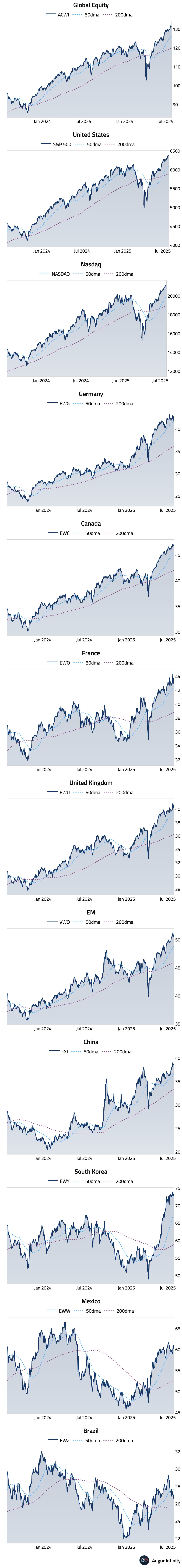
- Global equity markets were mixed, with US stocks holding steady after recent gains while European markets declined. The main US indices were flat, extending a six-day winning streak, while the Nasdaq rose 0.3% for its fourth straight day of gains. European markets broadly fell, with Germany (-2.7%) and France (-2.1%) seeing the largest declines. In emerging markets, Brazil (-1.6%) and Mexico (-1.6%) underperformed, with Brazil logging its third consecutive day of losses.
Fixed Income
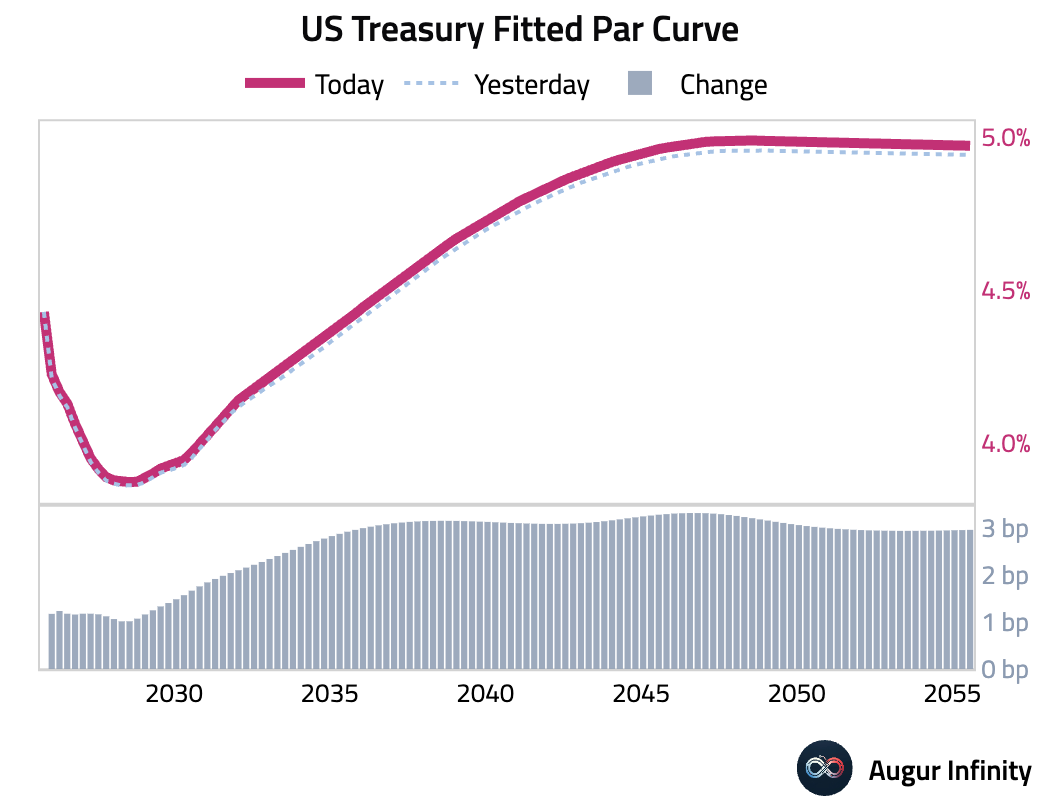
- US Treasury yields rose across the curve, resulting in a slight bear steepening. The 10-year yield climbed 2.9 bps, while the 2-year yield increased by 1.2 bps. The move came ahead of key inflation and employment data releases later in the week.
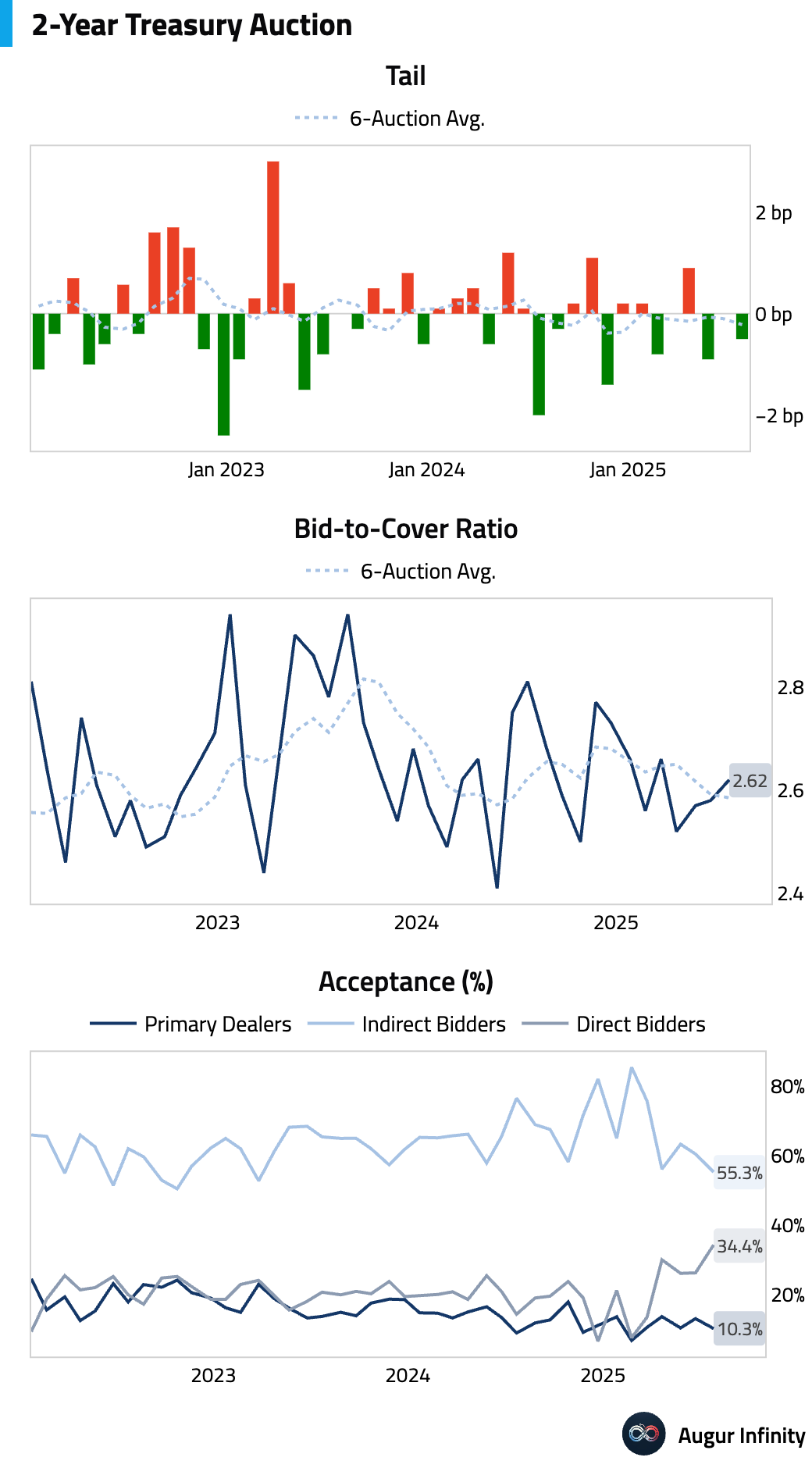
- Demand was strong at the Treasury's auction of $69 billion in 2-year notes. The auction priced at 3.920%, stopping through the when-issued yield by 0.5 bps. The bid-to-cover ratio improved to 2.62x, and a low dealer takedown of 10.3% pointed to solid real-money demand.
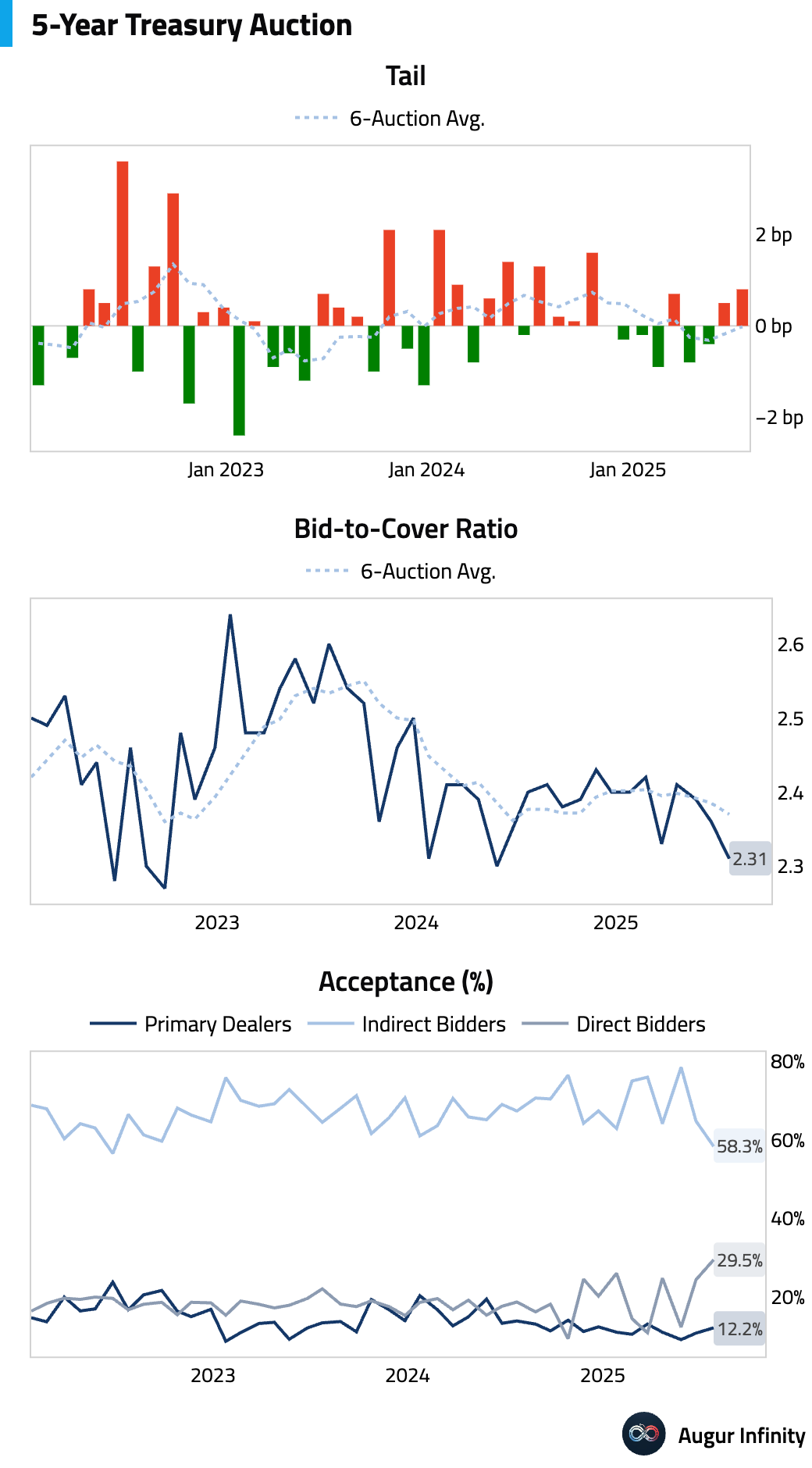
- The auction for $70 billion in 5-year notes was mixed. It priced with a modest 0.8 bps tail, and the bid-to-cover ratio of 2.31x was below average. A drop in indirect bidder participation was partially offset by strong direct bidder interest, leaving dealers with a larger-than-usual share of 12.2%.
FX
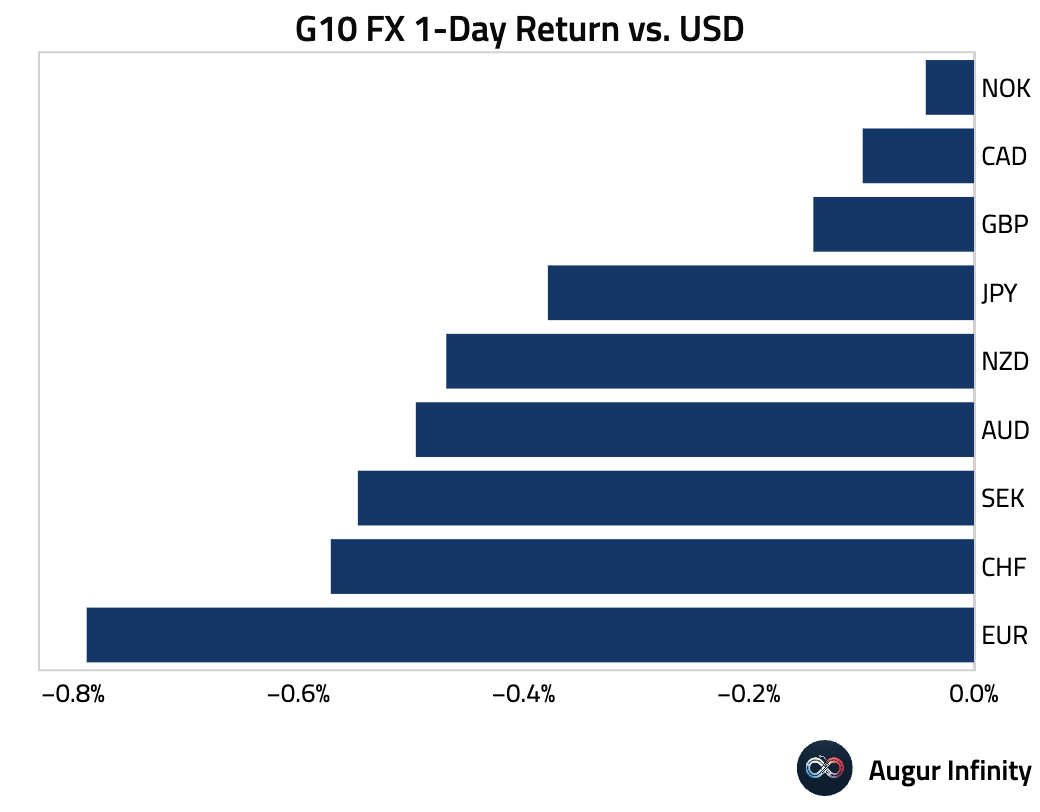
- The US dollar strengthened broadly against its G10 peers following the US-EU trade agreement. The euro was the weakest performer, falling 0.8% against the dollar. The Canadian dollar, British pound, Japanese yen, and Swiss franc all posted their third consecutive day of losses against the greenback.
Disclaimer
Augur Digest is an automated newsletter written by an AI. It may contain inaccuracies and is not investment advice. Augur Labs LLC will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your reliance on the information contained in the newsletter.

