Headlines
- President Trump to nominate Stephen Miran to be new Fed governor, replacing Adriana Kugler.
- President Trump threatened to impose a 100 percent tariff on semiconductor imports from companies without US production facilities and new tariffs on Chinese imports if China continues purchasing Russian oil.
- The Swiss federal council will hold an extraordinary meeting after trade negotiations with the United States ended without an agreement.
Global Economics
United States
- Atlanta Fed Wage Growth Tracker slipped to 4.1% in July (down from 4.2% in June). Job switchers held steady at 4.0%, while those staying put saw wages cool from 4.2% to 4.1%.
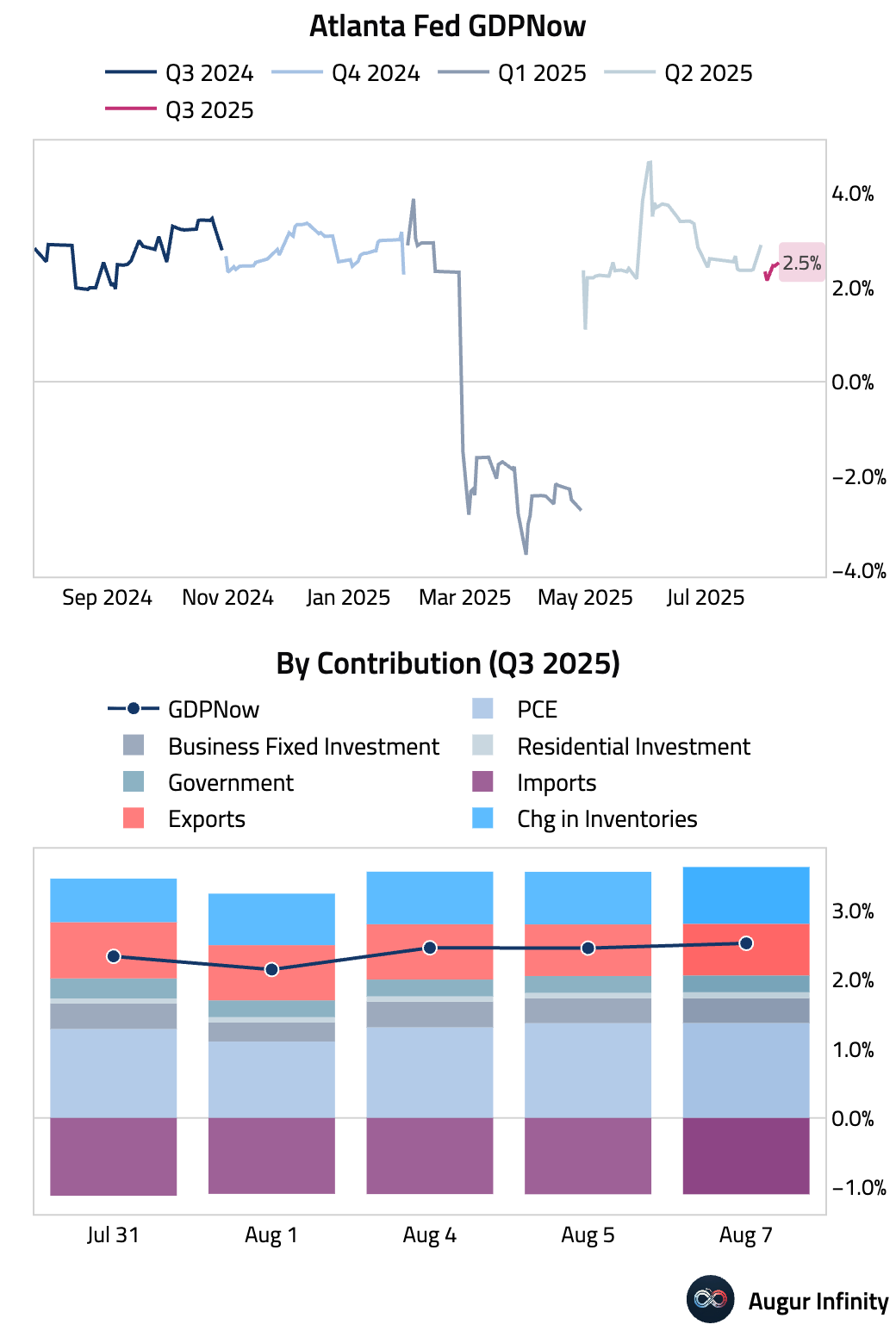
- The Atlanta Fed's GDPNow model is tracking Q3 GDP at 2.5% today, unchanged from August 5 after rounding.
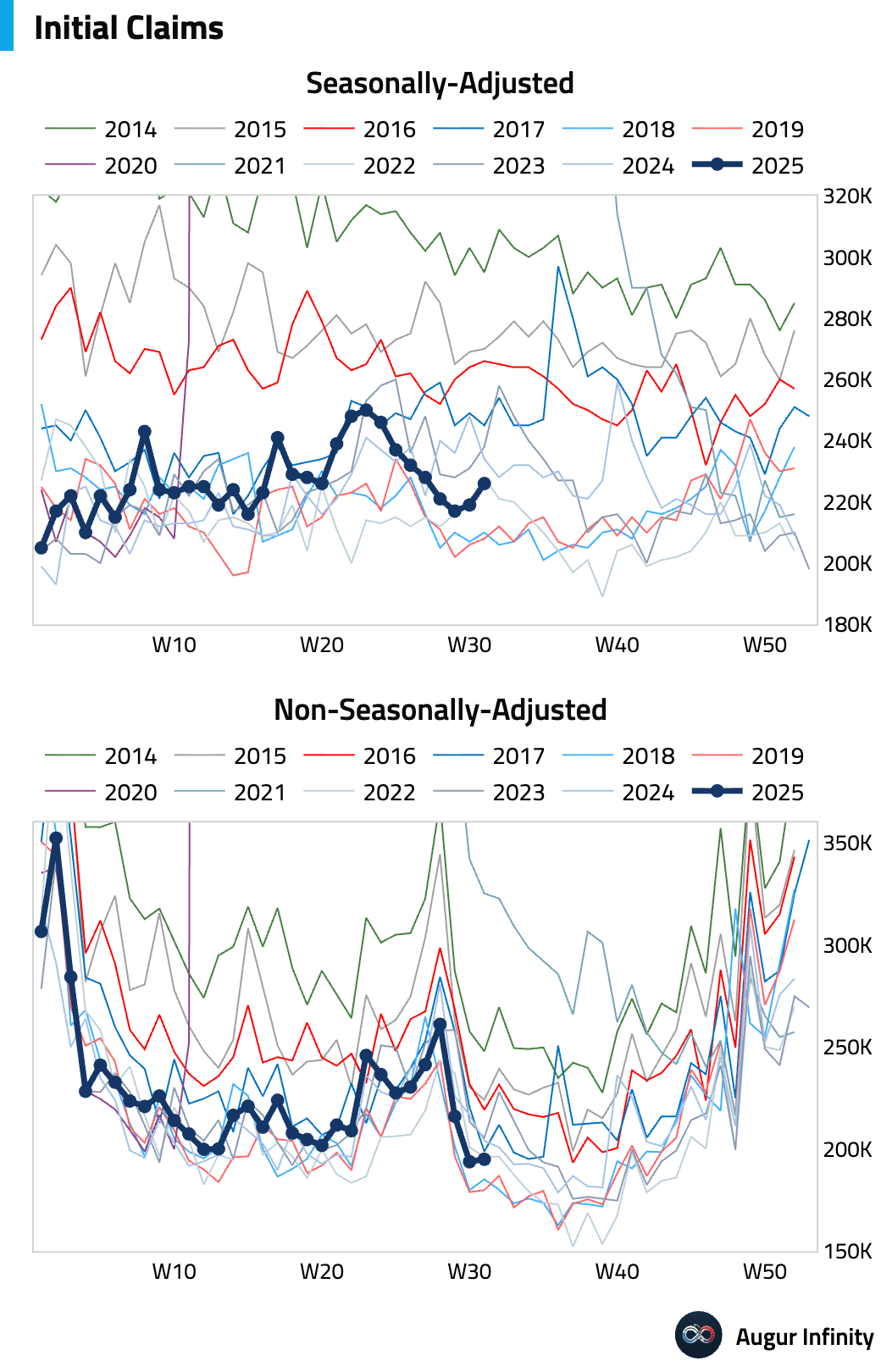
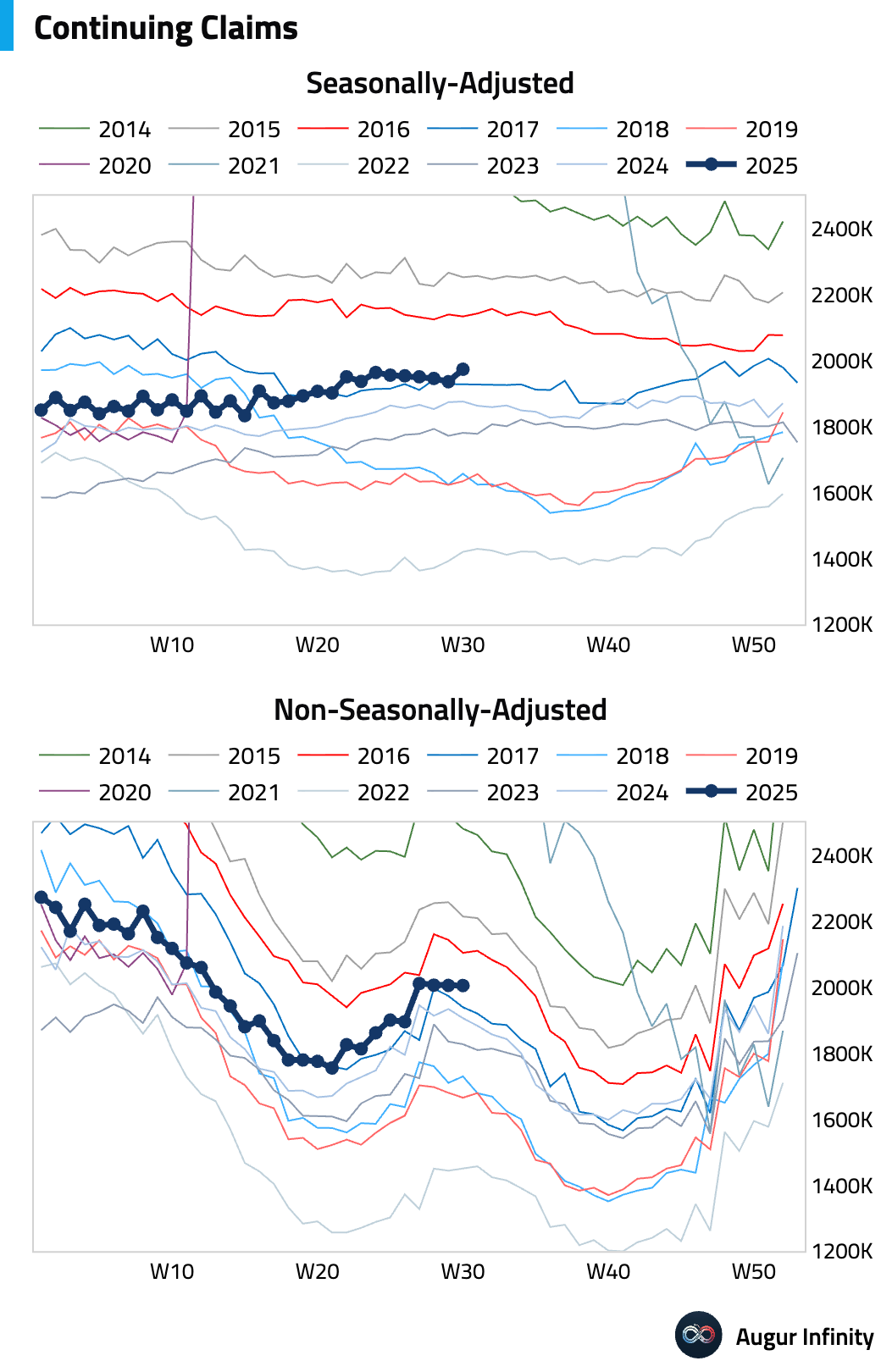
- Initial jobless claims for the week ending August 2 rose by 7,000 to 226,000, slightly above consensus. The four-week moving average remained stable at 221,000, suggesting a steady underlying trend in layoffs. Continuing claims for the week ending July 26 rose more than expected to 1.974 million, reaching their highest level since November 2021.
- Preliminary data for Q2 2025 showed Nonfarm Productivity rose by a seasonally adjusted annualized 2.4%, beating the 2.0% consensus forecast. The increase reflects strong output growth during the quarter.
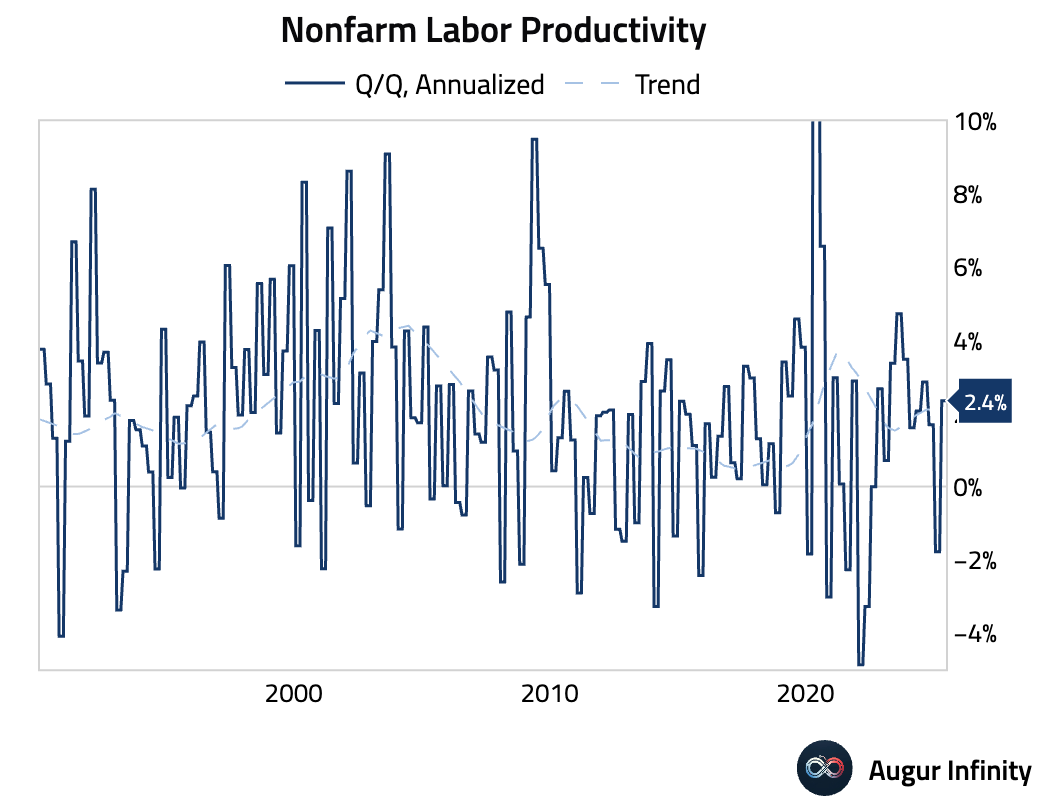
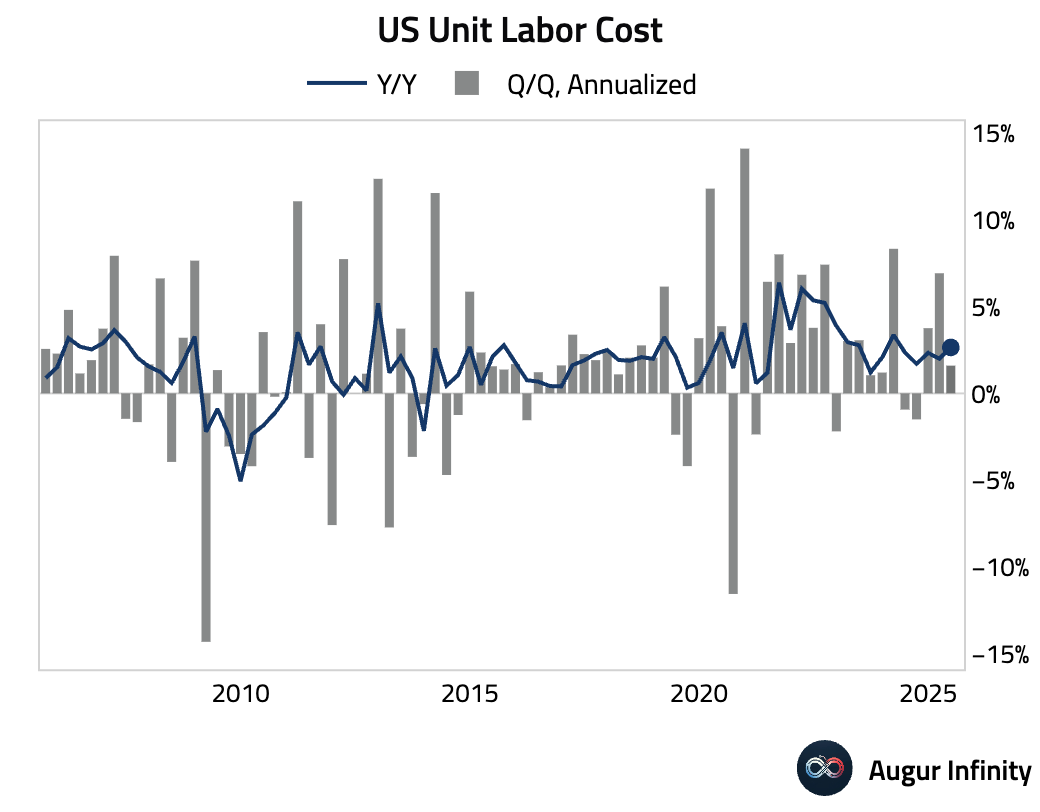
- Preliminary Unit Labor Costs for Q2 2025 increased by a seasonally adjusted annualized 1.6%, slightly above the 1.5% consensus. The year-over-year rate now stands at 2.6%, as compensation growth slowed to 4.0% but was outpaced by productivity gains.
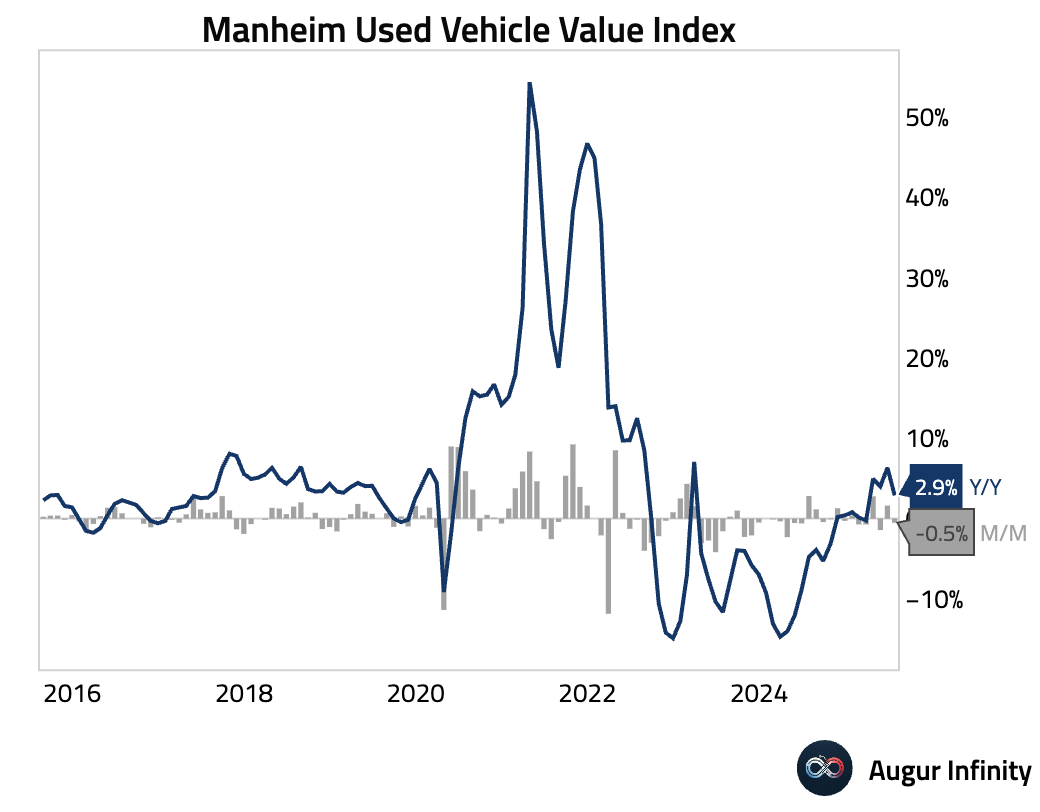
- The Manheim Used Vehicle Value Index fell 0.5% M/M in July, reversing a 1.6% gain in June. The year-over-year increase decelerated sharply to 2.9% from 6.3%.
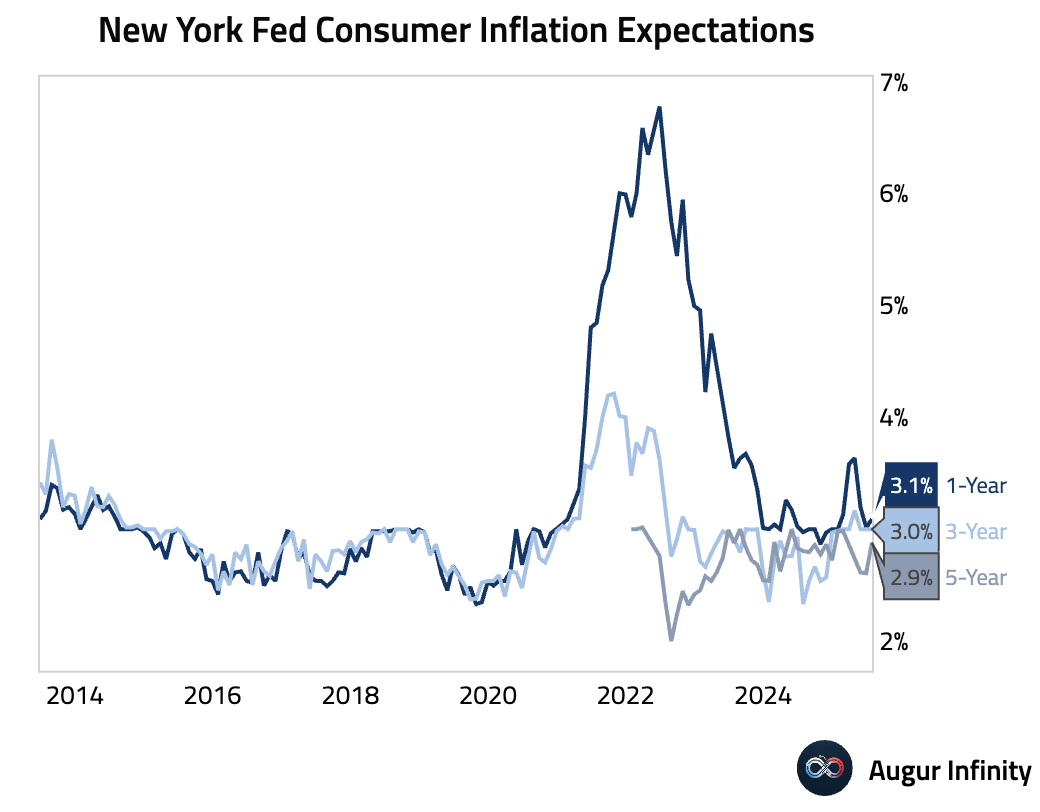
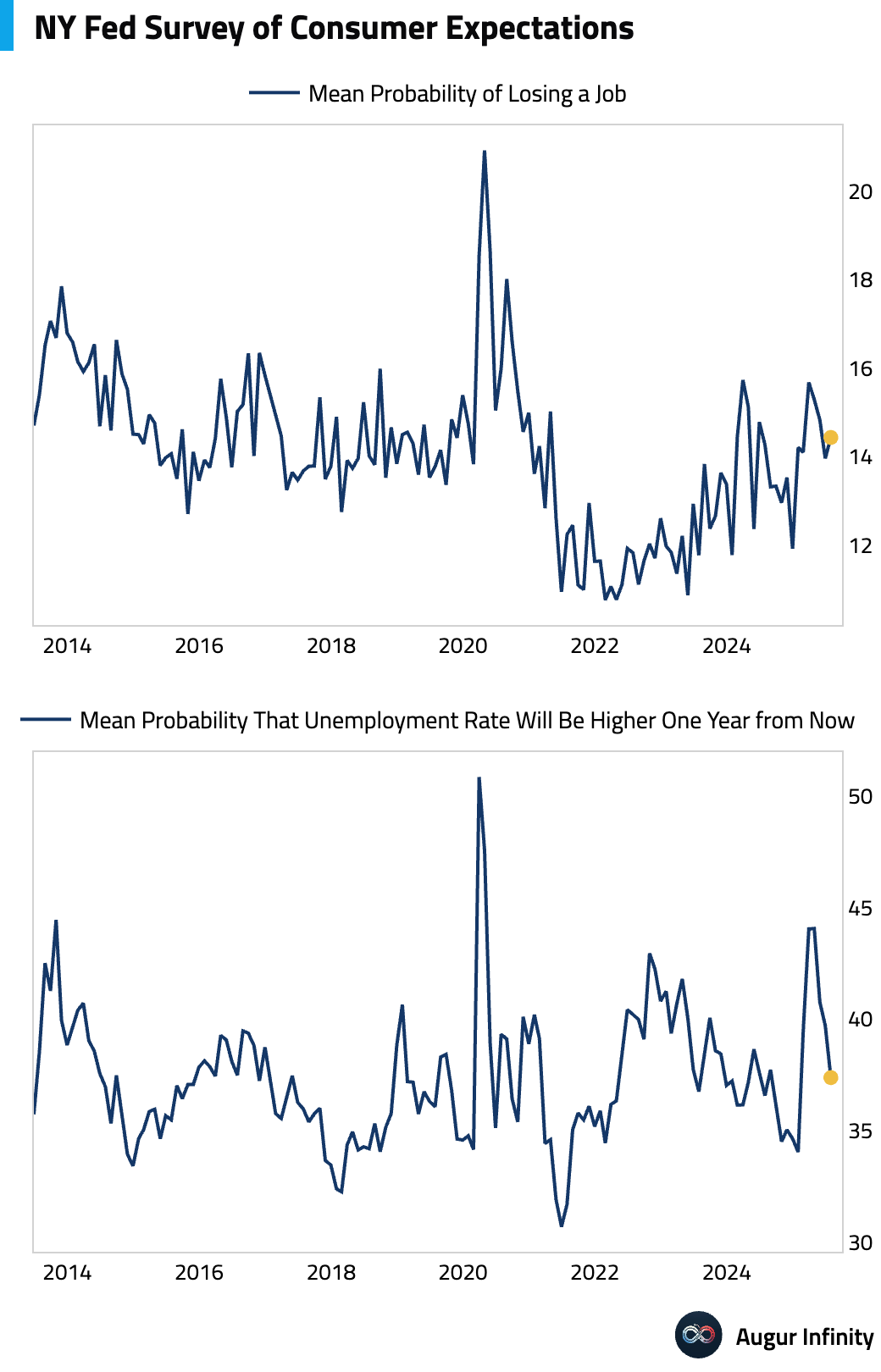
- The New York Fed's July Survey of Consumer Expectations showed a rise in one-year inflation expectations to 3.1% from 3.0%. For labor market, the perceived probability of personal job loss increased to 14.4%.
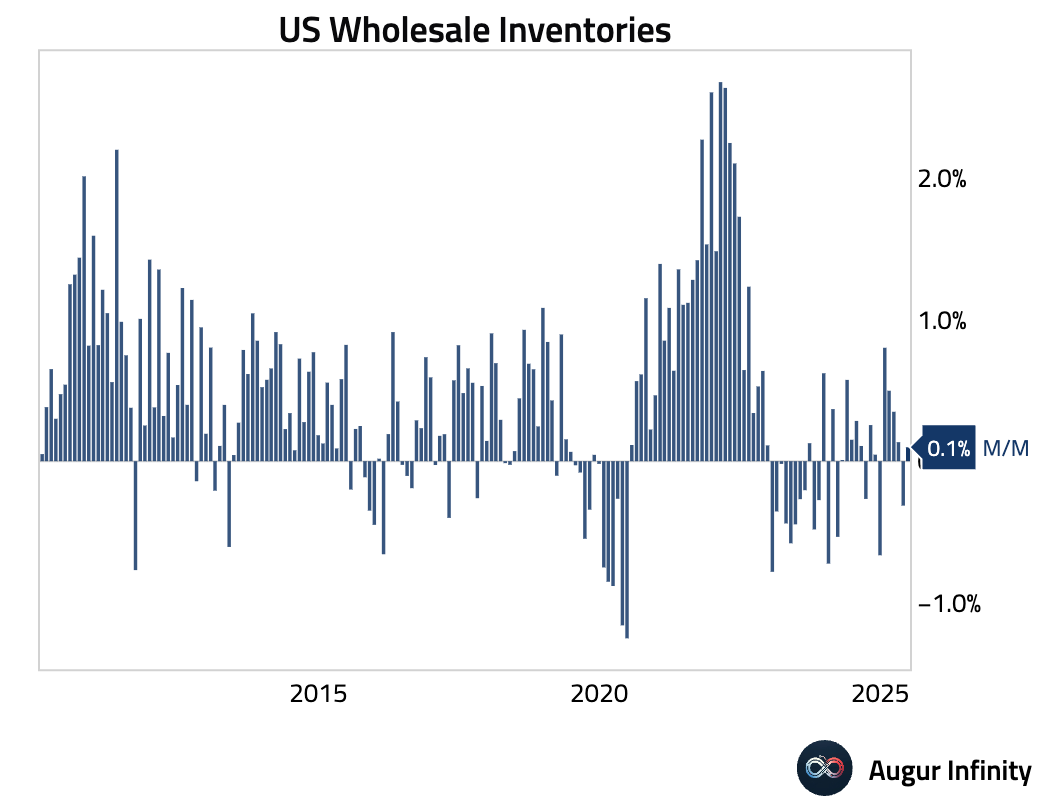
- Wholesale inventories rose 0.1% M/M in June, in line with the advance estimate and reversing a 0.3% decline in May.
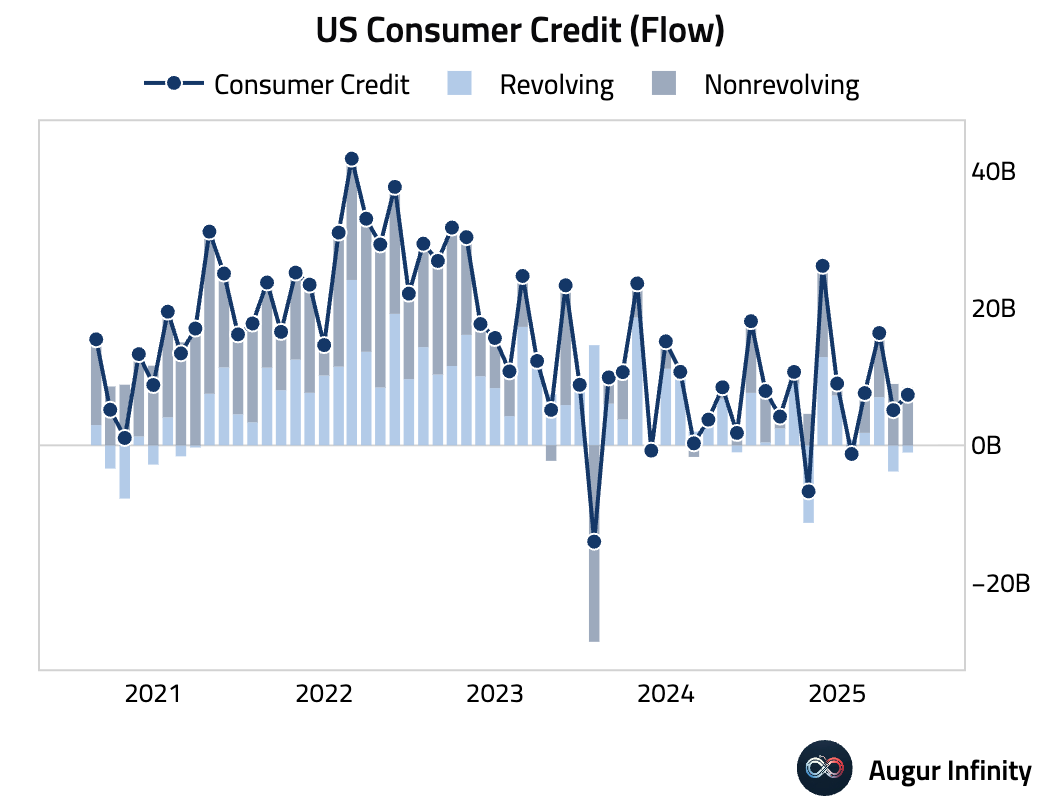
- Consumer credit rose by $7.37 billion in July, above consensus ($7 billion). The increase was driven entirely by nonrevolving credit.
Canada
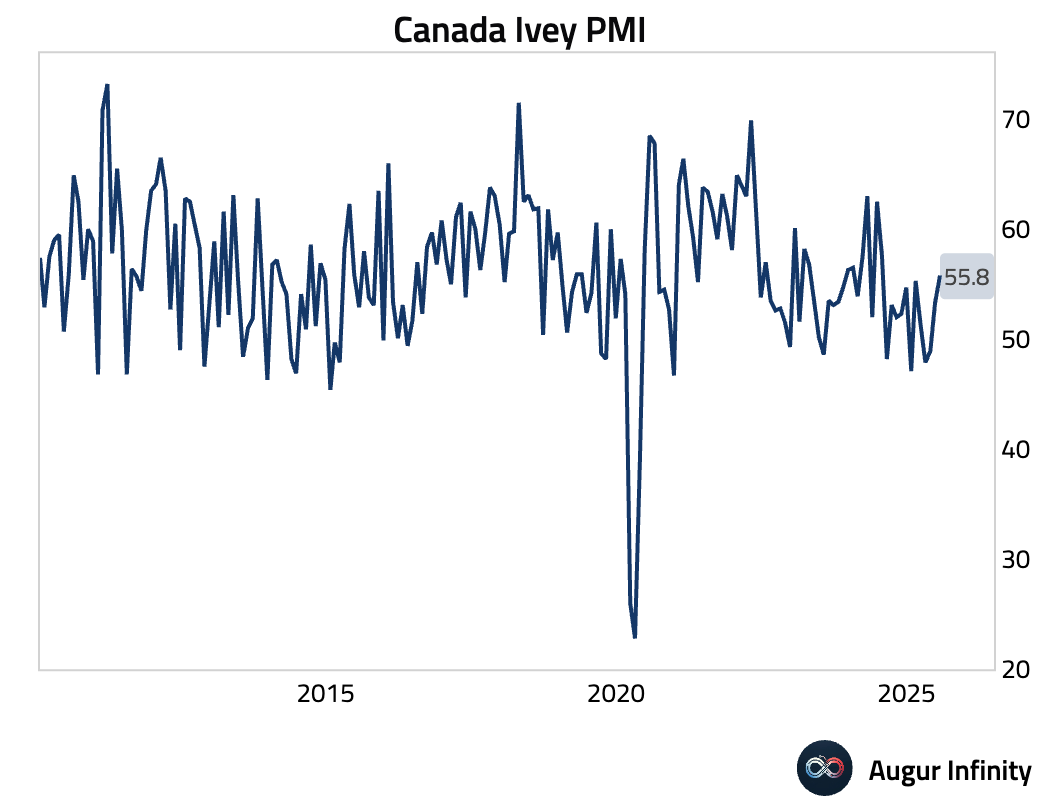
- The Ivey PMI rose to 55.8 in July from 53.3, beating the consensus of 55.2 and marking its highest reading in a year.
Europe
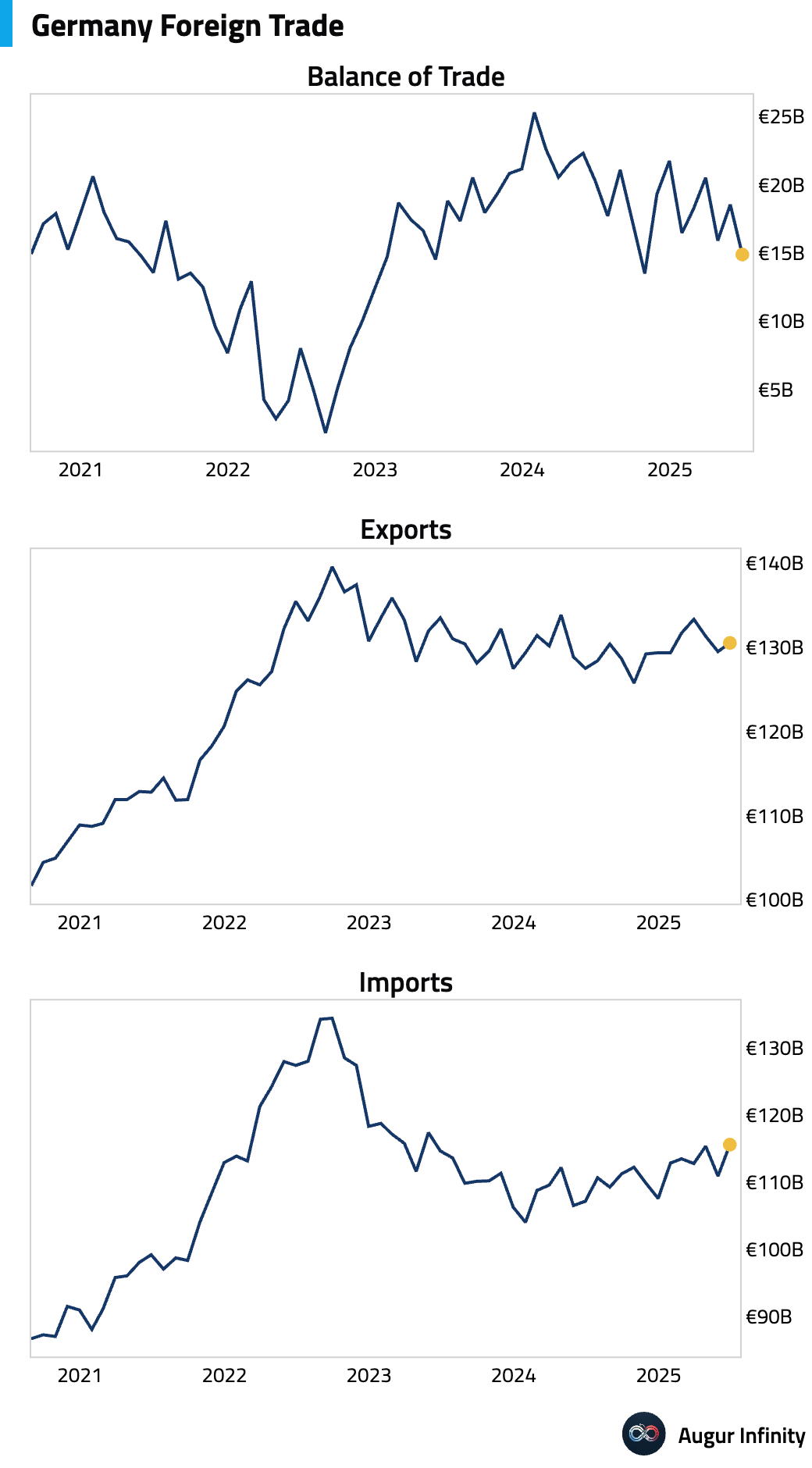
- Germany's trade surplus narrowed to a seasonally adjusted €14.9 billion in June, missing the €17.3 billion consensus. The miss was driven by a larger-than-expected 4.2% M/M surge in imports (cons. +1.0%), which outpaced a solid 0.8% M/M rise in exports.
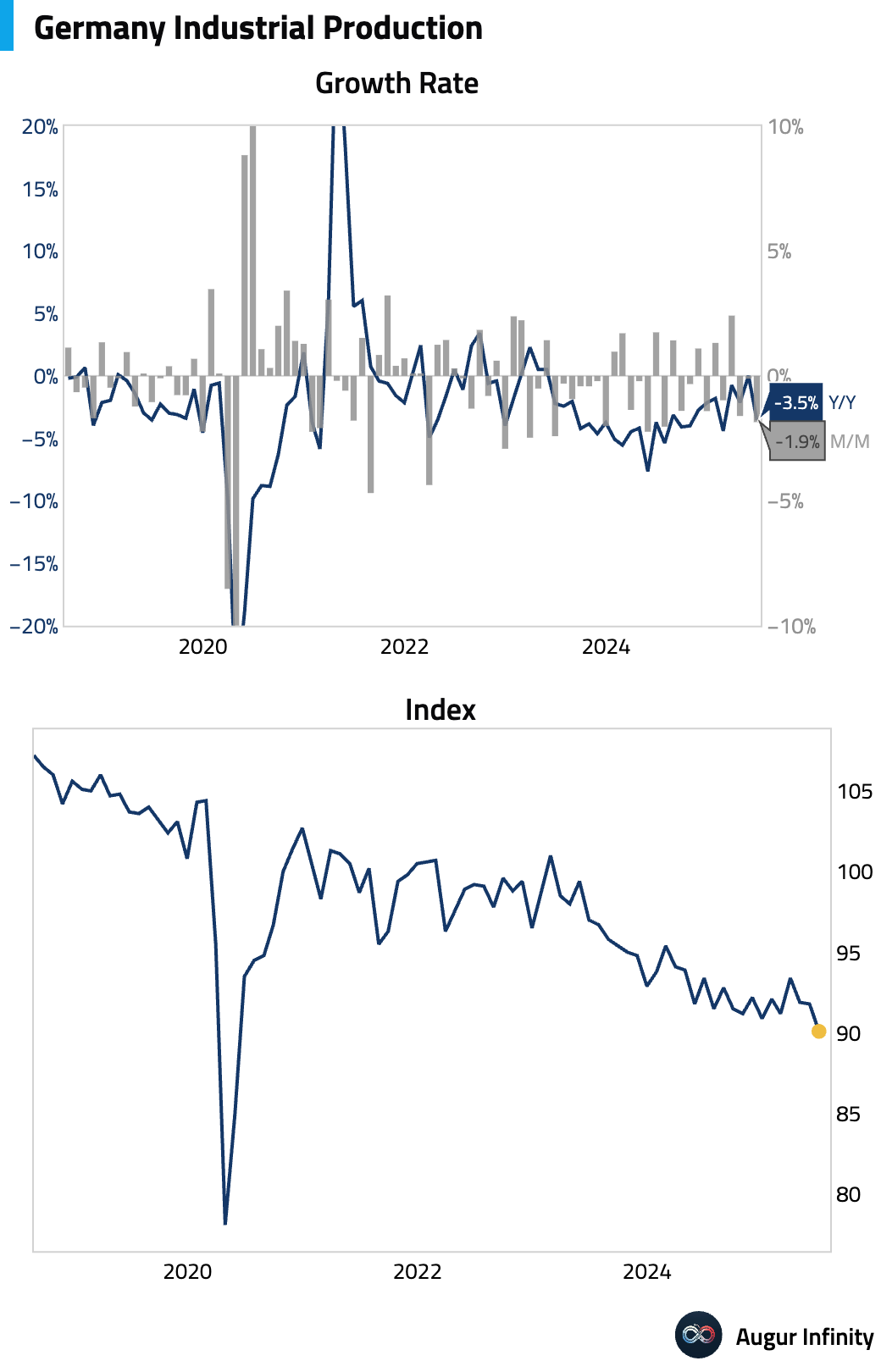
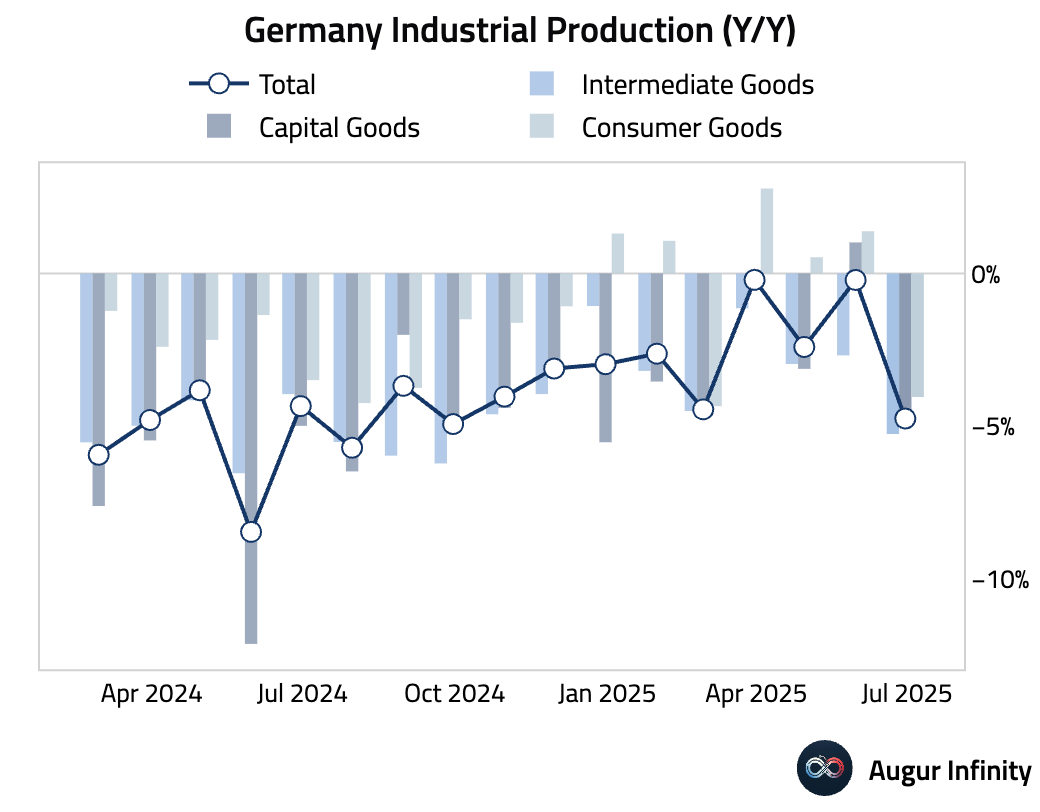
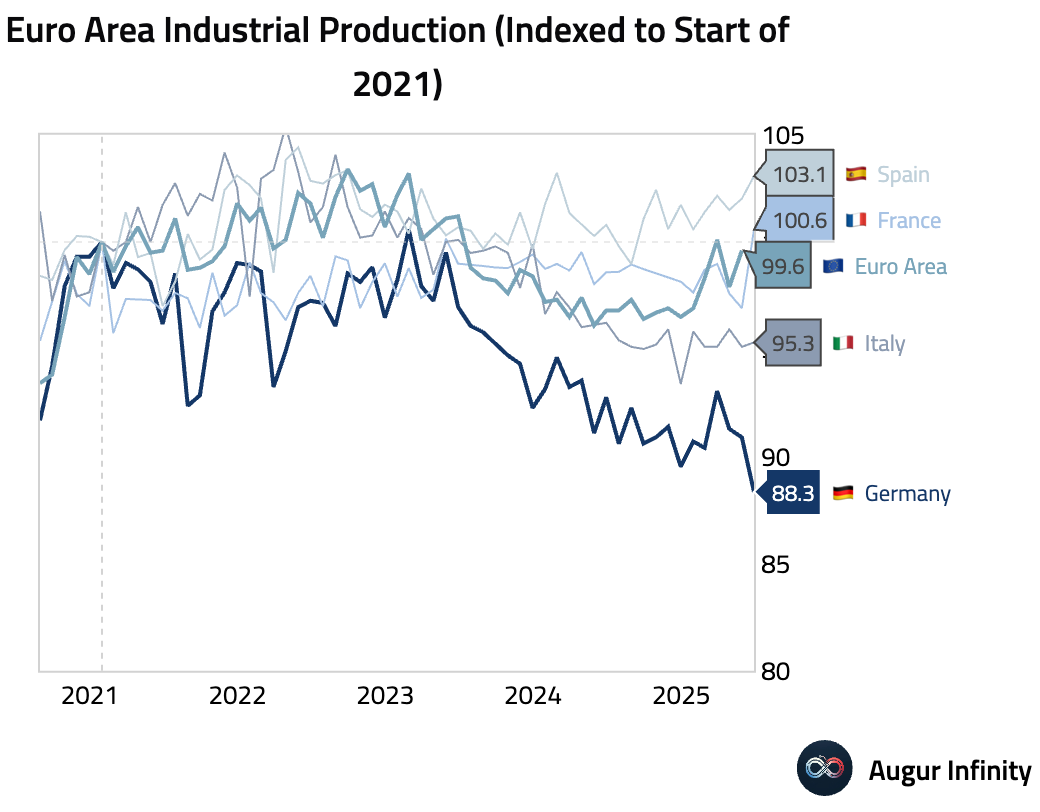
- German industrial production fell 1.9% M/M in June, a significant disappointment compared to the -0.5% consensus forecast and the steepest decline in a year. The drop was led by a sharp contraction in the production of capital goods.
- The Bank of England cut its policy rate by 25 basis points to 4.00%, as expected, but the Monetary Policy Committee was sharply divided. The decision passed on a narrow 5-4 vote, with the four dissenters preferring to hold rates steady due to persistent inflation risks. The BoE raised its Q3 2026 inflation forecast to 2.7% from 2.4%, signaling a high bar for further easing.
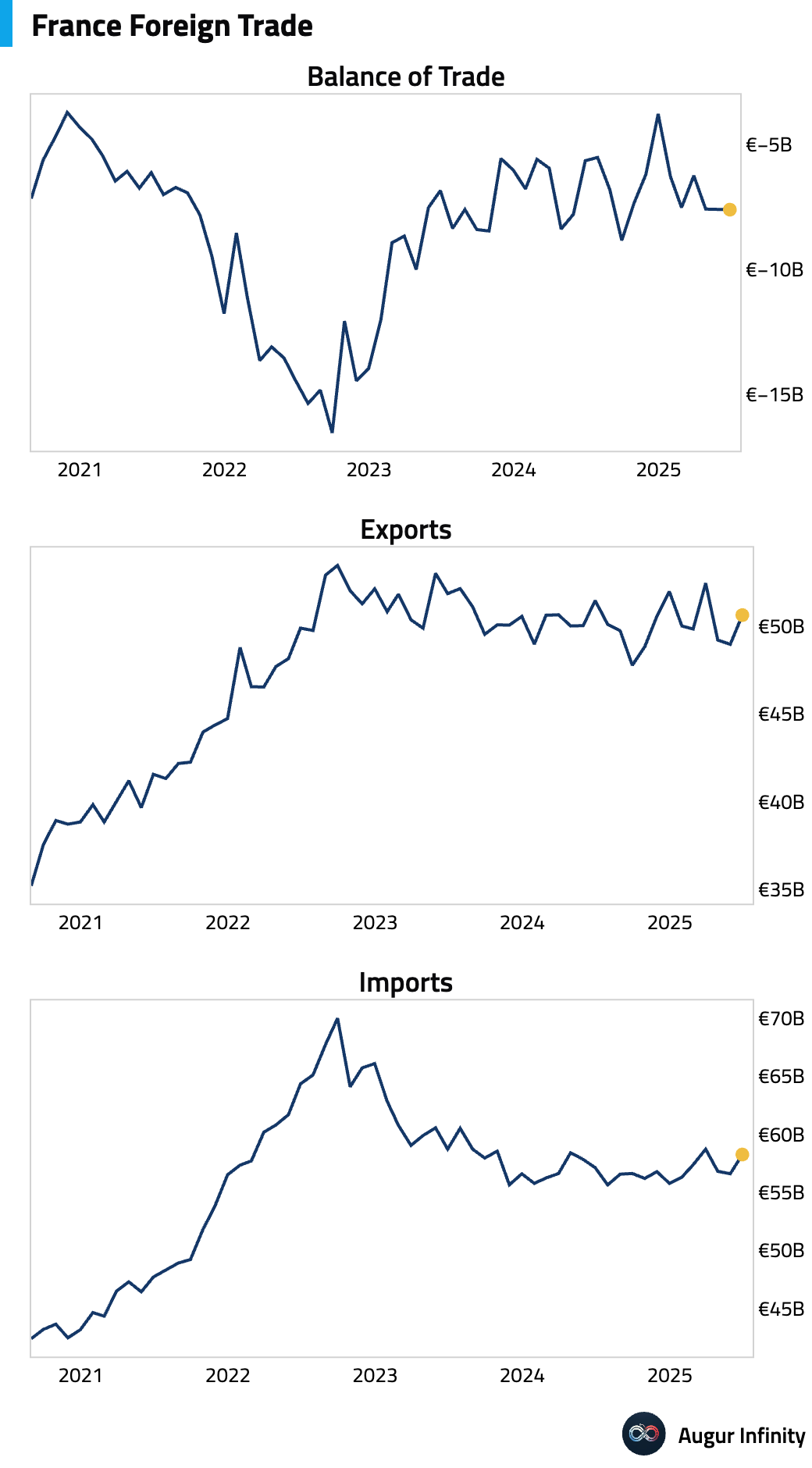
- France's trade deficit was unchanged at a seasonally adjusted -€7.6 billion in June, in line with expectations, as both exports and imports increased.
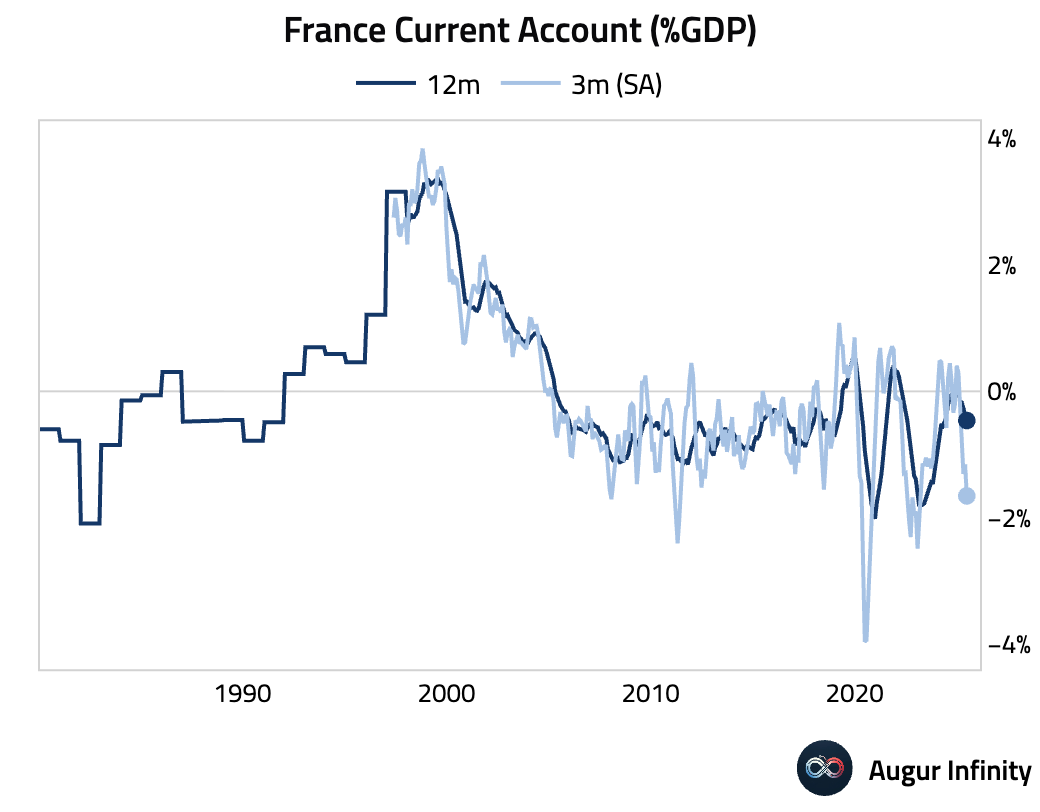
- France's current account deficit widened to a seasonally adjusted -€3.4 billion in June from -€2.6 billion in the prior month.
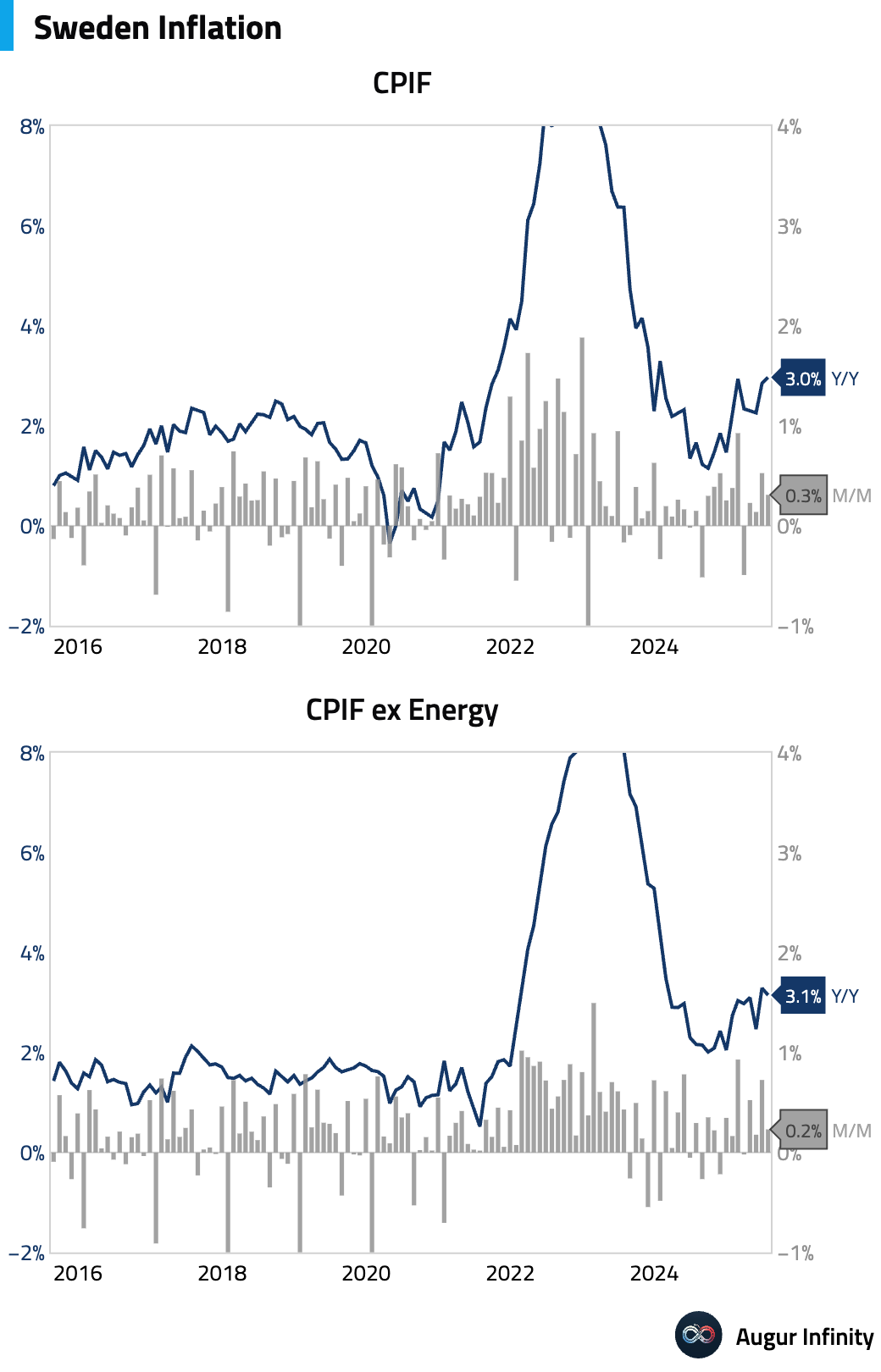
- Sweden's preliminary CPIF inflation came in at 3.0% Y/Y and 0.3% M/M in July, broadly in line with expectations. The core measure excluding energy slowed to 3.1% Y/Y, a slight downside surprise. Despite the moderation, which may be a payback for a strong June print, underlying price pressures remain elevated, suggesting the Riksbank is likely to hold its policy rate at its upcoming meeting.
- Switzerland's unemployment rate held steady at 2.7% in July, matching the prior month's reading but slightly missing the 2.8% consensus.
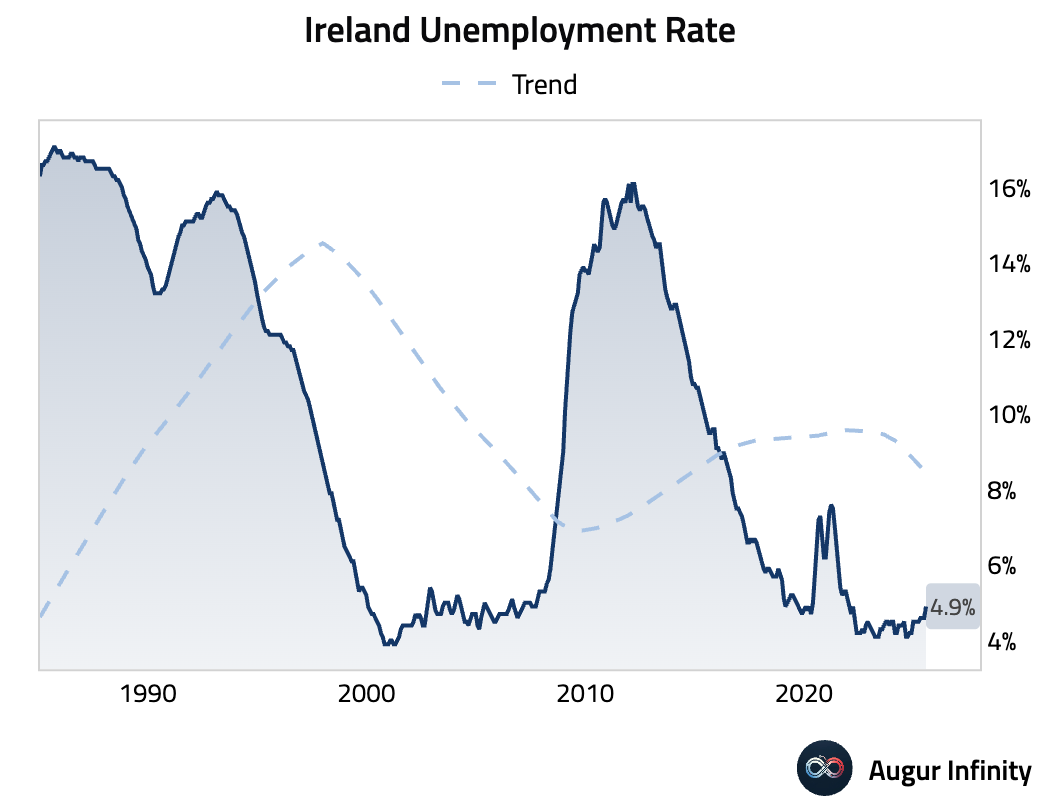
- Ireland's unemployment rate rose to 4.9% in July from 4.6% in June, its highest level since January 2022.
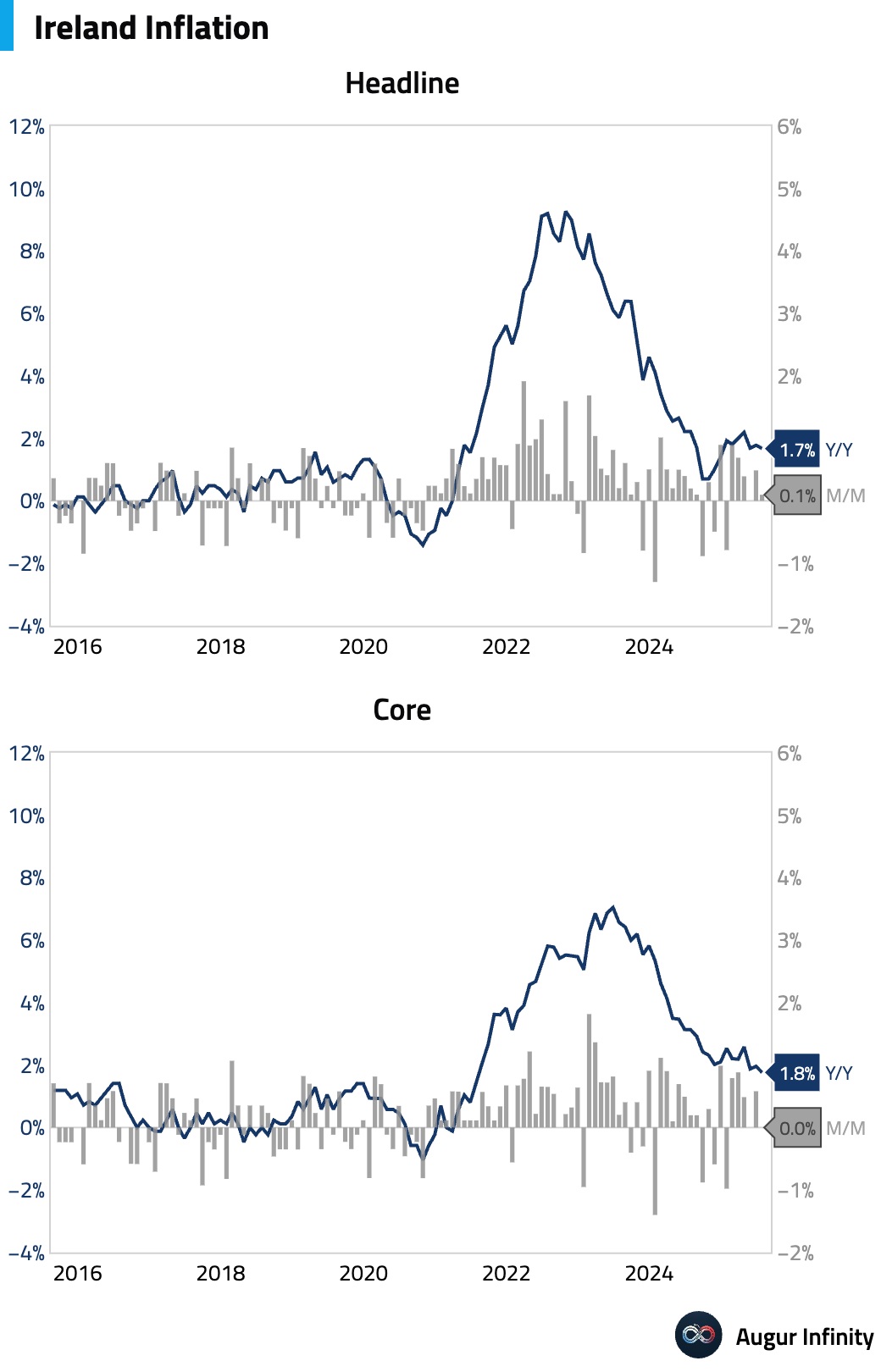
- Final Irish inflation for July was confirmed at 1.7% Y/Y (0.1% M/M), a slight deceleration from June's 1.8% rate. The harmonized HICP measure was also confirmed at 1.6% Y/Y.
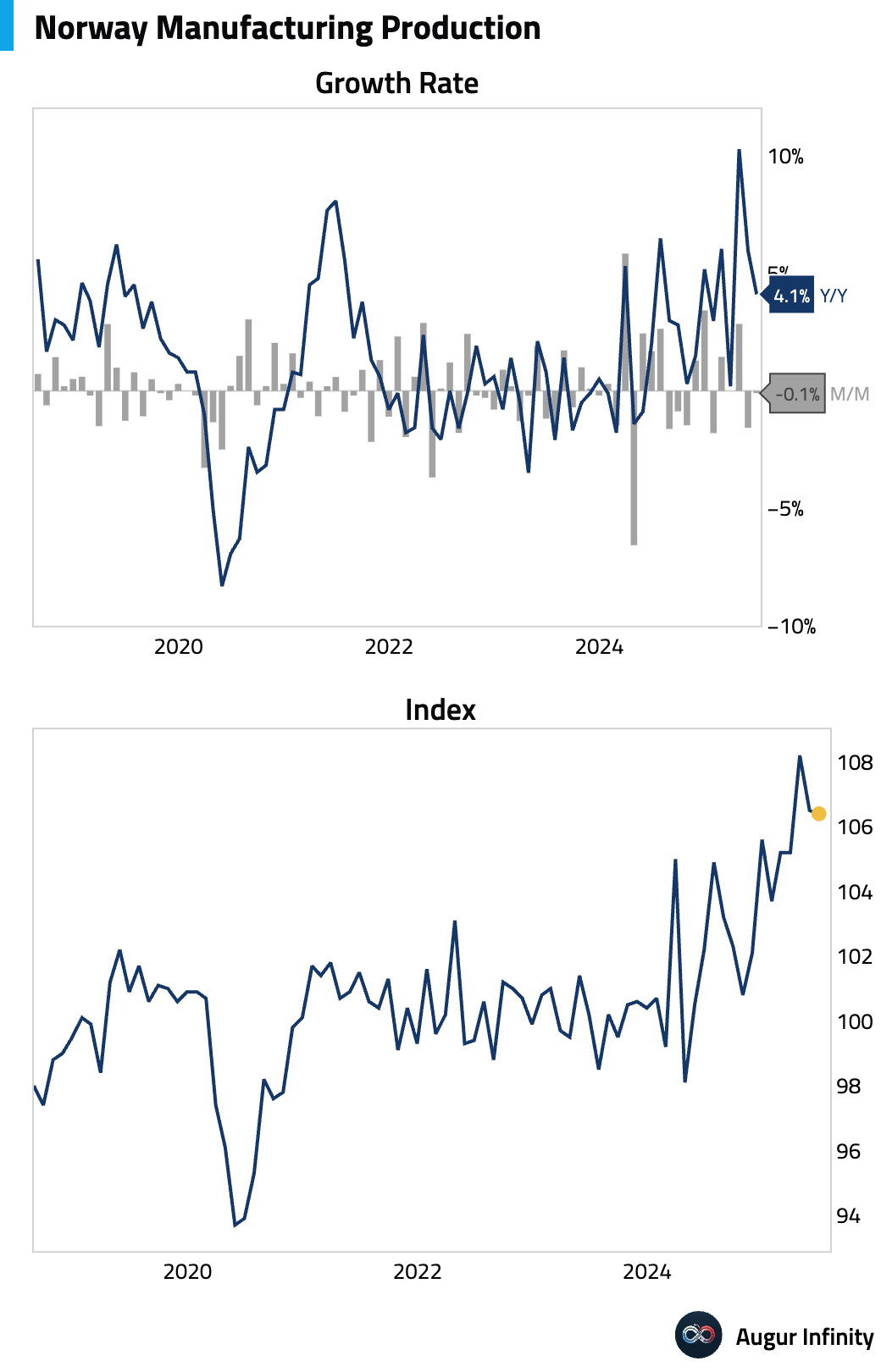
- Norway's manufacturing production fell 0.1% M/M in June after a 1.6% drop in May.
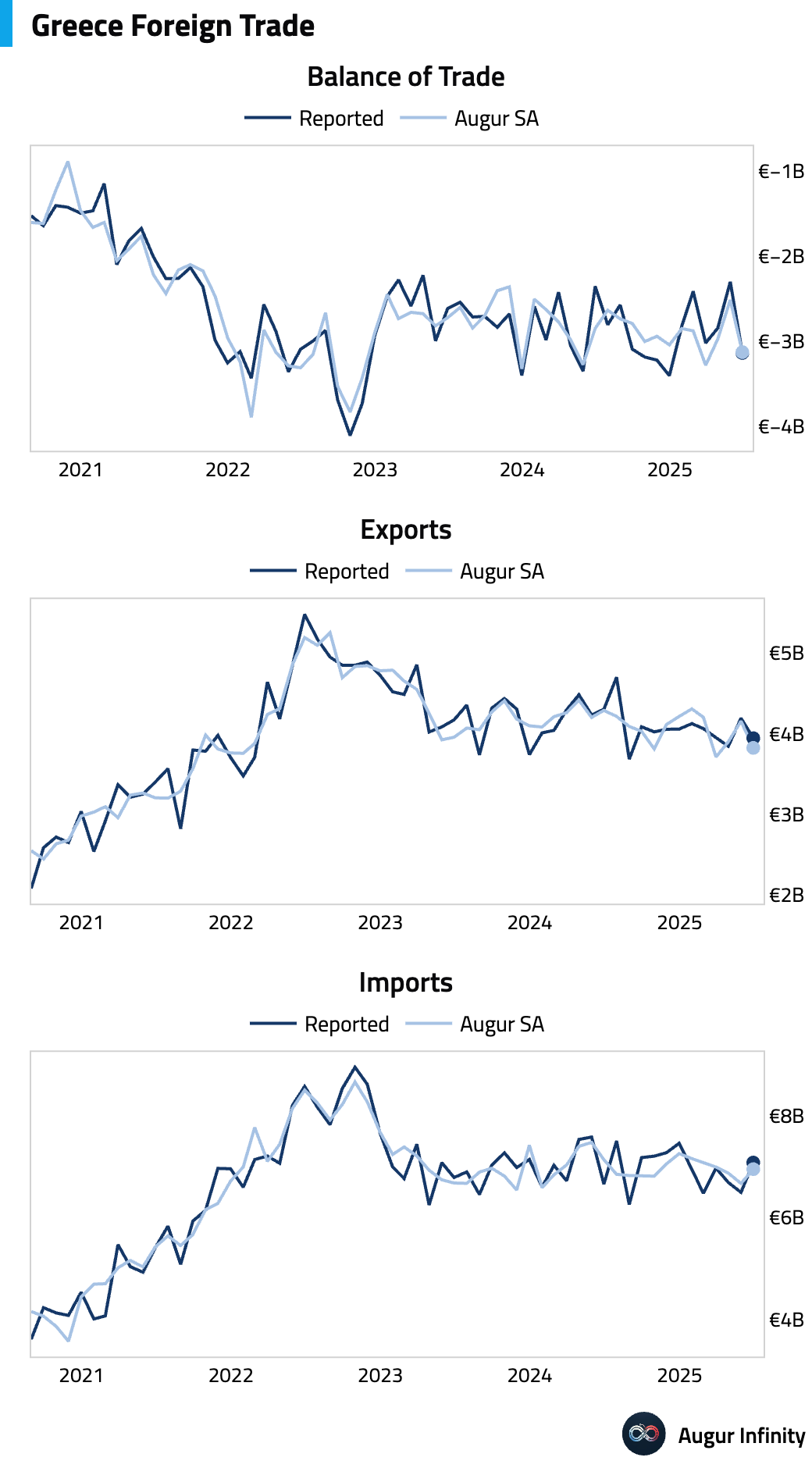
- Greece's trade deficit widened to -€3.1 billion in June from -€2.3 billion in May.
Asia-Pacific
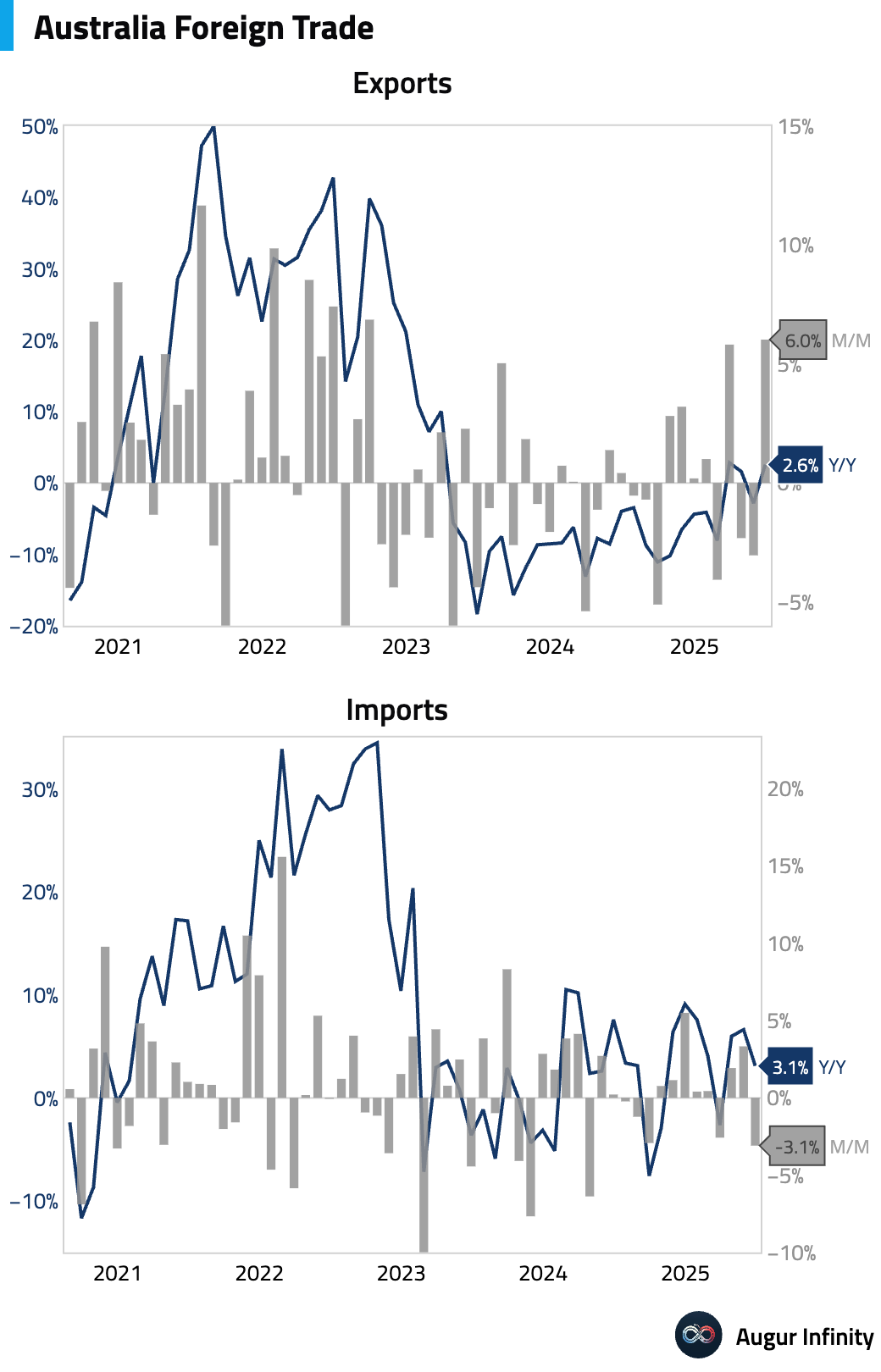
- Australia's trade surplus widened significantly to A$5.37 billion in June, far exceeding the A$2.5 billion consensus. The result was driven by a 6.0% M/M surge in exports, largely due to a 36.7% jump in volatile non-monetary gold shipments. Imports fell 3.1%, with broad-based weakness in consumption and capital goods suggesting softer domestic demand. The strong net export figure is estimated to add 0.3 percentage points to Q2 GDP growth.
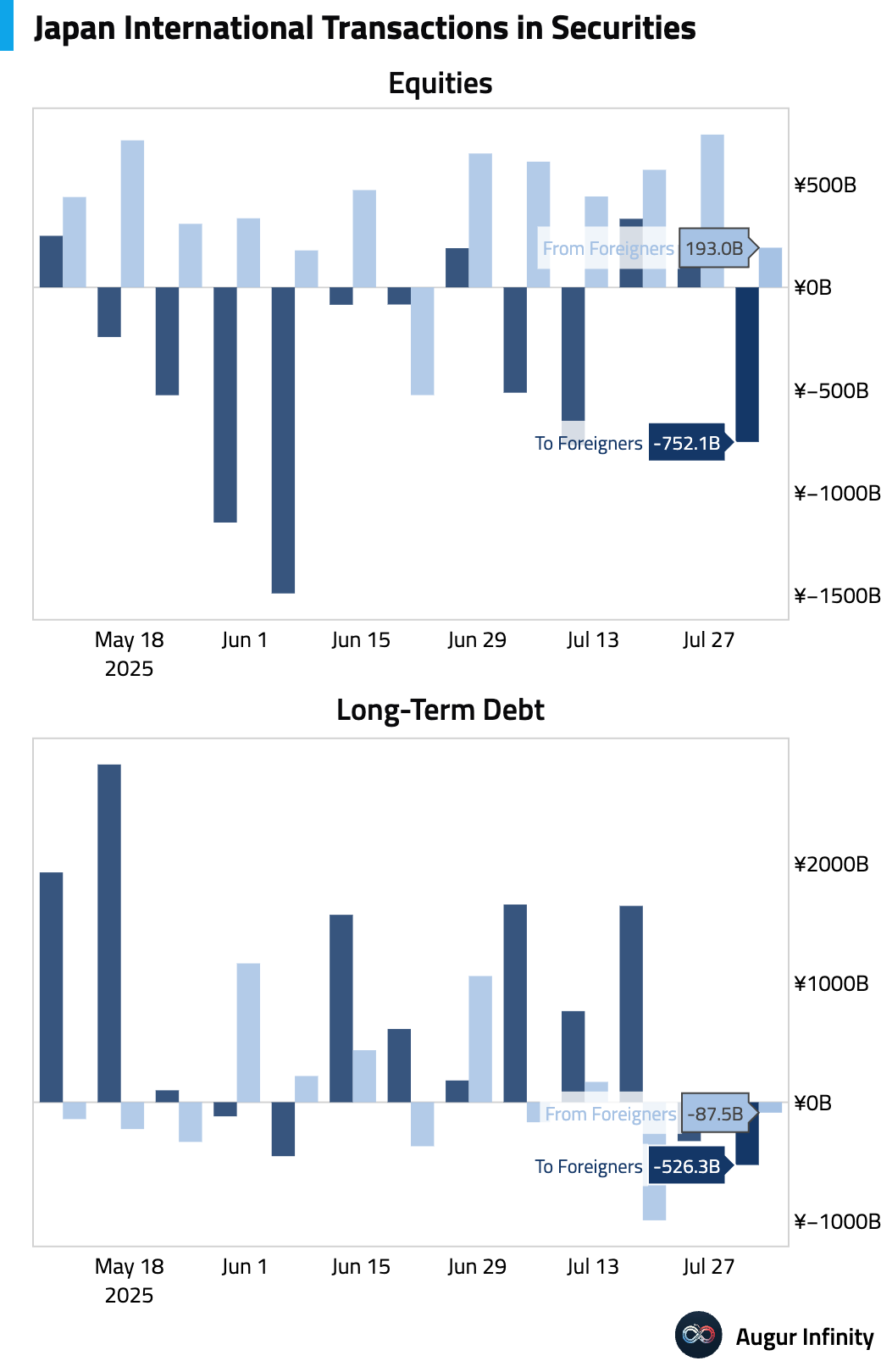
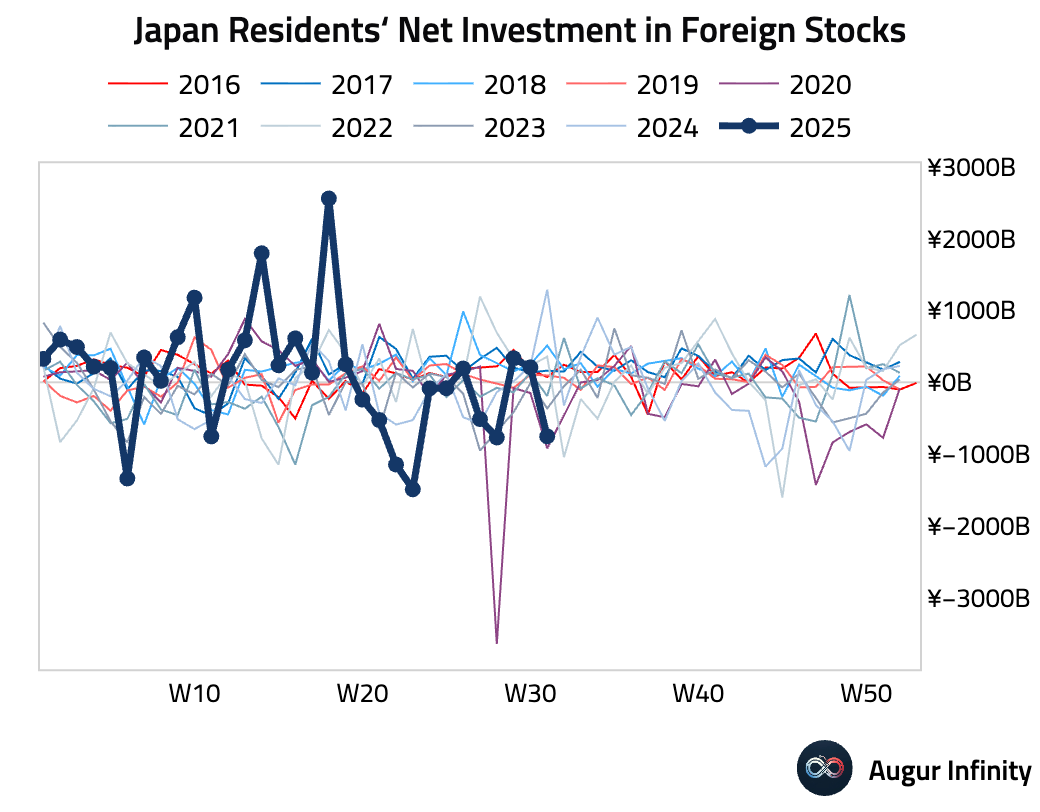
- Japanese investors were net sellers of foreign bonds to the tune of ¥526.3 billion in the week ending August 2, while foreign investors were net buyers of Japanese stocks, purchasing ¥193.0 billion.
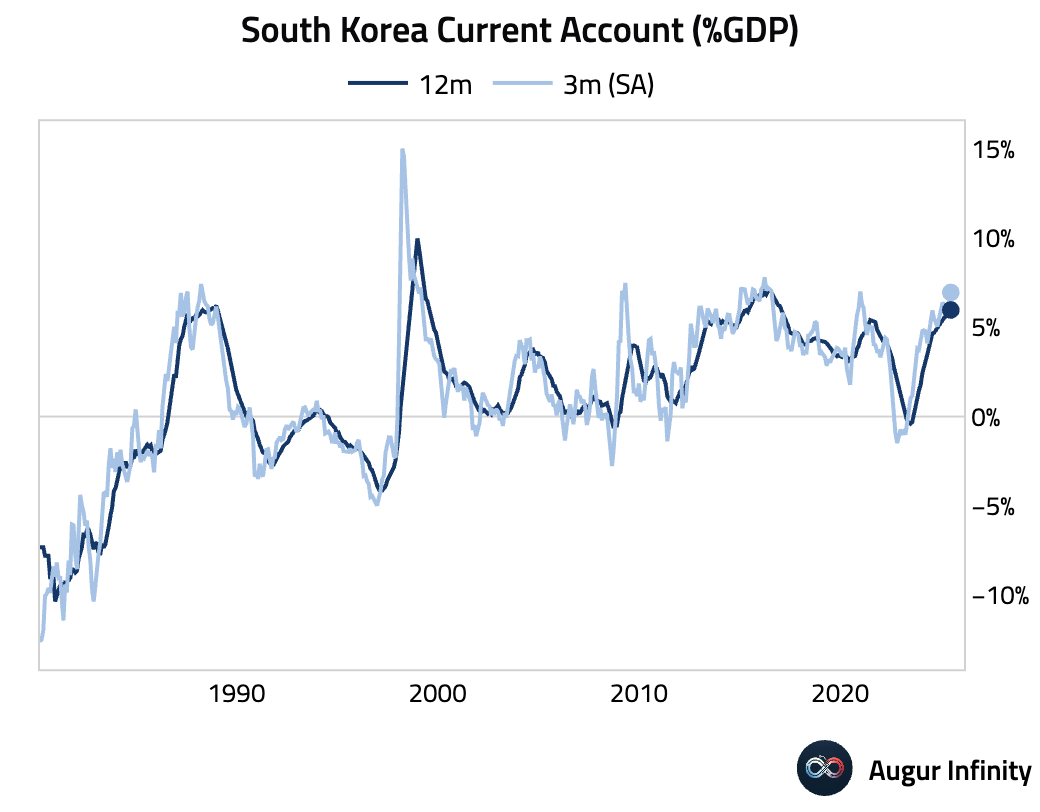
- South Korea’s current account surplus expanded to $14.27 billion in June.
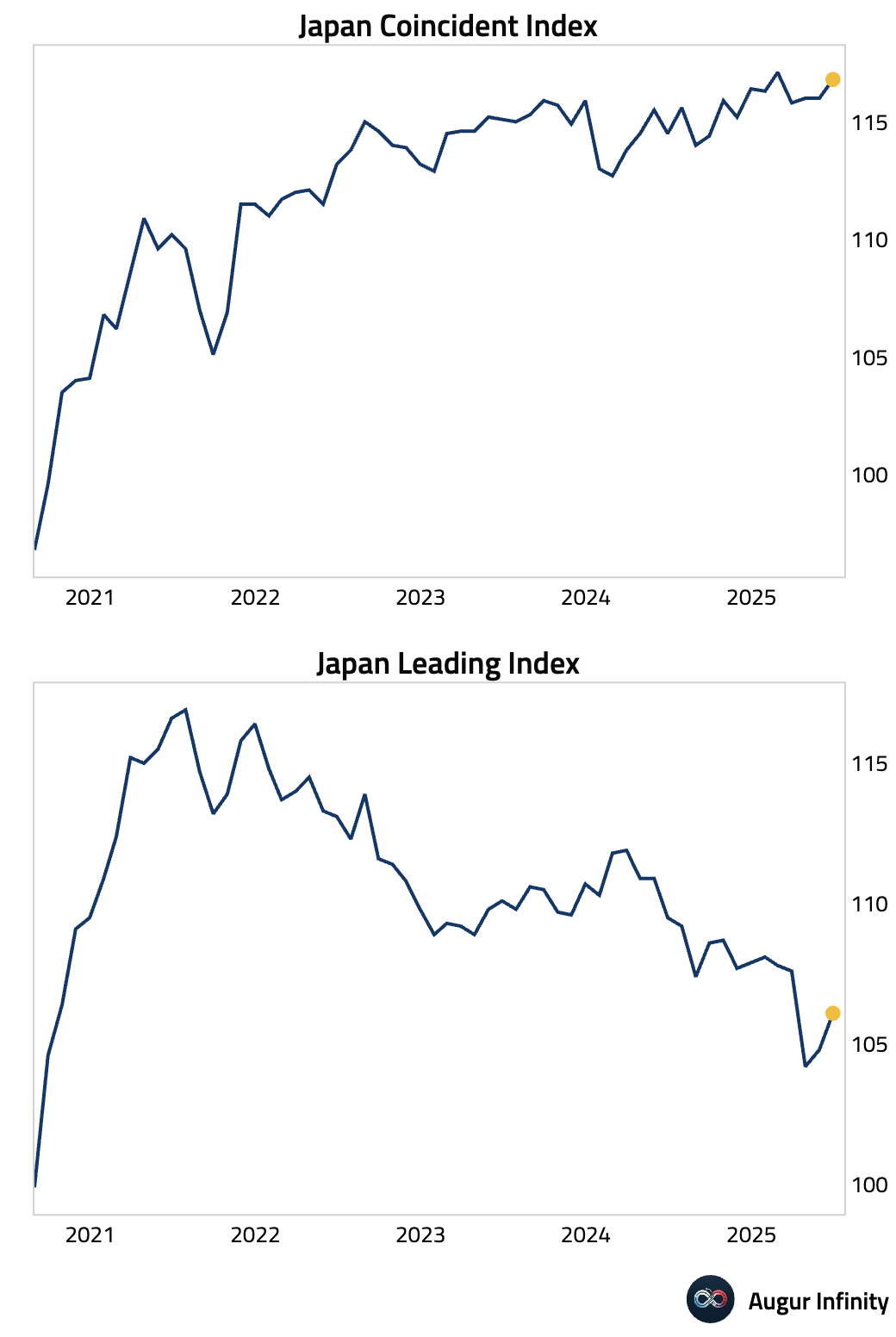
- Japan's preliminary Coincident Index rose to 116.8 in June from 116.0, while the Leading Economic Index increased to 106.1 from 104.8, suggesting a stable economic outlook.
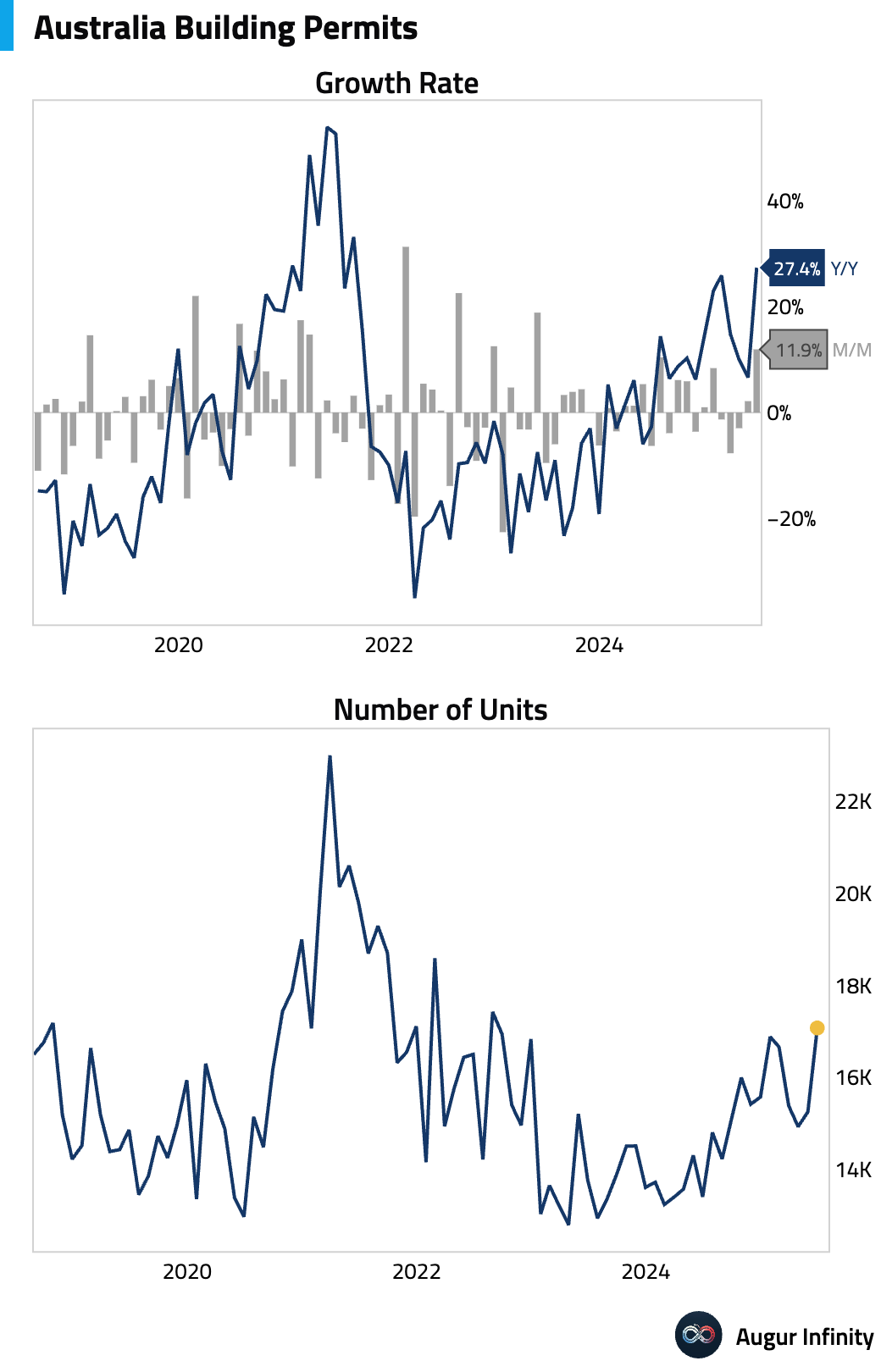
- Australia's final building permits for June rose 11.9% M/M, a two-year high, confirming the preliminary estimate.
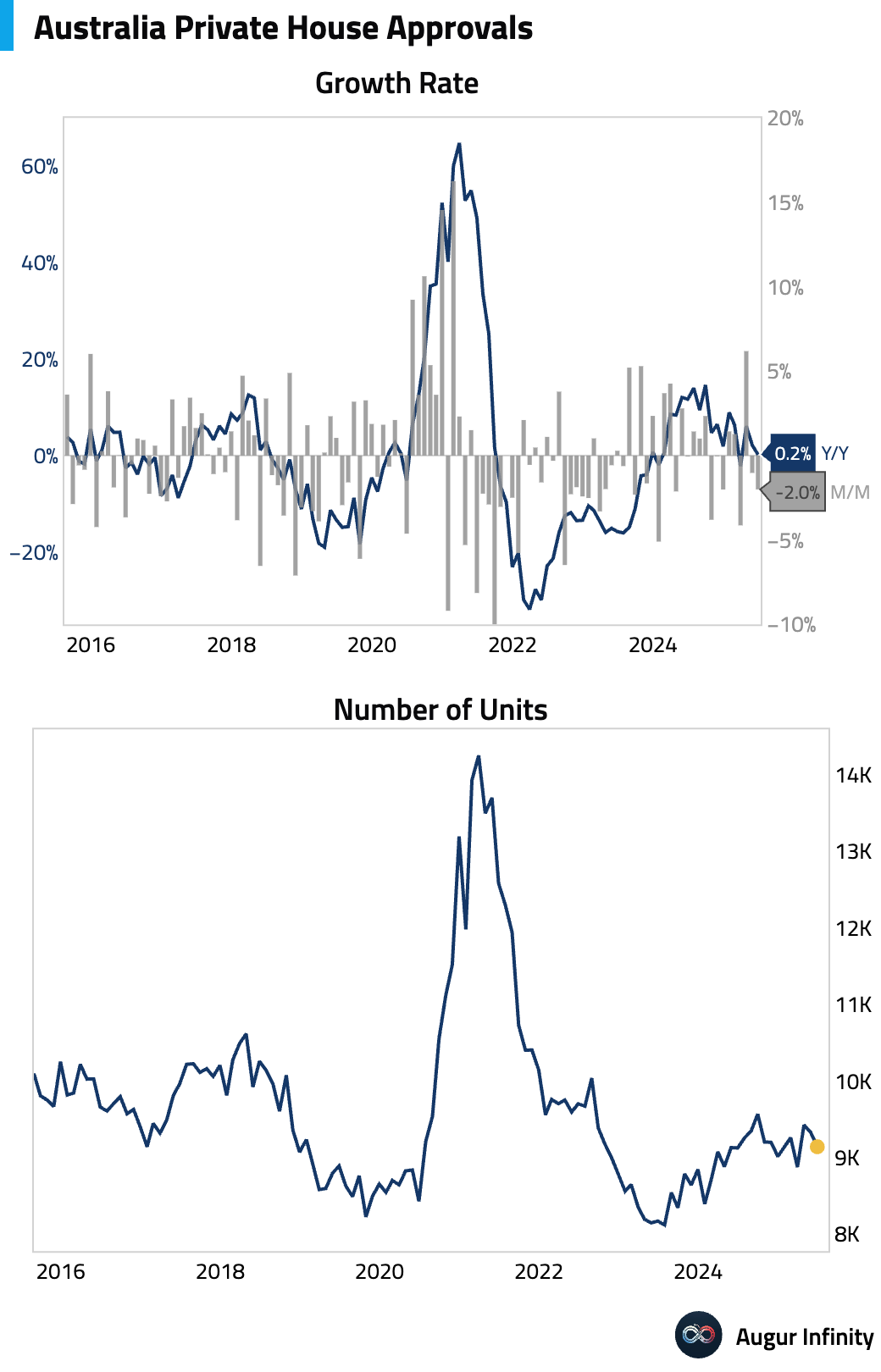
- Final data showed Australian private house approvals fell 2.0% M/M in June, following a 1.0% decline in May.
China
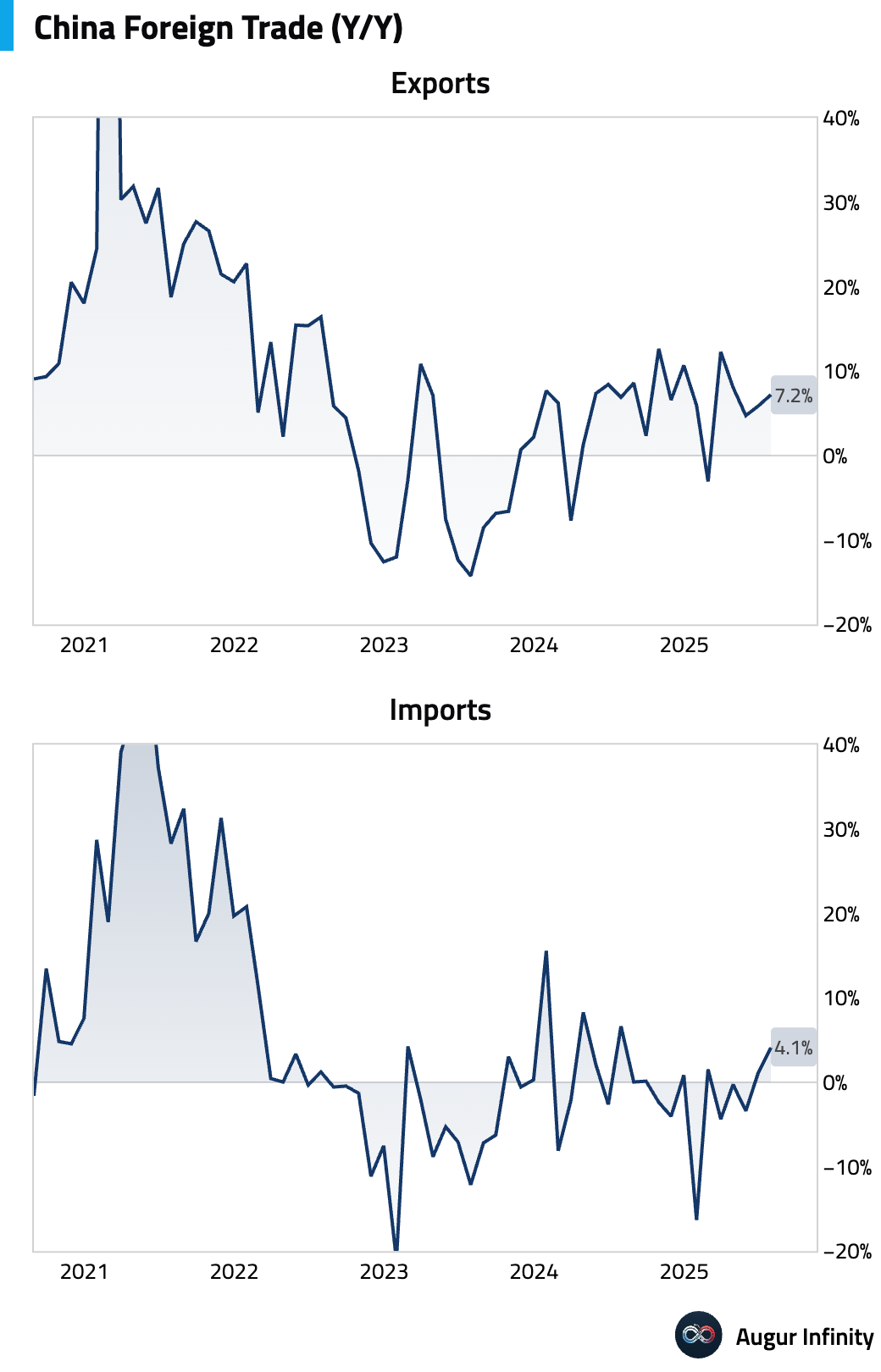
- China's trade surplus narrowed to $98.2 billion in July, below consensus, but was accompanied by stronger-than-expected trade flows. Exports rose 7.2% Y/Y, beating the 5.4% forecast, driven by shipments to the EU and emerging markets, which offset continued weakness in exports to the US (-21.6% Y/Y). Imports surprisingly surged 4.1% Y/Y, a stark reversal from the -1.0% expected decline and marking the highest growth in a year, partly due to a significant jump in crude oil import volumes that suggests strategic stockpiling.
Emerging Markets ex China
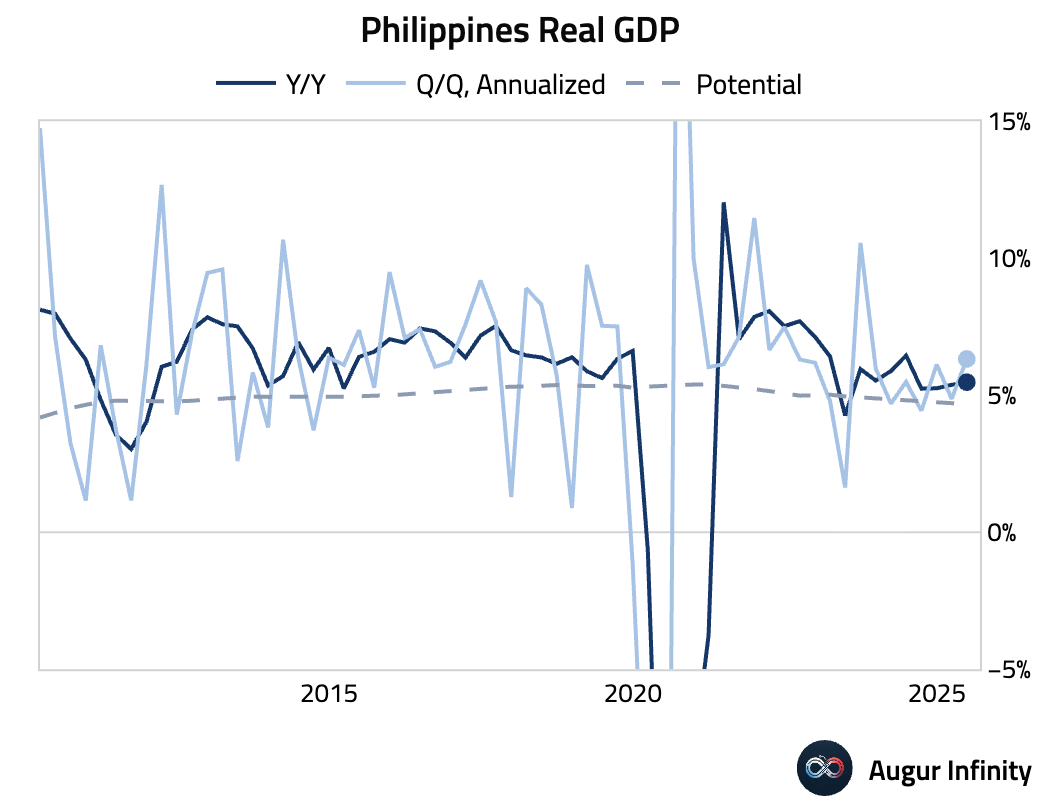
- The Philippine economy grew 5.5% Y/Y in Q2, slightly beating the 5.4% consensus, while Q/Q growth accelerated to 1.5%. However, the headline strength masked underlying weakness in domestic demand. Growth in private consumption was concentrated in non-discretionary items, while investment growth collapsed to 2.6% Y/Y from 6.5% in Q1. The soft domestic activity and subdued inflation support expectations for further monetary easing by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP).
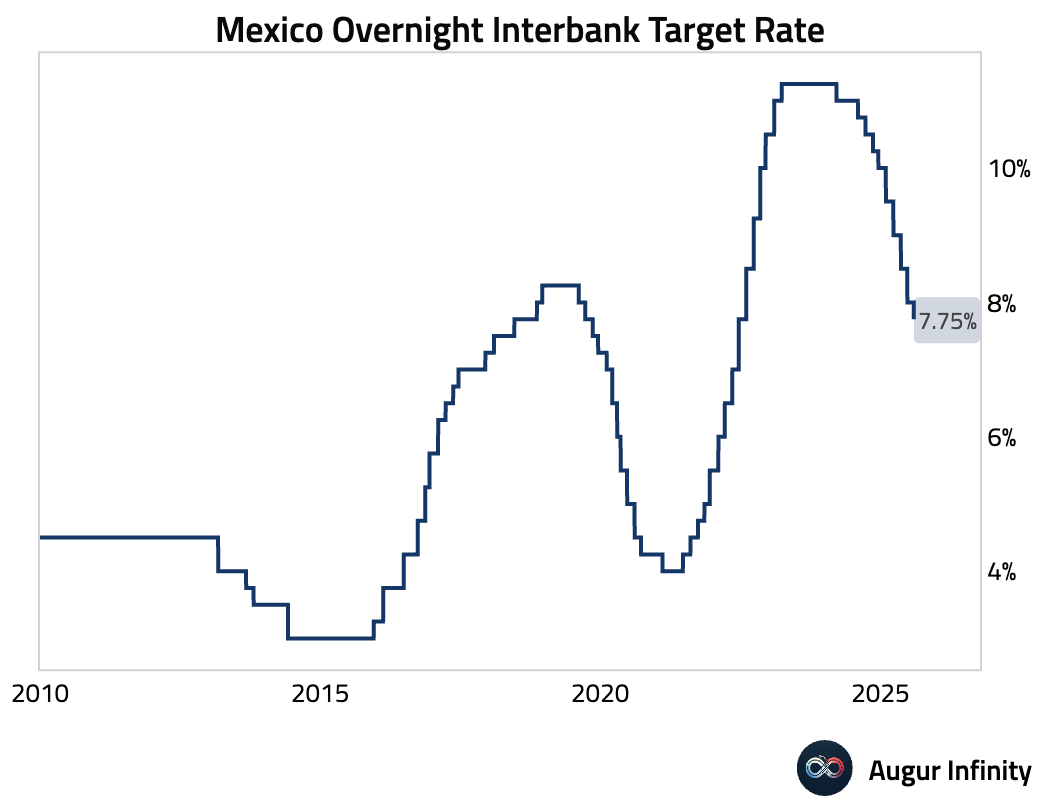
- Bank of Mexico cut rate by 25 bps to 7.75%, in line with market expectations.
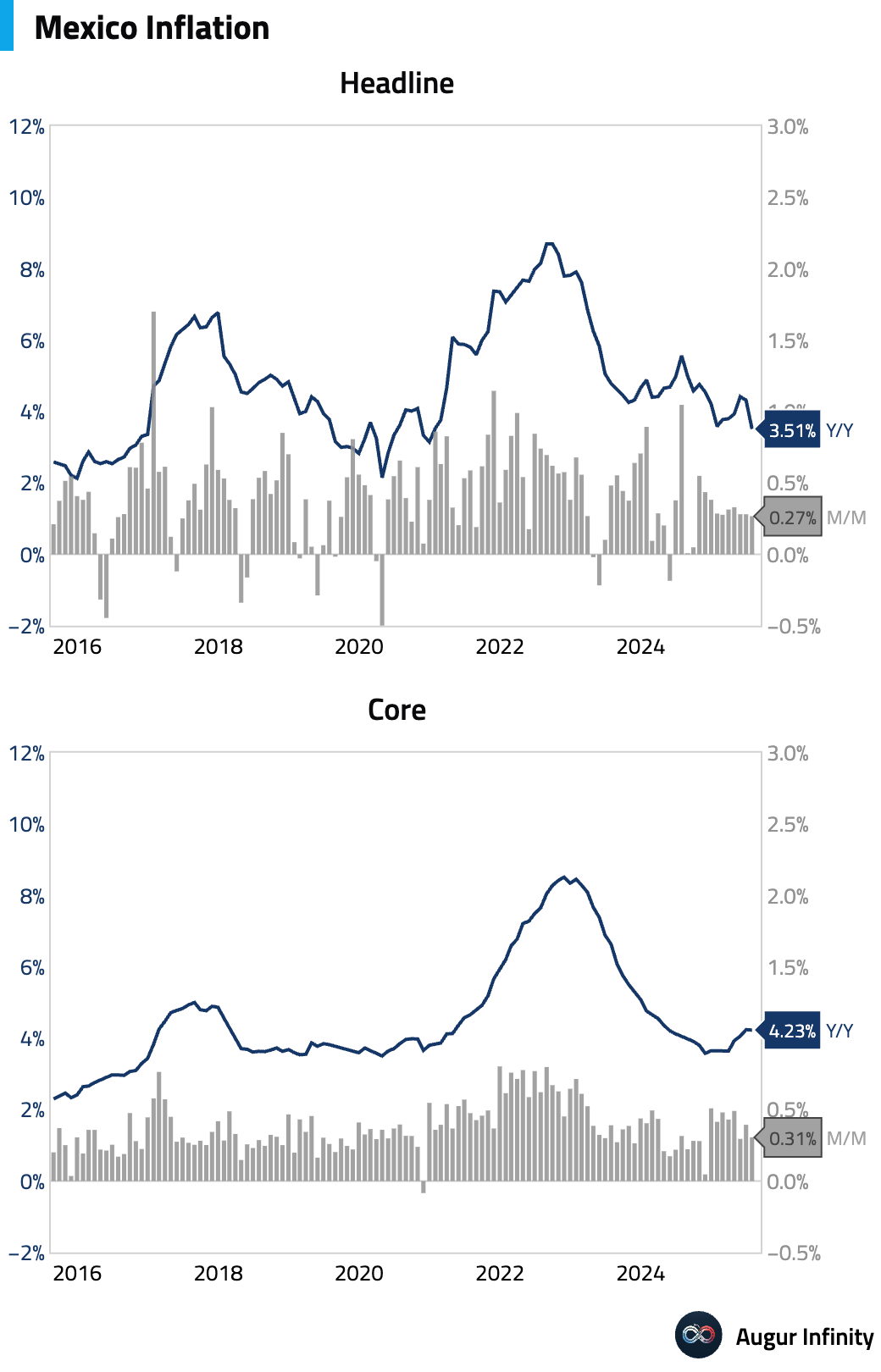
- Mexico's headline inflation rate decelerated to 3.51% Y/Y in July, the lowest since December 2020, from 4.32% in June. The M/M rate was 0.27%. Core inflation also moderated slightly to 4.23% Y/Y.
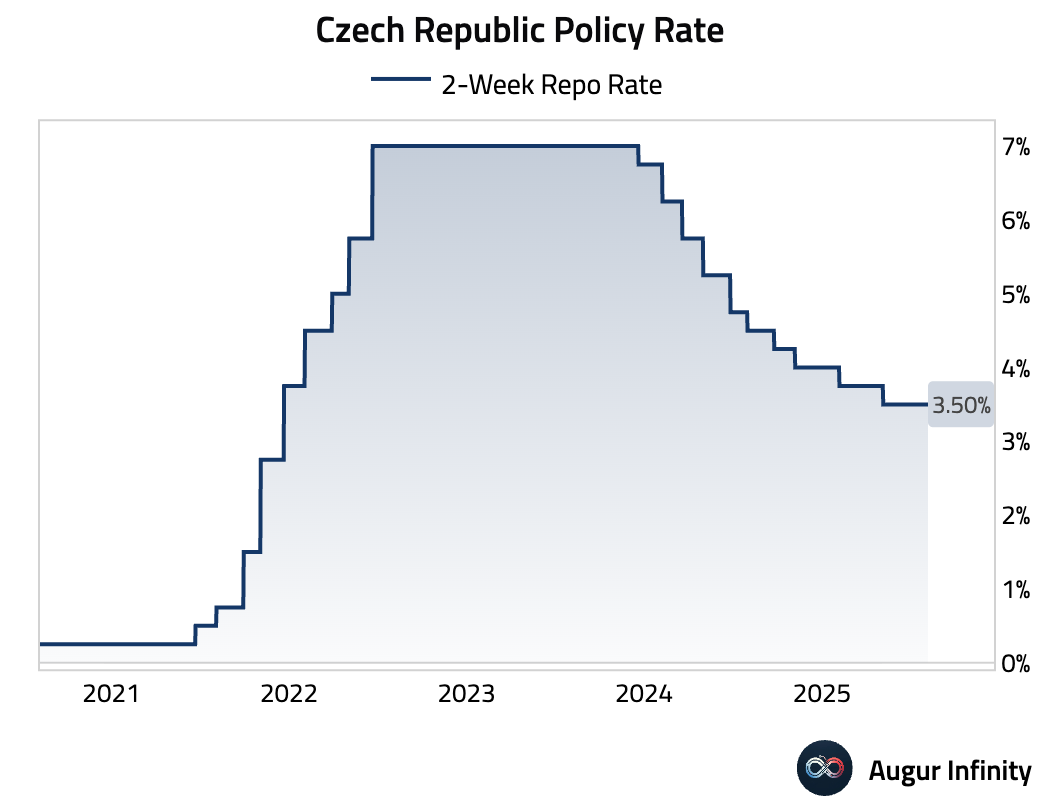
- The Czech National Bank held its main interest rate at 3.50%, as widely expected. The messaging was explicitly hawkish, with the Board emphasizing that ongoing domestic inflationary pressures (demand, property prices) currently prevent a rate cut. Governor Michl characterized both his comments and the policy statement as hawkish.
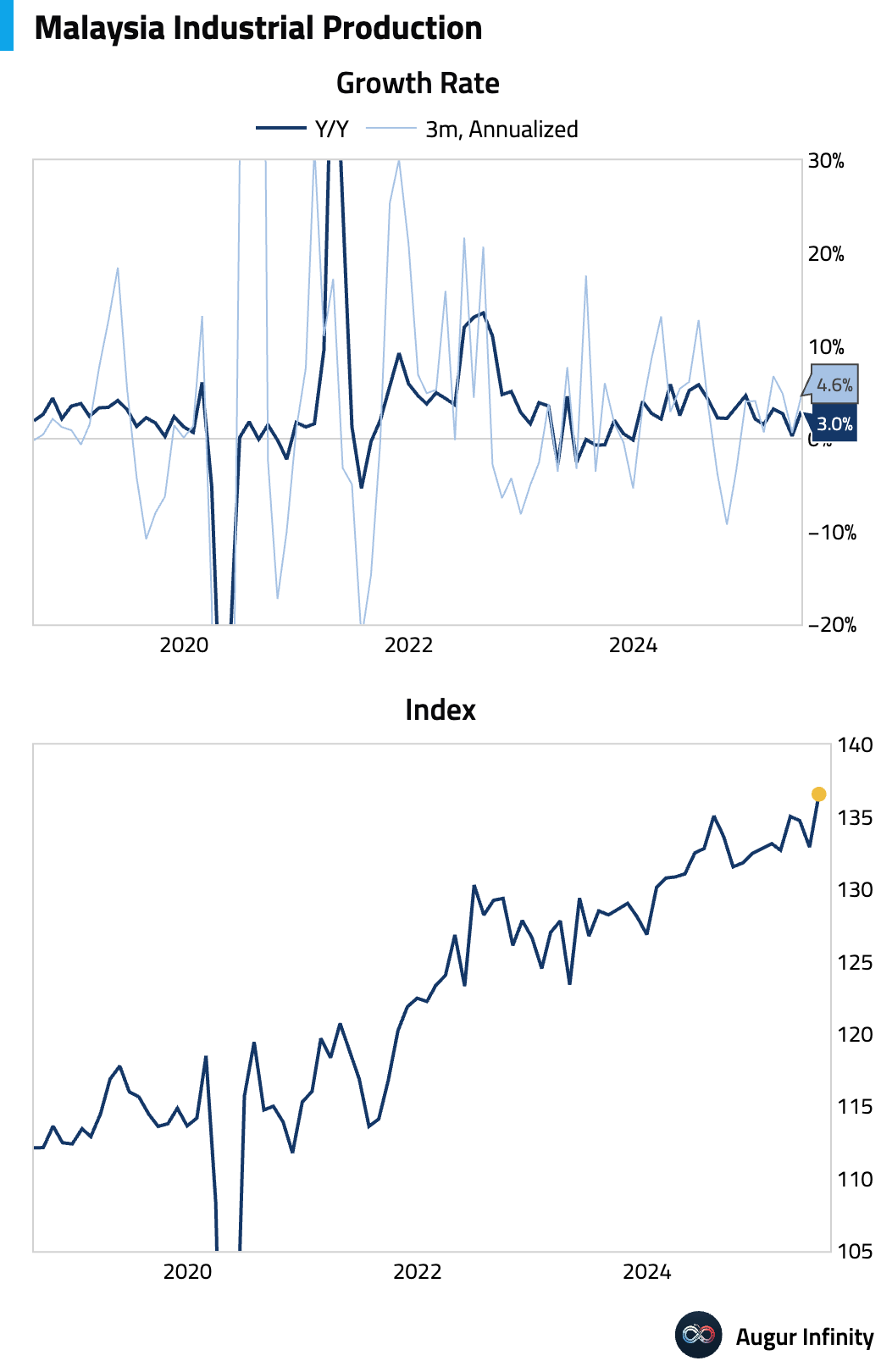
- Malaysian industrial production expanded 3.0% Y/Y in June, significantly beating the 1.0% consensus forecast and accelerating from a 0.3% pace in May.
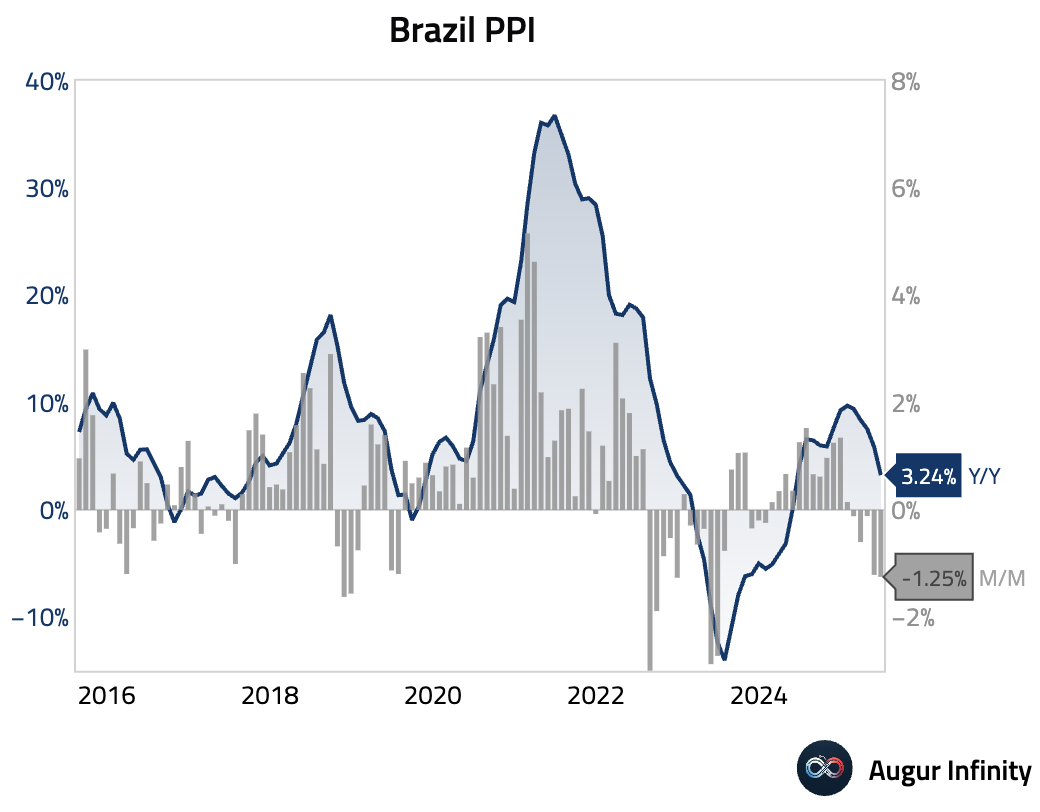
- Brazil's producer price index fell 1.25% M/M in June, a steeper decline than the previous month's 1.21% drop. The annual rate of producer inflation slowed to 3.24% from 5.86%.
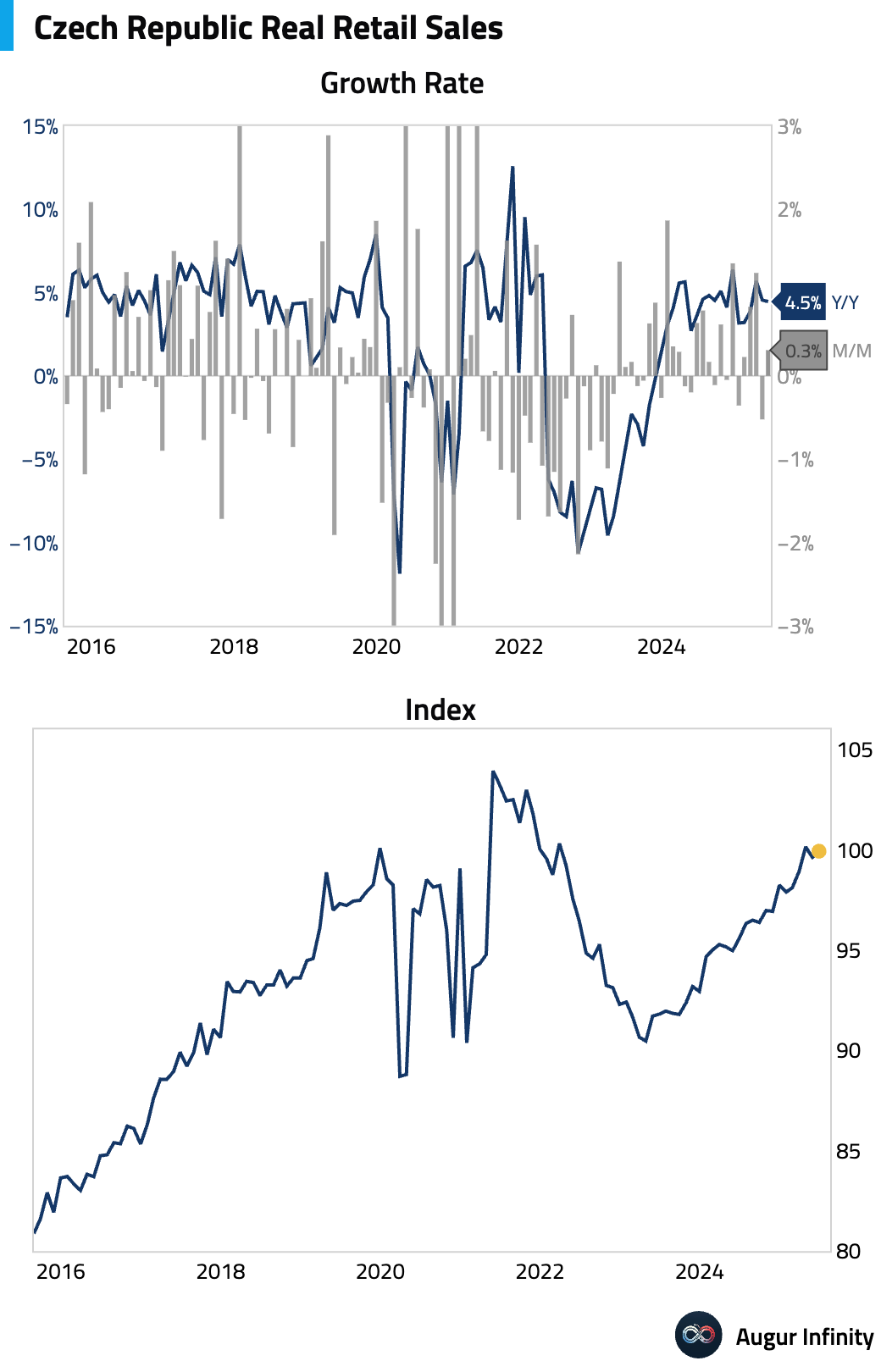
- The Czech Republic's retail sales (ex. autos) grew 4.5% Y/Y in June, a slight slowdown from the 4.6% pace in May and below the 5.0% consensus. M/M sales rose 0.3%.
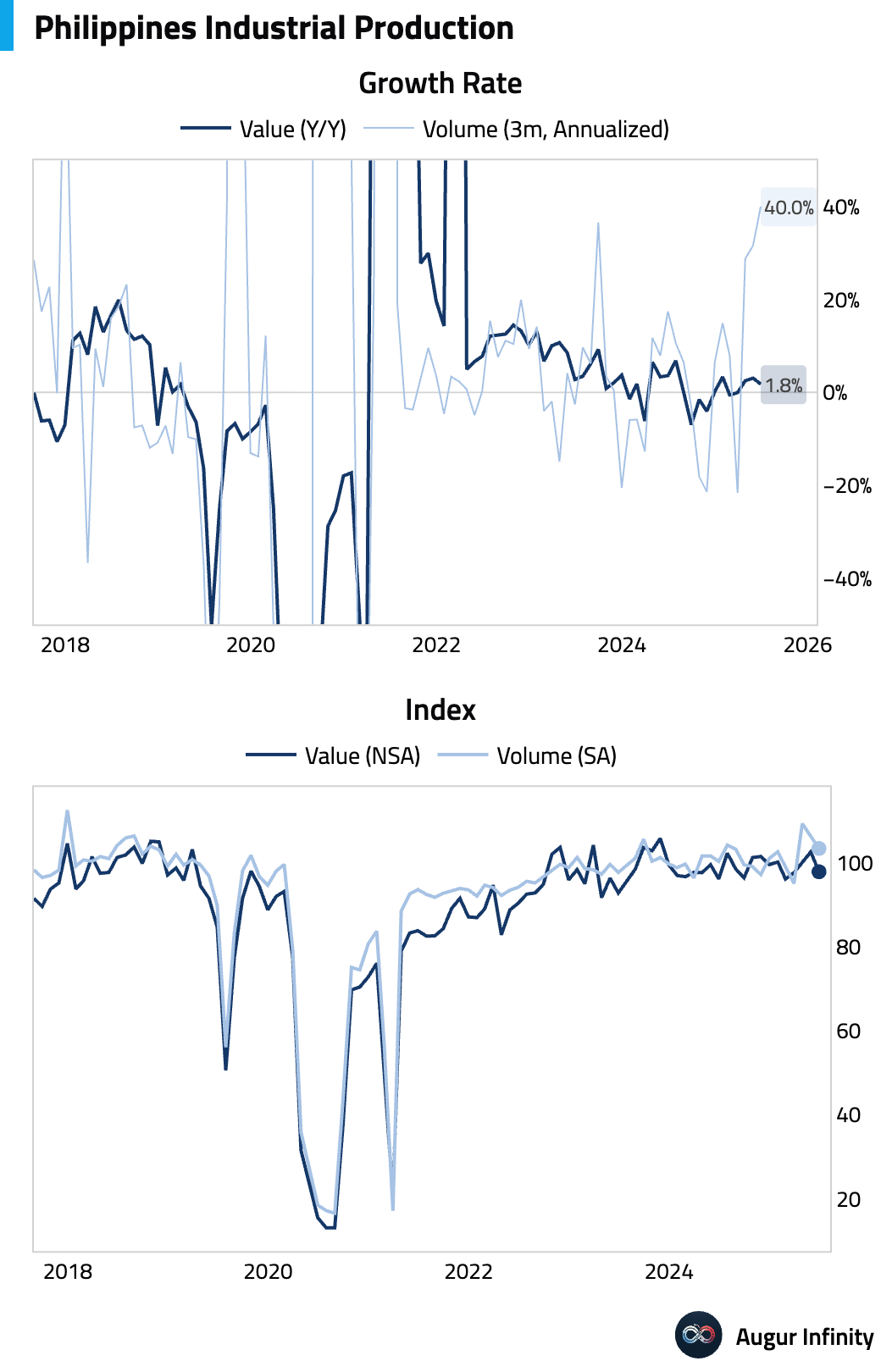
- Philippine industrial production value rose 1.8% Y/Y in June, decelerating from 3.1% in the prior month.
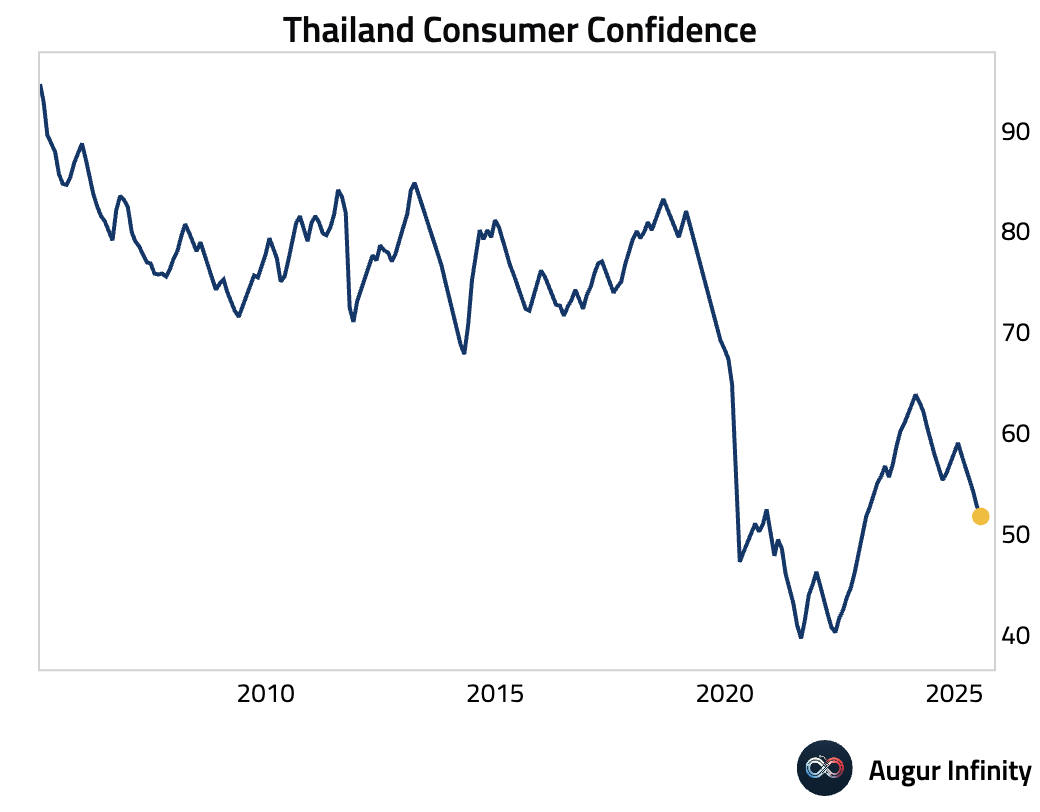
- Thailand's consumer confidence index edged down to 51.7 in July from 52.7, its lowest reading since December 2022.
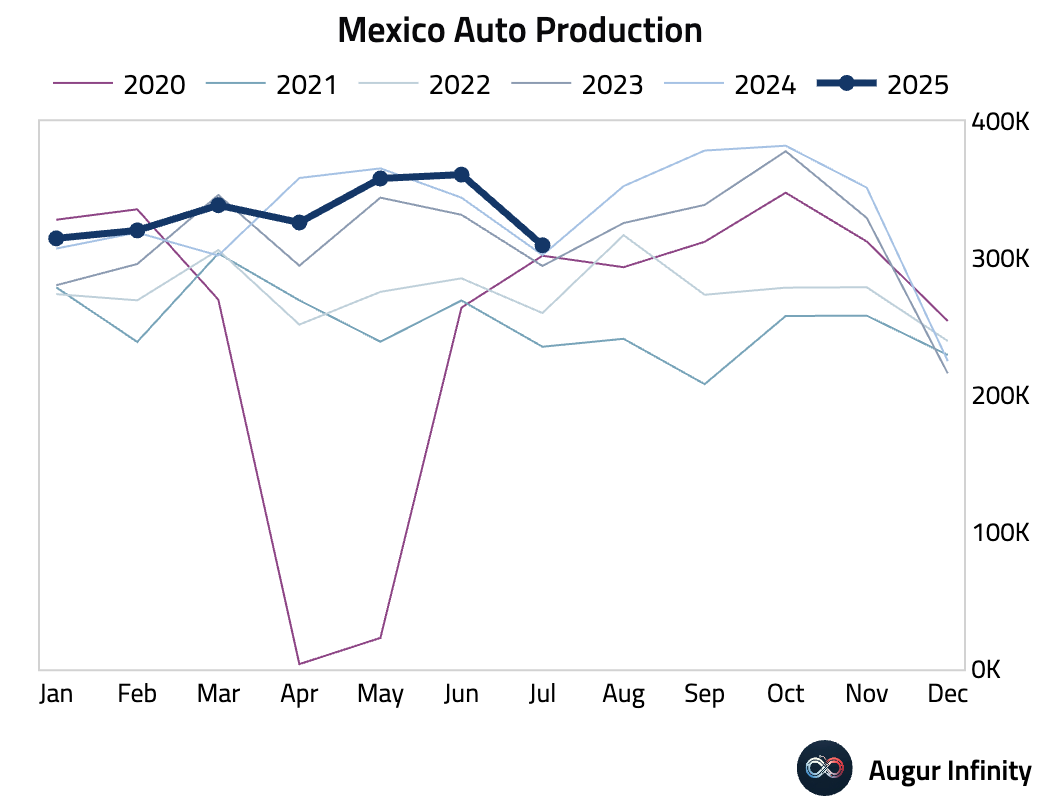
- Mexican auto production growth slowed to 2.4% Y/Y in July from 4.9% in June.
- Brazilian new car registrations jumped 14.2% M/M in July, while car production surged 15.7% M/M.
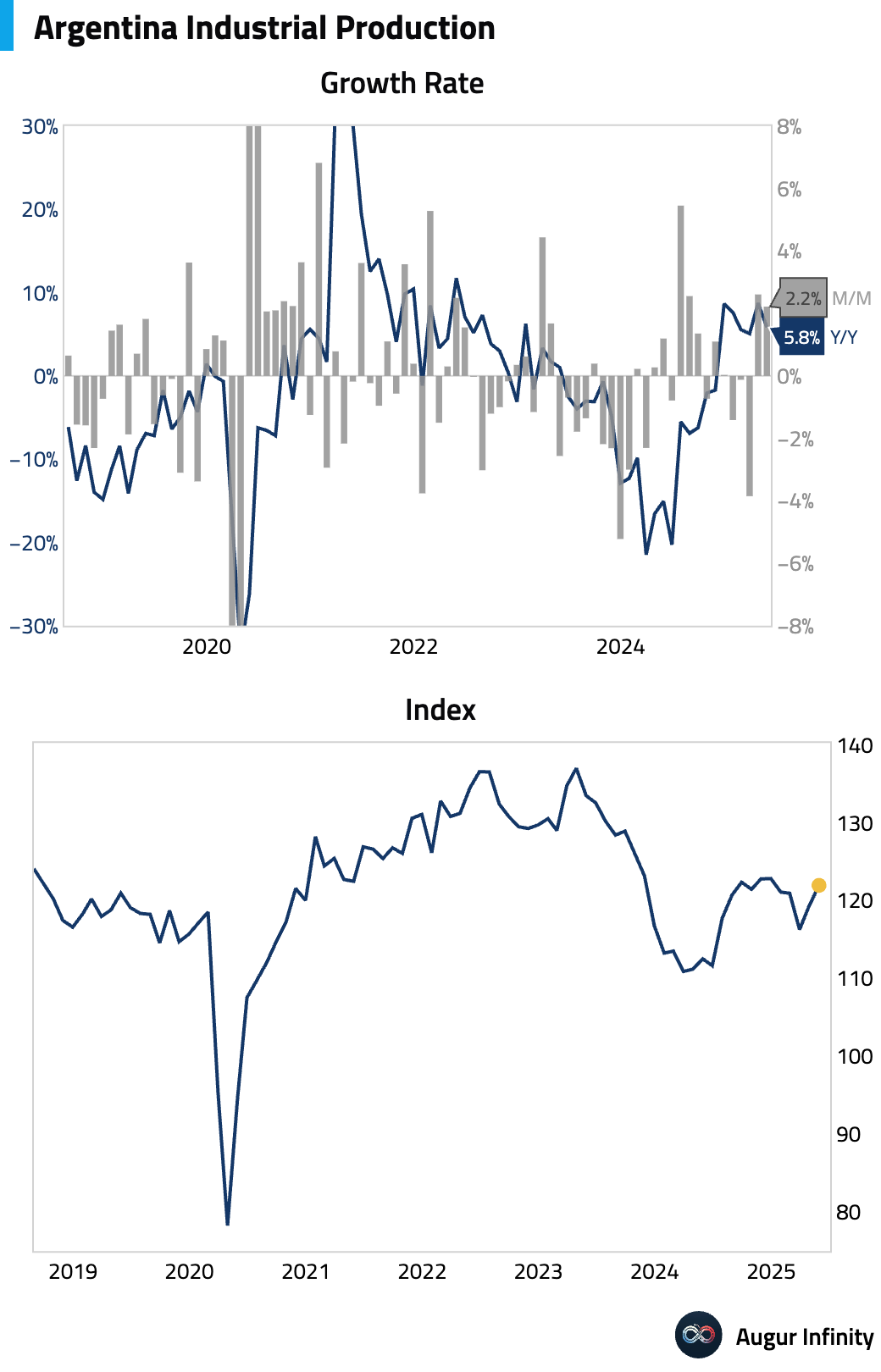
- Argentina Industrial Production rose 9.3% Y/Y in June, accelerating from the prior month's 5.8%.
Global Markets
Equities
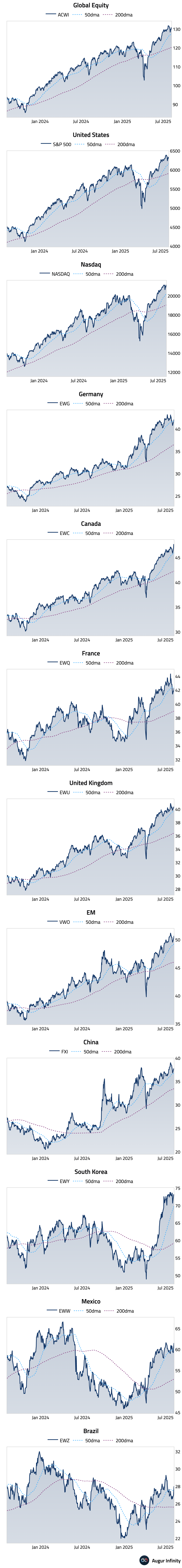
- US equities ended a multi-day rally, with the S&P 500 declining 0.08% amid new tariff threats from the White House. The downturn came despite an early session rally, as concerns over trade policy overshadowed positive sentiment.
- European markets closed higher, with Germany advancing 1.17% for its fourth consecutive day of gains and France rising 0.8%. The UK market was flat but recorded its fifth straight day of gains.
- Emerging market equities outperformed, rising 0.6% for a fourth consecutive day. Brazilian stocks surged 2.1%, marking a fifth day of gains, while Mexican equities rose 1.4% for a third straight day.
Fixed Income
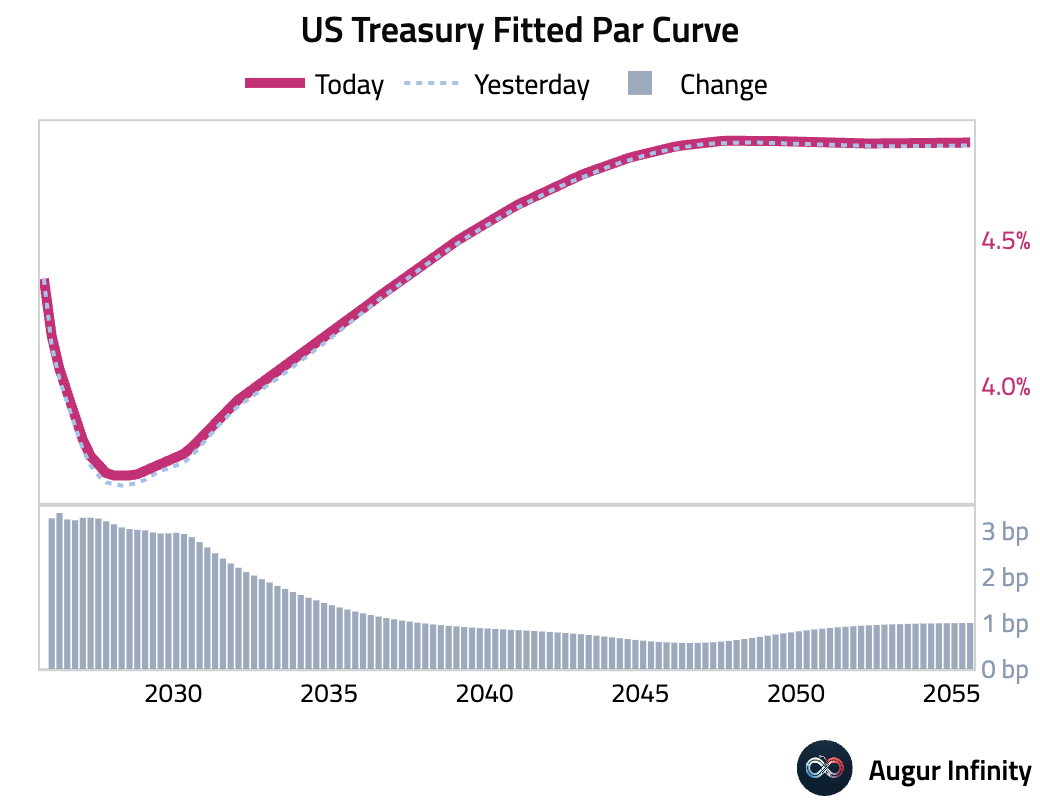
- US Treasury yields rose modestly across the curve, with the 10-year yield up 1.1 bps and the 2-year yield up 2.4 bps. The moves came amid uncertainty over US trade policy and growing expectations for Federal Reserve rate cuts, which were tempered slightly by weak demand at the recent 10-year Treasury auction.
FX
- The US dollar was mixed against G10 currencies. The British pound was the standout performer, gaining 0.6% against the dollar. The rally followed the Bank of England’s 25 bps rate cut, where a narrow 5–4 vote suggested policymaker division and potential resistance to further easing, supporting the currency.
- The Swedish krona rose 0.4% for its fifth consecutive day of gains. Conversely, the Swiss franc weakened 0.1% after news that a US–Switzerland trade deal was not finalized.
Disclaimer
Augur Digest is an automated newsletter written by an AI and edited by humans. It may contain inaccuracies and is not investment advice. Augur Labs LLC will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your reliance on the information contained in the newsletter.

