Headlines
- US Treasury Secretary Bessent publicly advocated for the Federal Reserve to implement a 50-basis-point interest rate cut in September.
- Japan launched an antidumping investigation into steel products imported from China and South Korea.
- The British government announced plans to tighten rules on inheritance transfers, a policy change projected to generate an additional £1.5 billion in annual revenue by 2029.
Charts of the Day
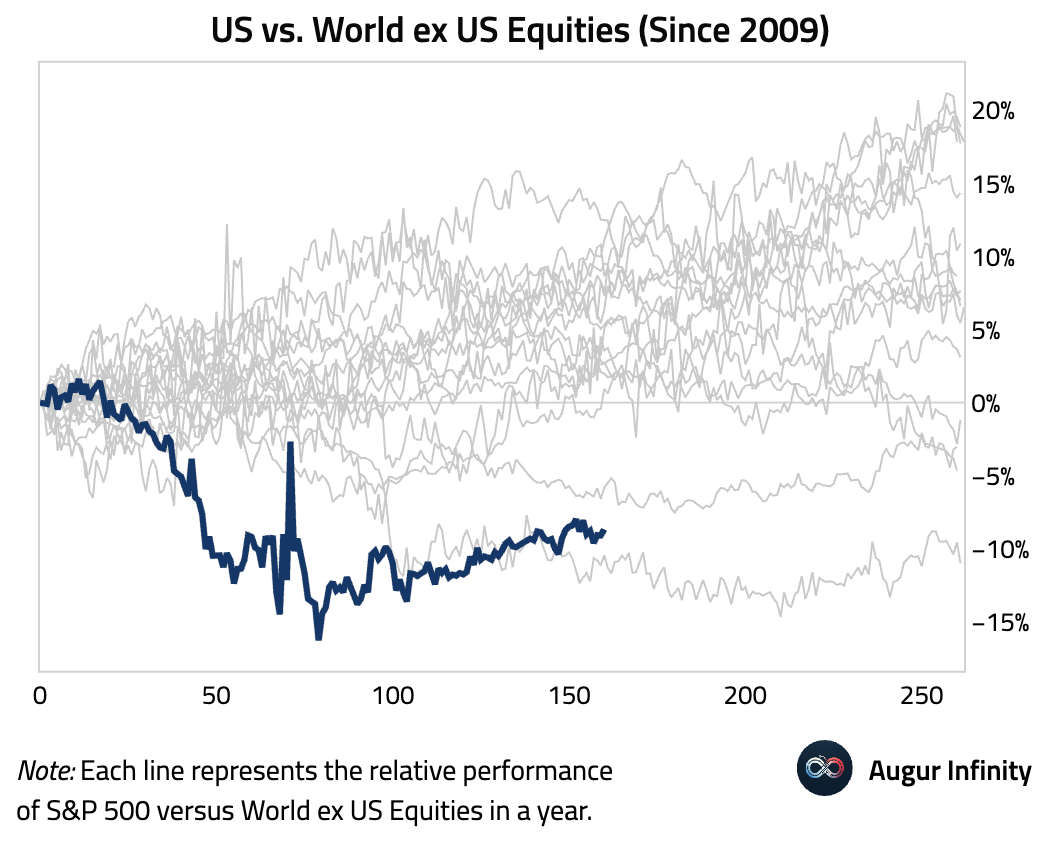
- US equities have underperformed the rest of the world by over 10 percentage points year-to-date. This is the worst underperformance since 2009.
Global Economics
United States
- US CEO Confidence jumped to 49 in Q3 from 34, driven by easing recession fears and lower trade concerns. The reading, however, remains just shy of optimistic territory (<50). Despite the improved sentiment, hiring plans soured: for the first time since 2020, more CEOs plan to shrink their workforce (34%) than expand (27%). To manage costs, firms are expected to pass price hikes to consumers (64%), while capital expenditure plans remain weak.
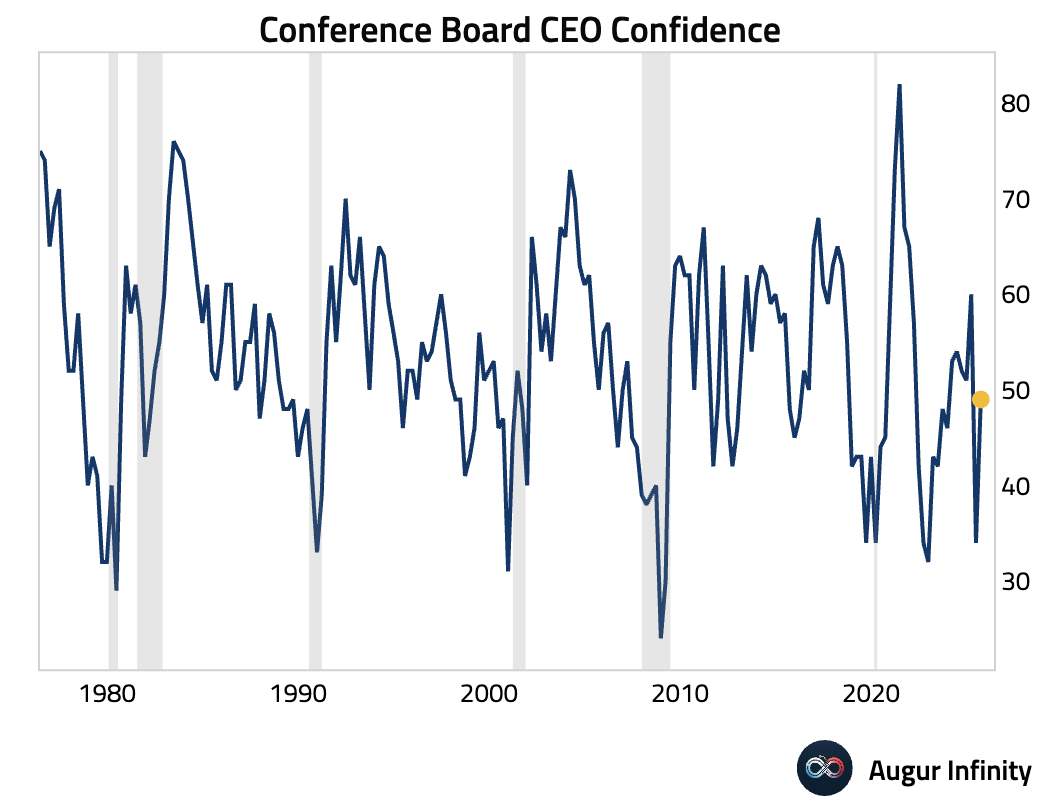
Source: The Conference Board
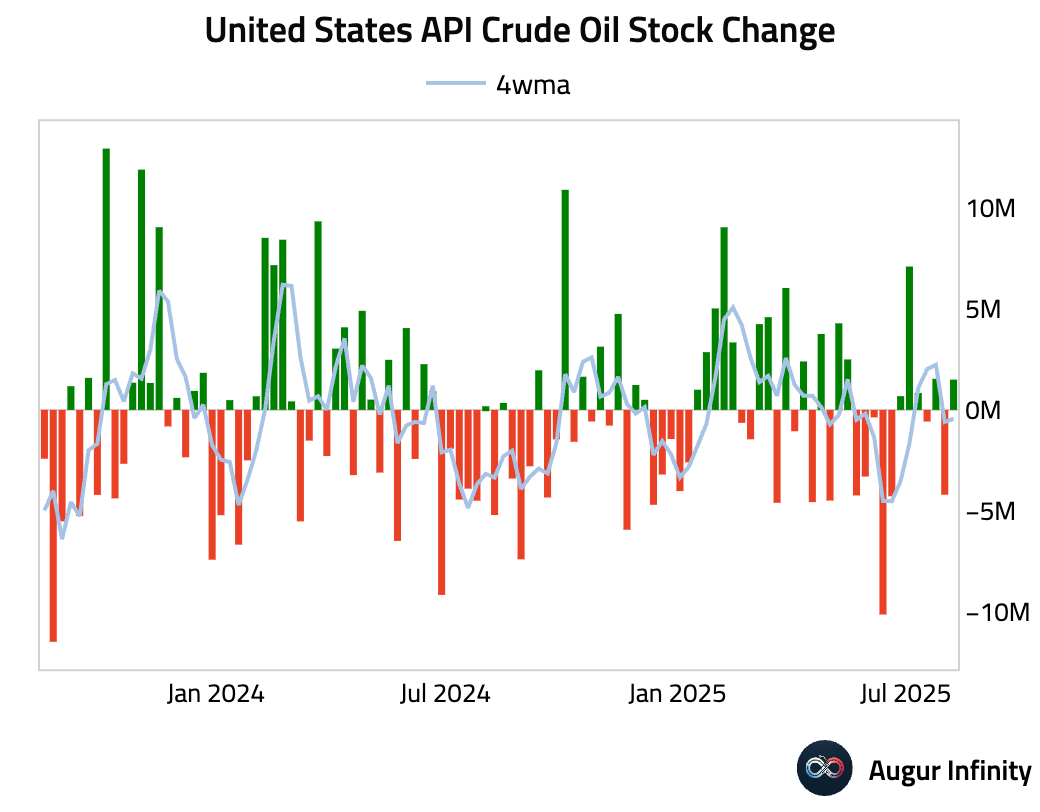
- US crude oil inventories unexpectedly rose by 1.5 million barrels last week, bucking consensus expectations for a draw of 0.8 million barrels and reversing the prior week's 4.2 million barrel decline.
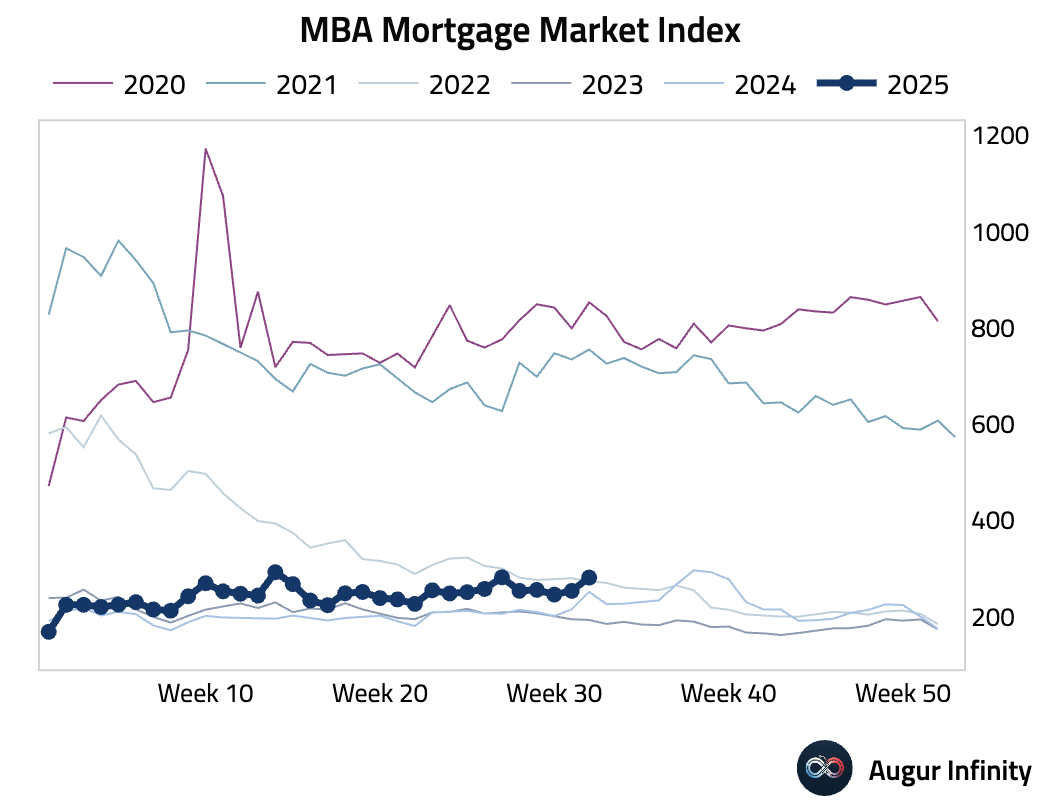
- The MBA Mortgage Market Index jumped 10.9% week-over-week, driven by a surge in refinancing activity. The Refinance Index soared 23.0%, reaching its highest level since early April, while the Purchase Index posted a modest 1.4% gain.
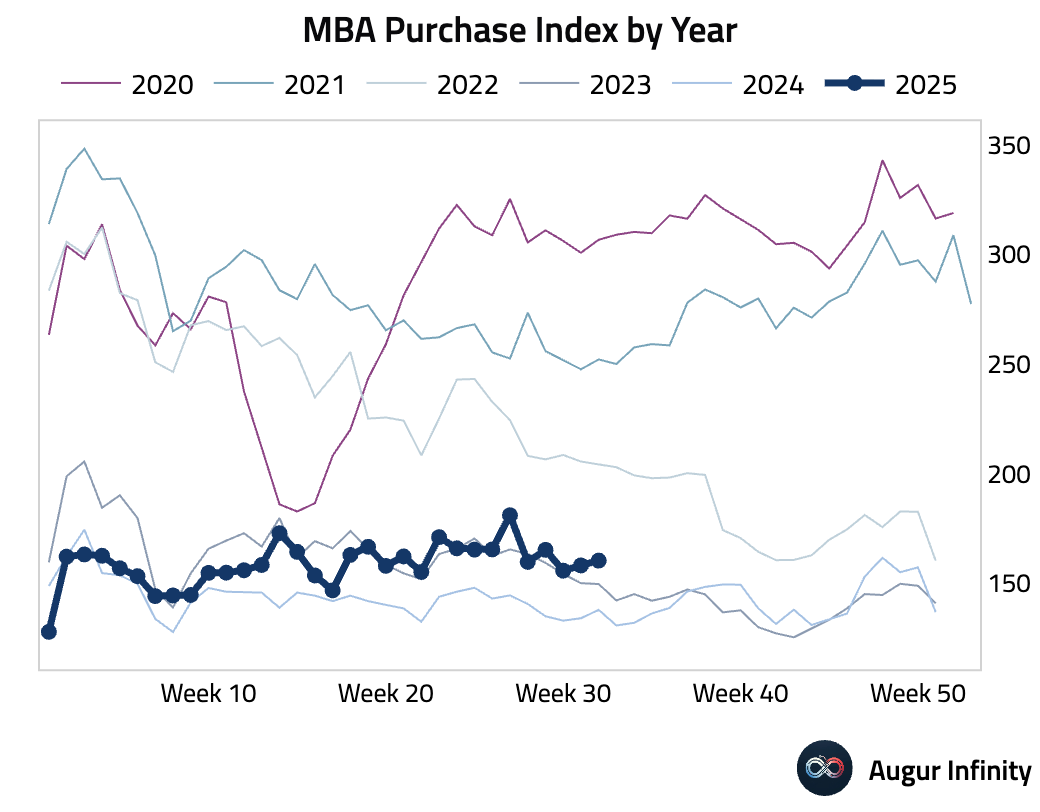
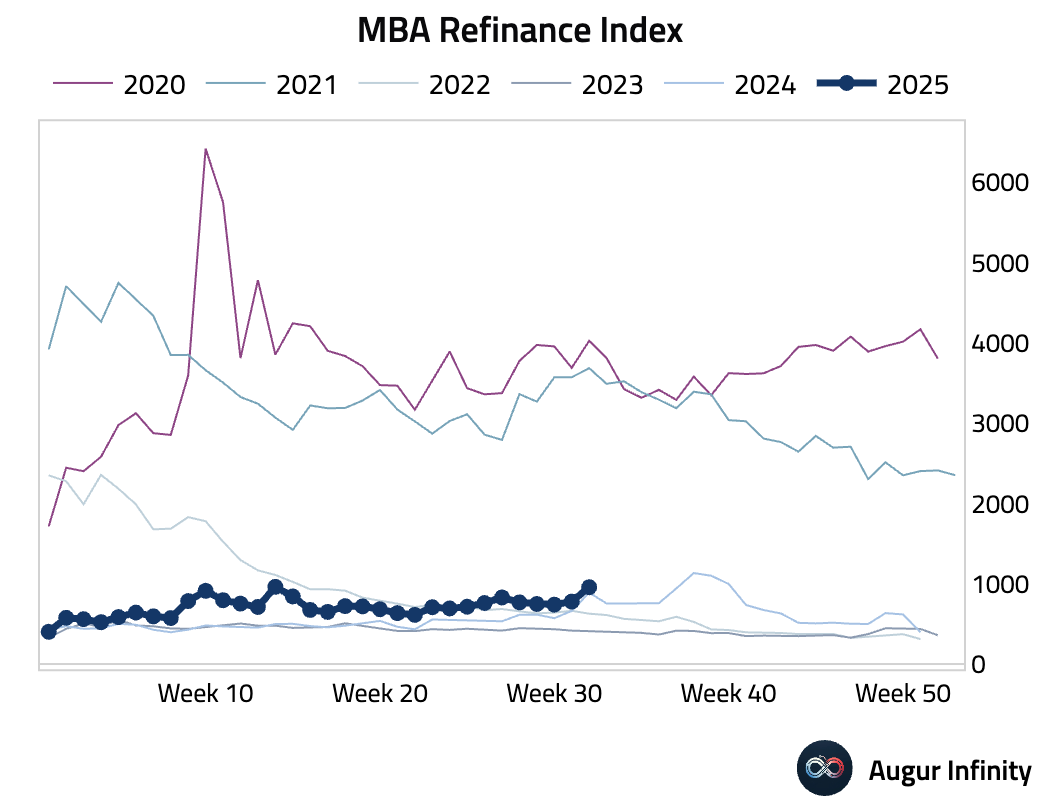
Europe
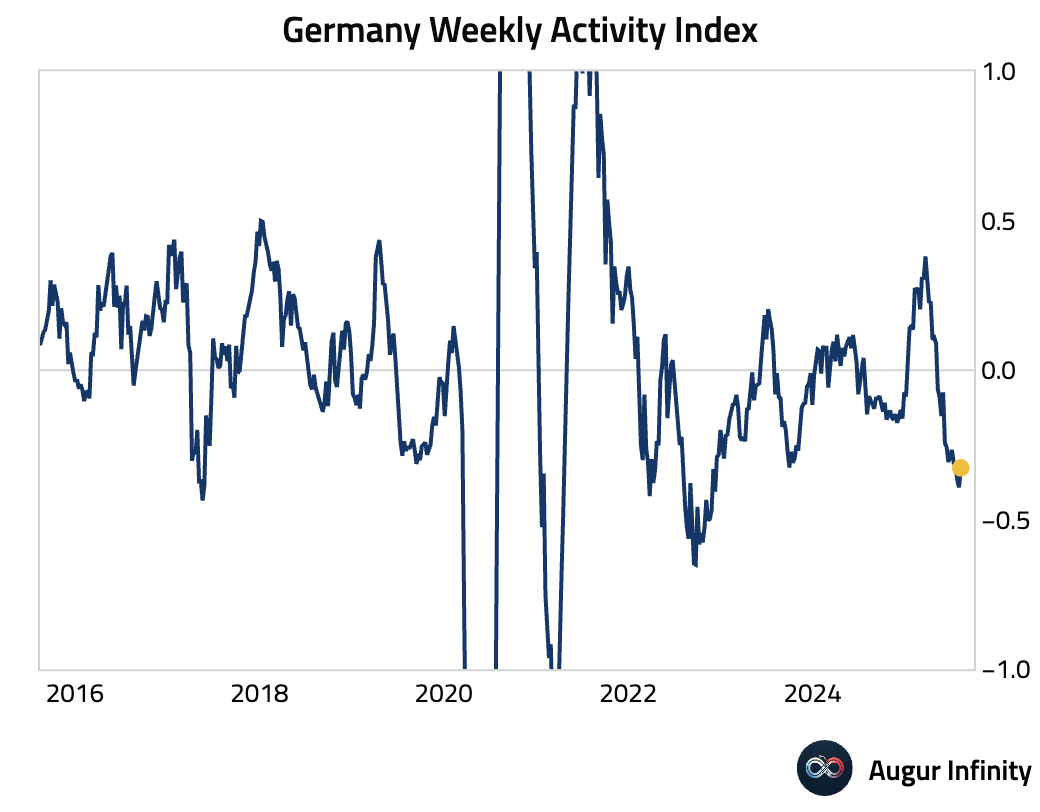
- After four consecutive weeks of declines, Germany’s Weekly Activity Index edged higher but remains close to its weakest level in two and a half years.
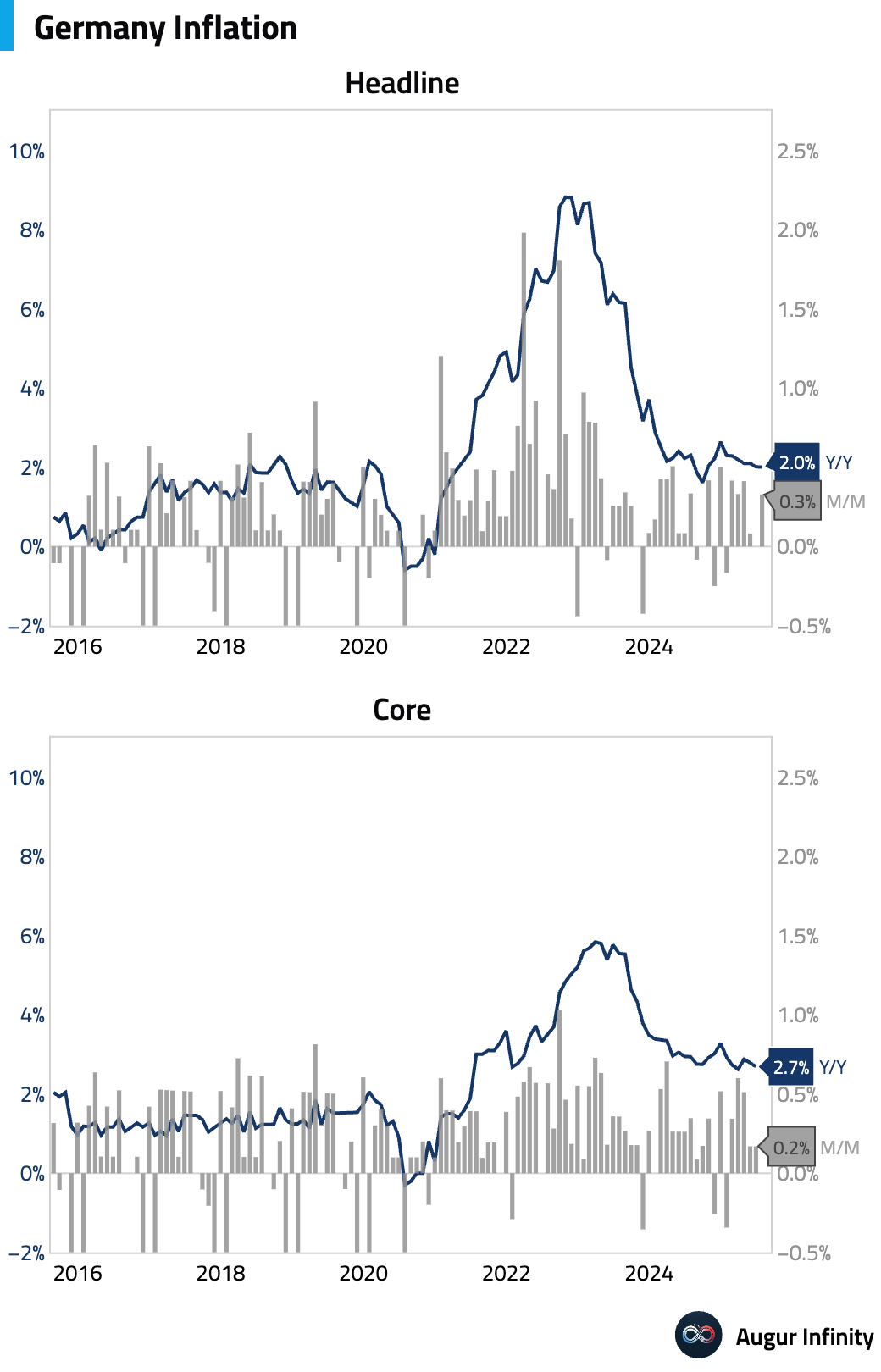
- Final inflation data for Germany confirmed prices rose 0.3% M/M and 2.0% Y/Y in July, matching both preliminary estimates and consensus. The annual rate held steady from June.
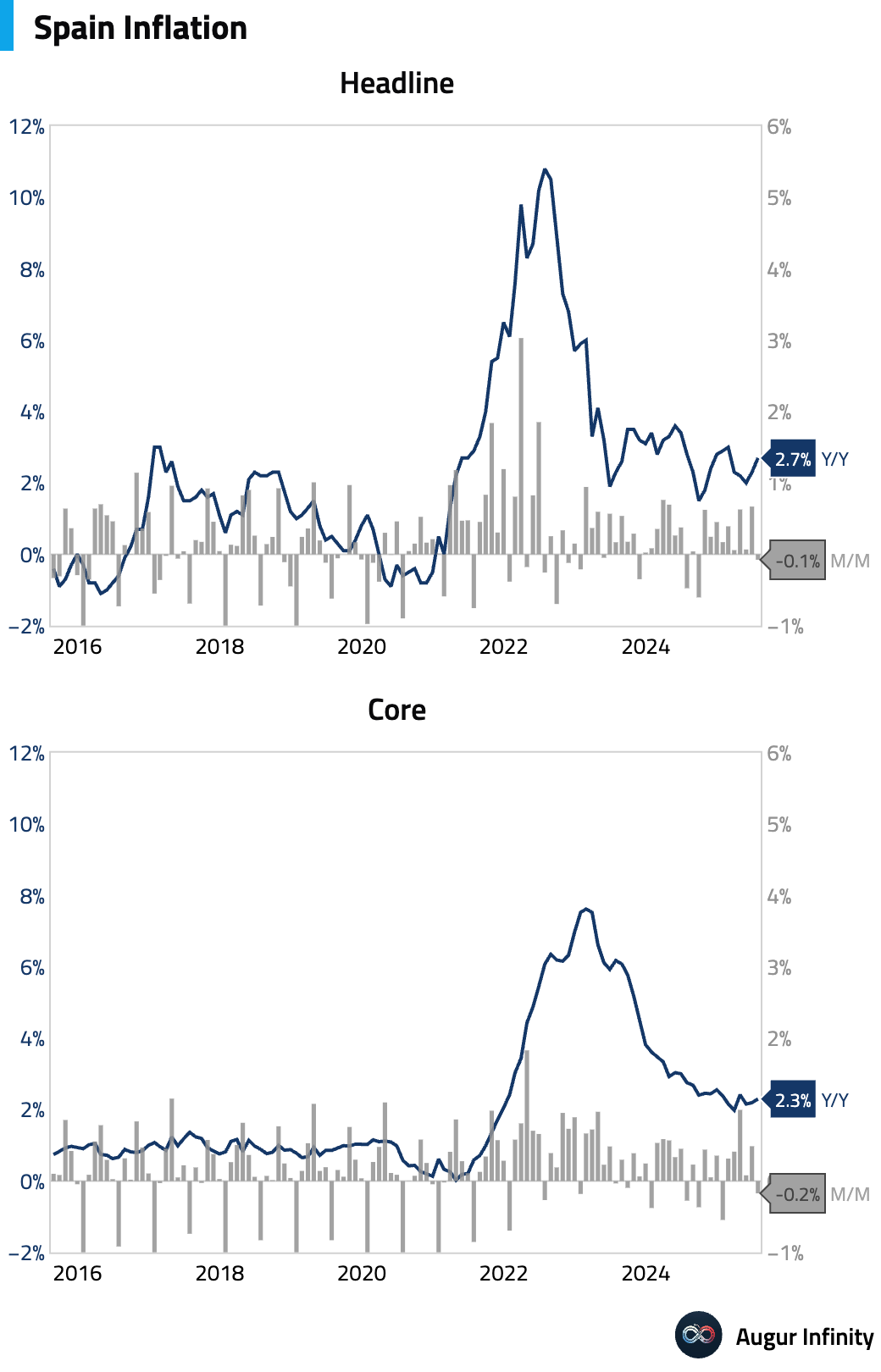
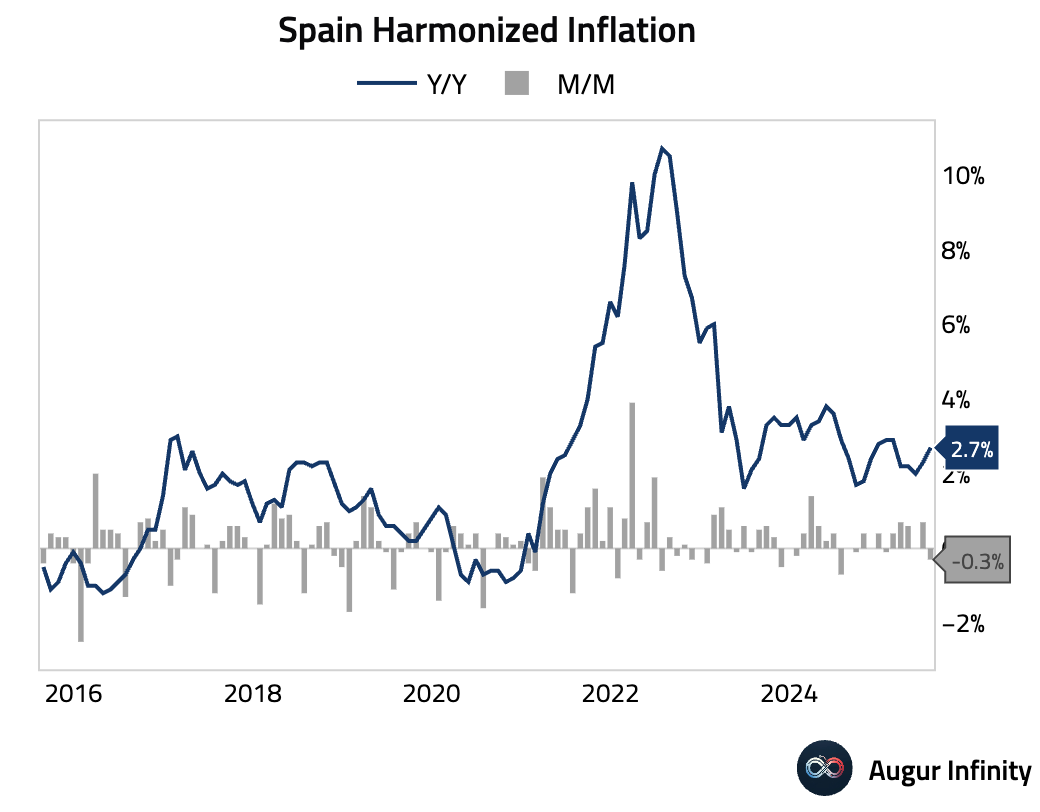
- Spain's final July inflation data confirmed an acceleration in price pressures. The headline CPI rose to 2.7% Y/Y from 2.3%, while core inflation ticked up to 2.3% Y/Y. The EU-harmonized rate also increased to 2.7% Y/Y.
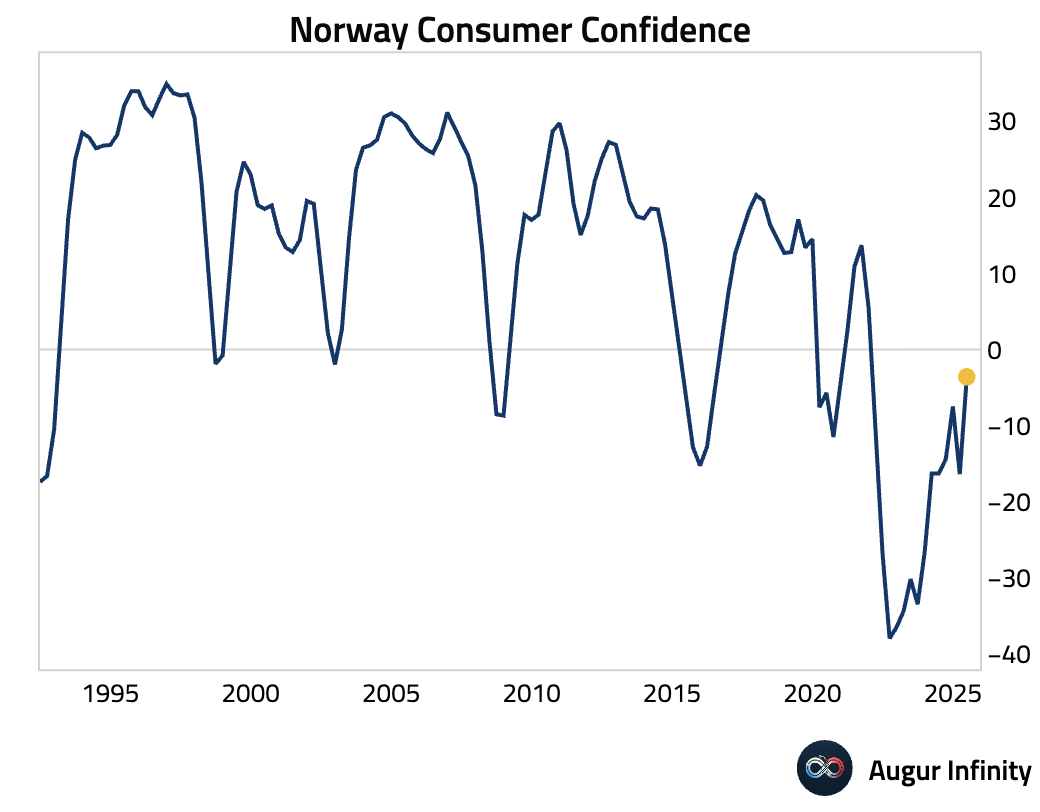
- Norwegian consumer confidence improved significantly, rising to -3.6 from -9.1 in Q3. This marks the highest level of confidence since Q1 2022.
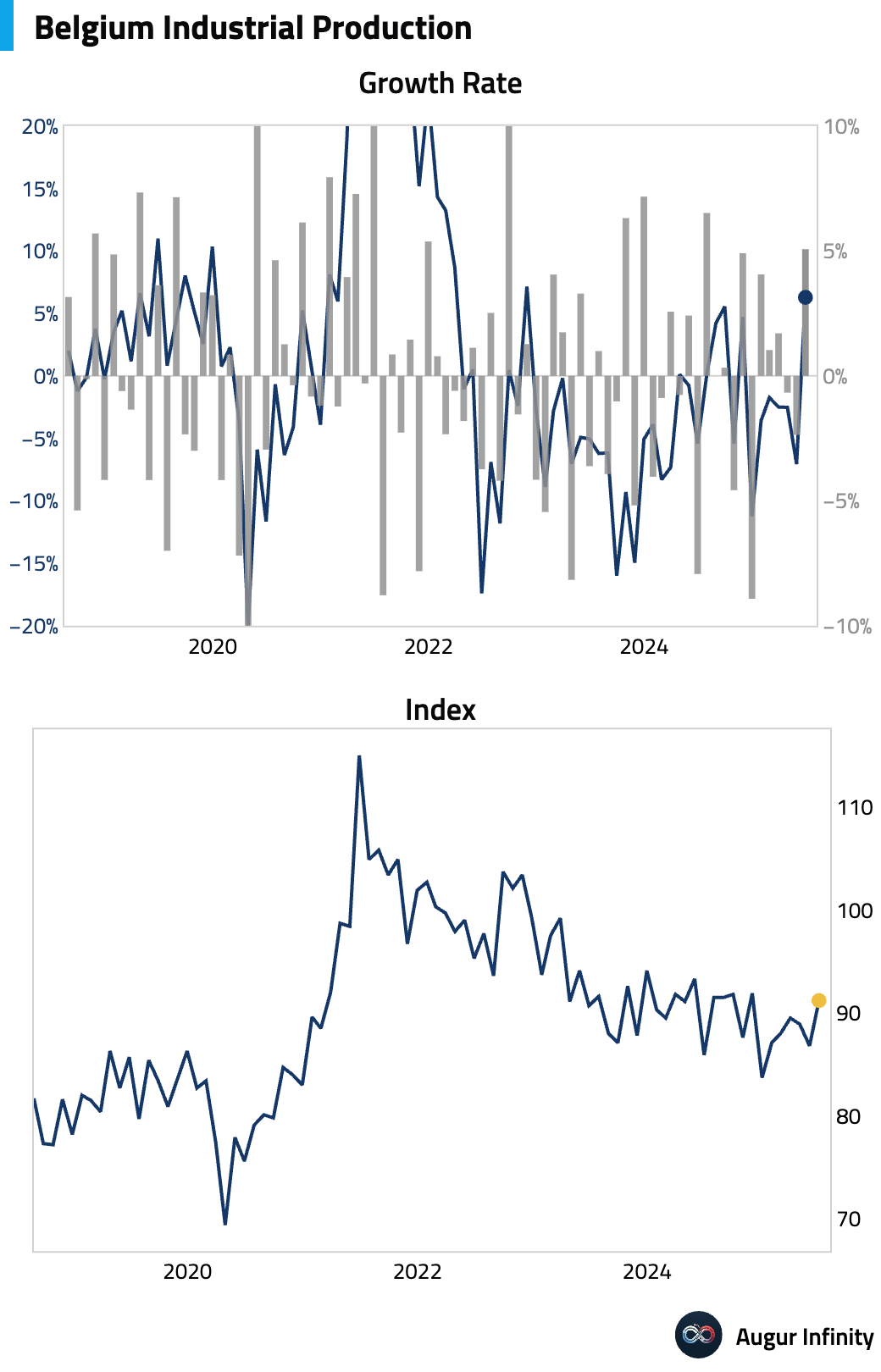
- Belgian industrial production rebounded strongly in June, rising 5.2% M/M after a 2.4% fall in May. The year-over-year figure surged to 6.3%, the strongest annual growth since November 2022.
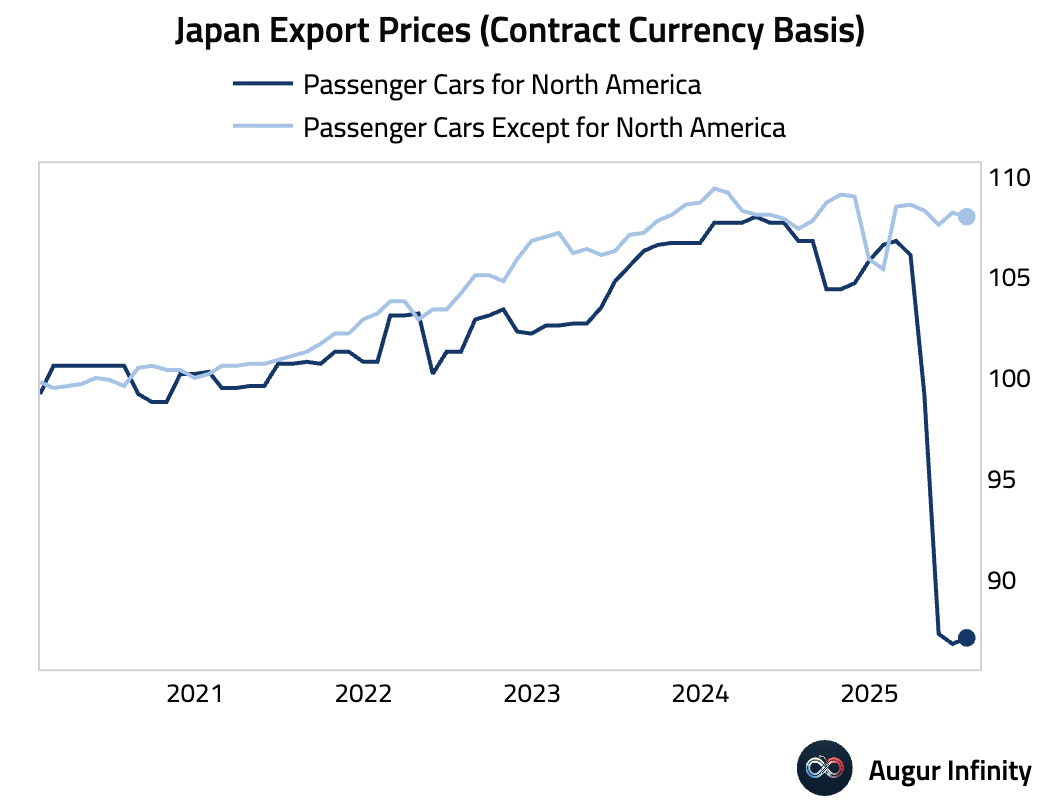
- Japan's passenger car export prices to North America rose 0.3% M/M—the first increase since February after declining by over 18%. Exporters cut prices to mitigate a 27.5% US tariff imposed in April. With the tariff expected to be reduced to 15%, this could signal the start of a price recovery for auto exporters.
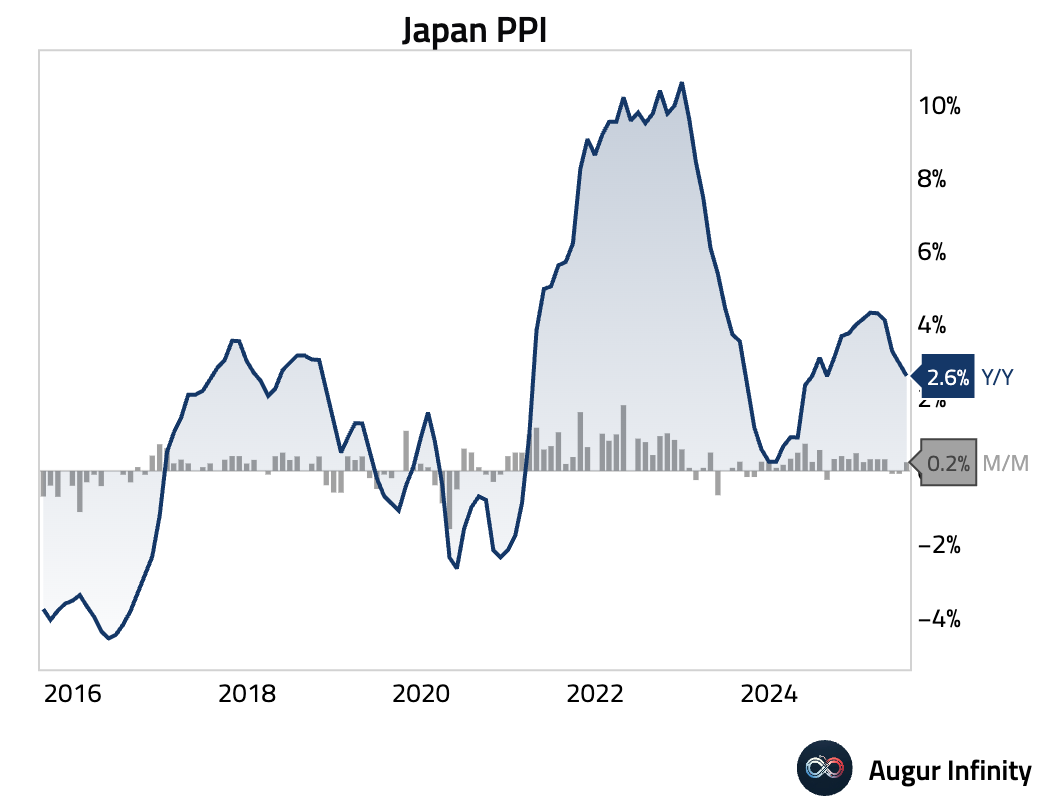
- Japan's Producer Price Index rose 0.2% M/M in July, the first increase in three months, driven by higher petroleum and coal prices and a summer electricity surcharge. The annual rate decelerated to 2.6% Y/Y from 2.9%.
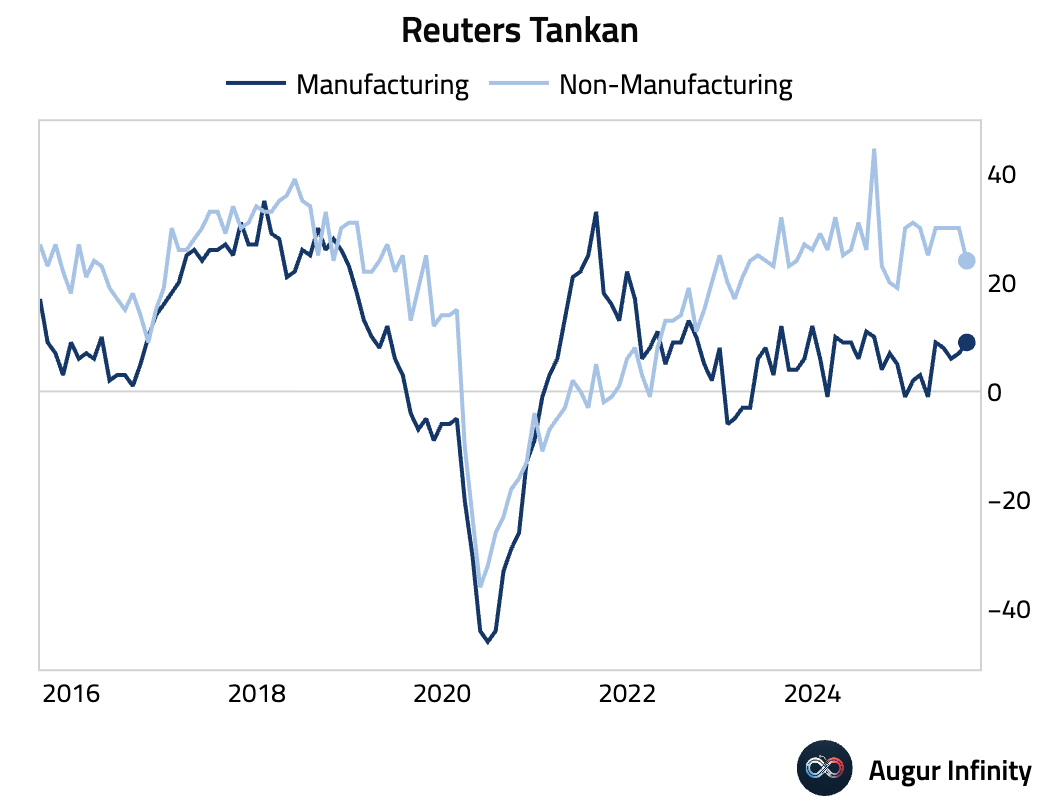
- The Reuters Tankan Index for manufacturers improved to 9.0 in August from 7.0, reaching its highest level in nearly a year. However, the Non-Manufacturing Index declined by 6 points to 24.
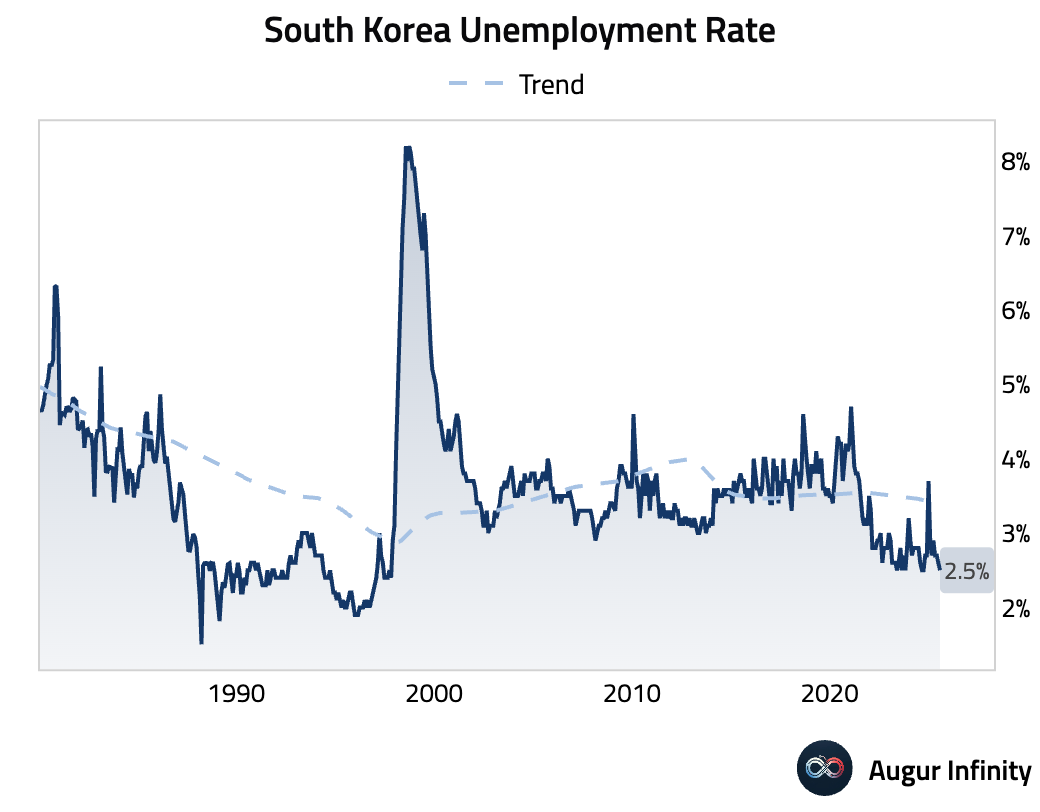
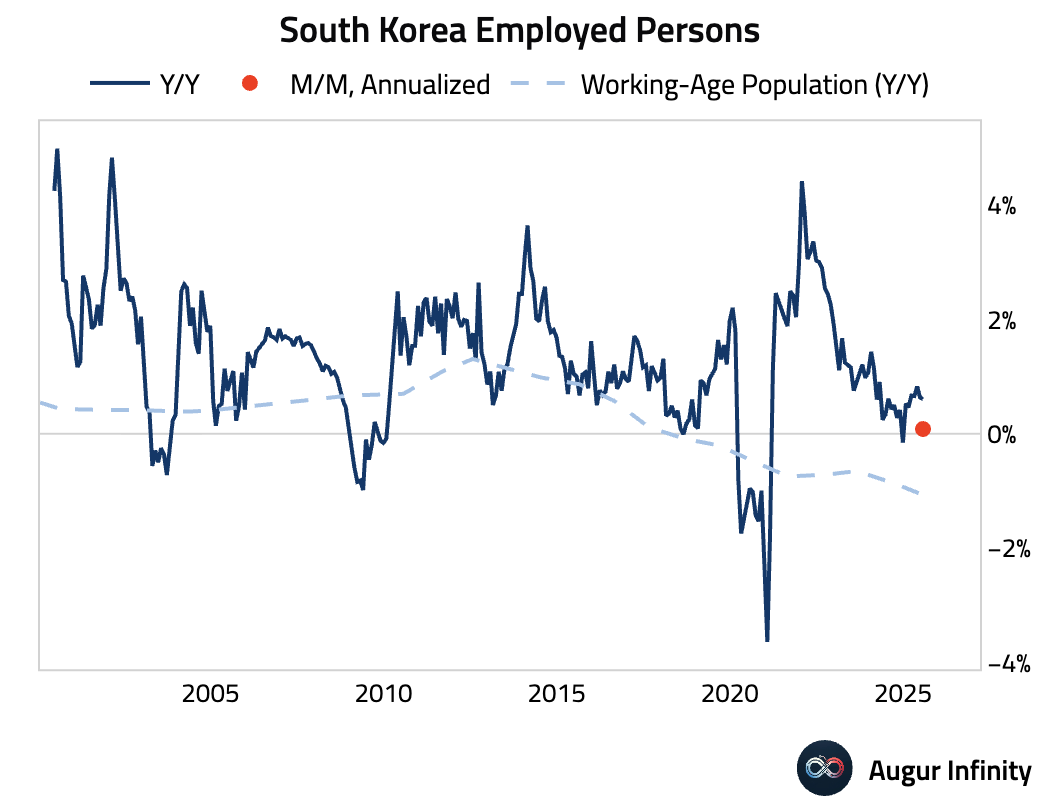
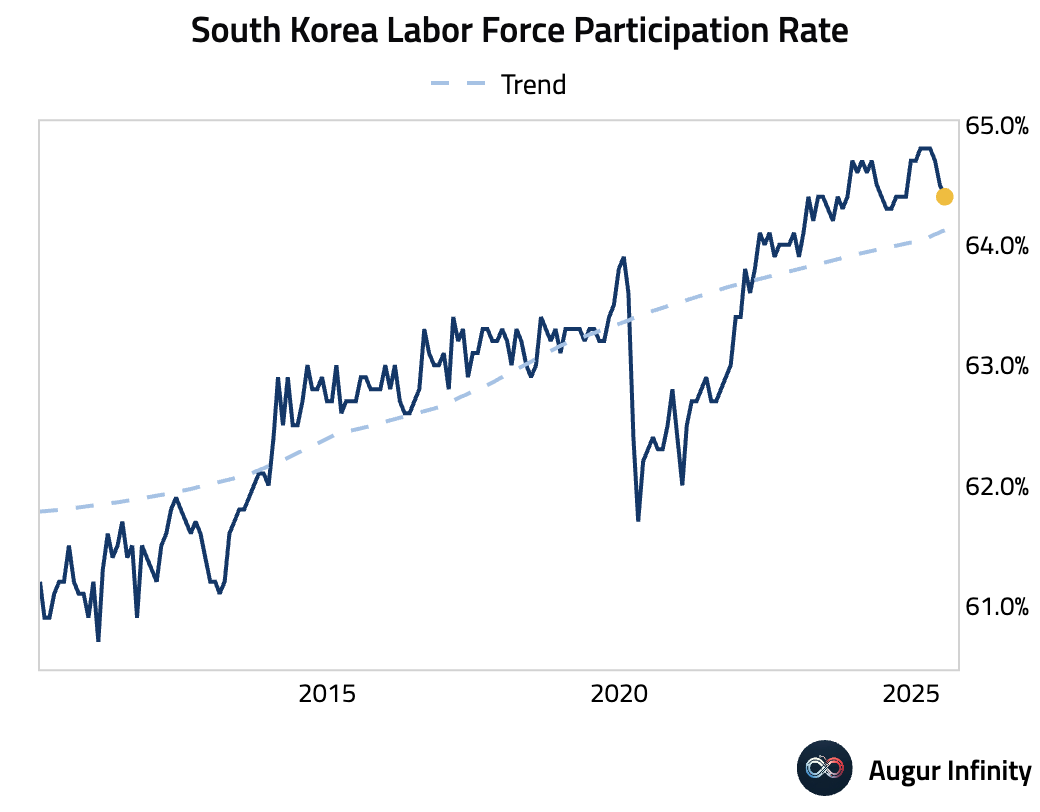
- South Korea's unemployment rate fell to 2.5% in July from 2.6%, its lowest level since October 1997.
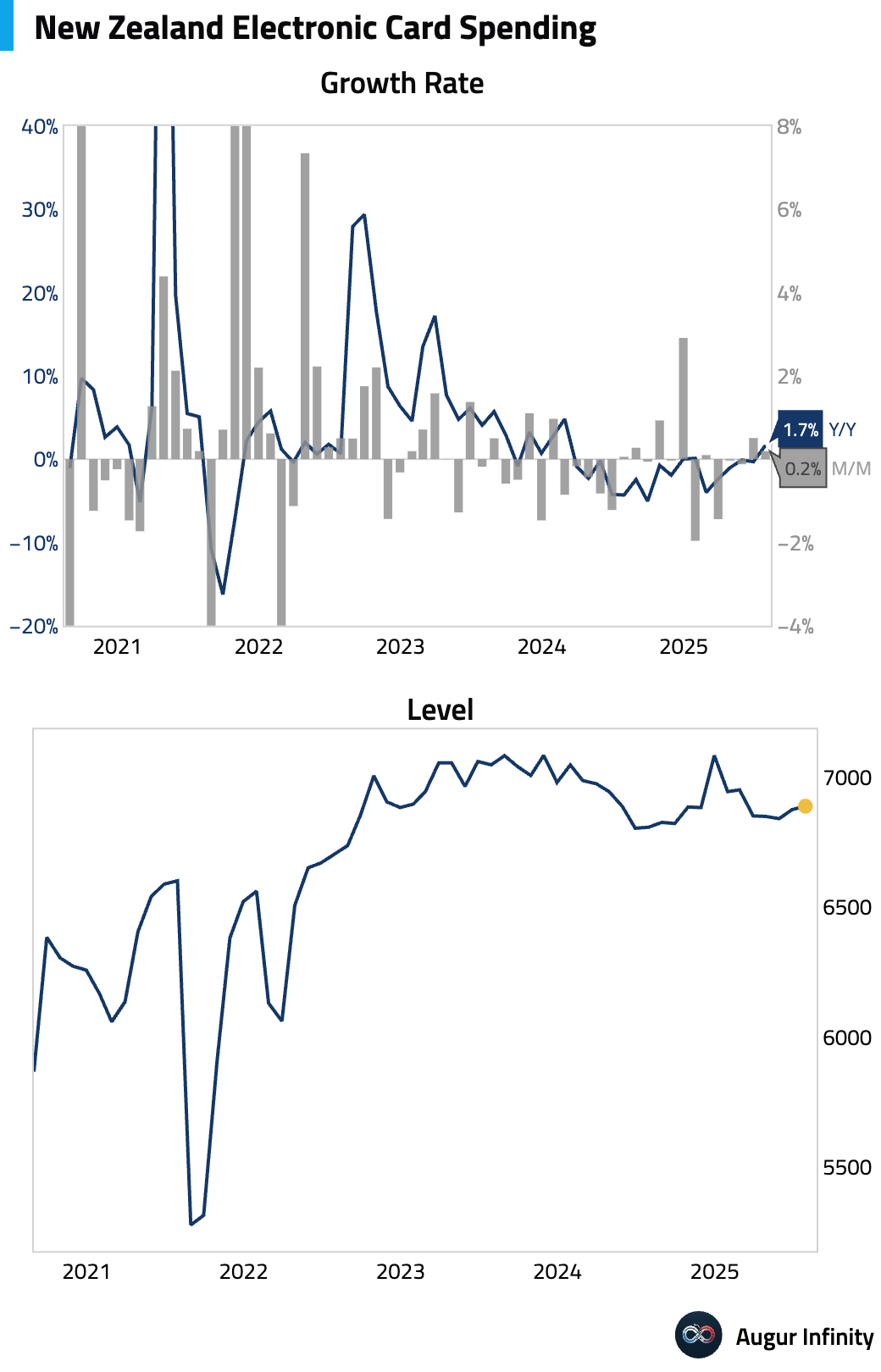
- New Zealand's electronic retail card spending recovered in July, rising 0.2% M/M and 1.7% Y/Y. This follows a 0.5% M/M increase and a 0.3% Y/Y decline in the previous period.
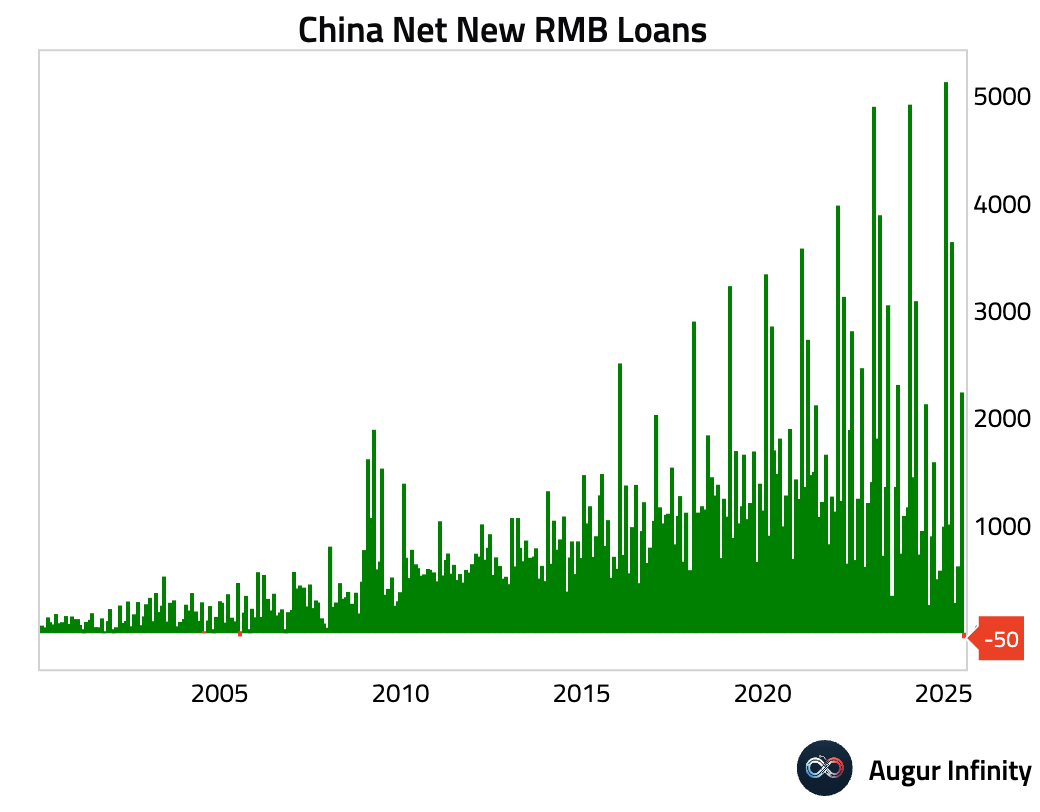
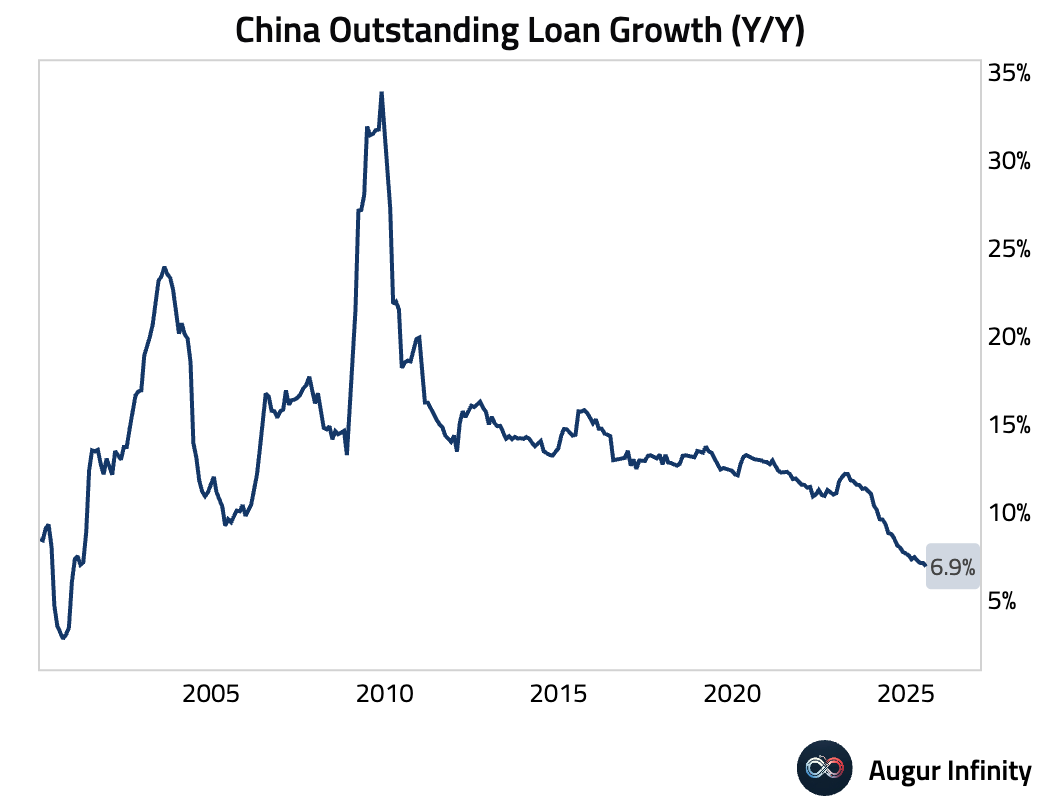
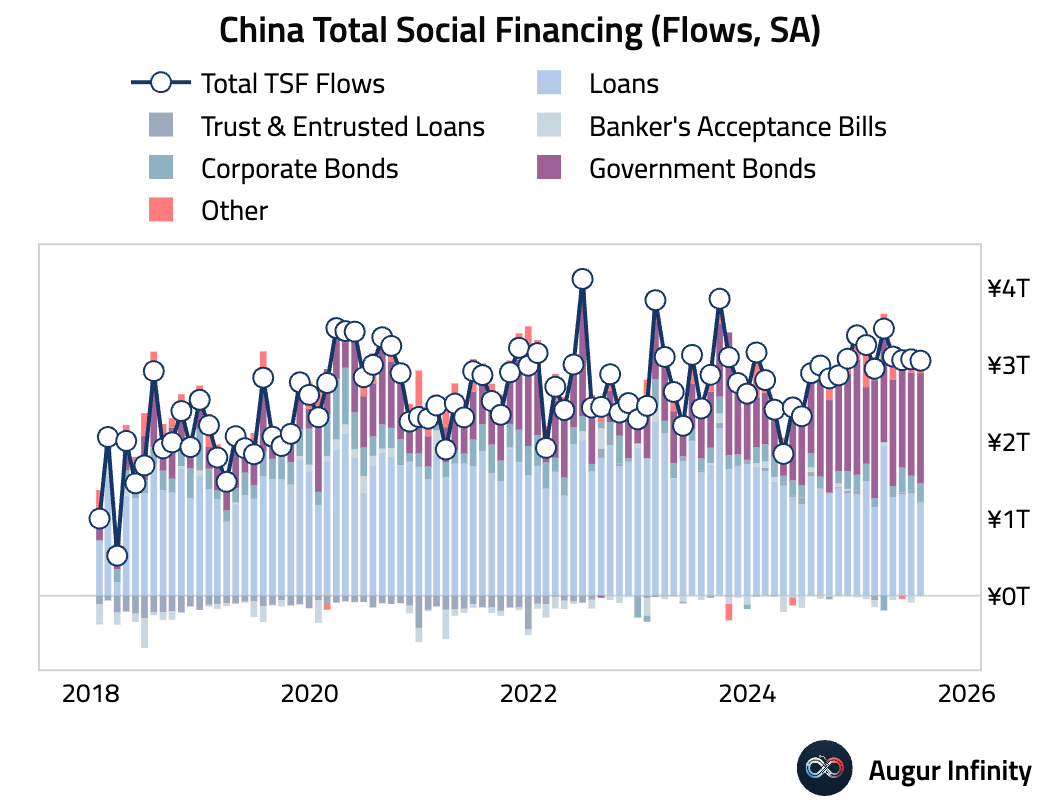
- China's July credit data revealed severe weakness in private sector demand. New yuan loans unexpectedly contracted by RMB 50 billion, the first negative print since 2005 and a massive miss of the RMB 300 billion consensus. Outstanding loan growth slowed to 6.9% Y/Y, a record low dating back to 2000. Total Social Financing (TSF) also missed expectations at RMB 1.16 trillion. The weakness in private credit was masked by strong government bond issuance, which helped push outstanding TSF growth up to 9.0% Y/Y. The data points to extremely weak credit demand from households and corporates, with a record surge in short-term bill financing suggesting banks are padding loan quotas amid a lack of real borrowers.
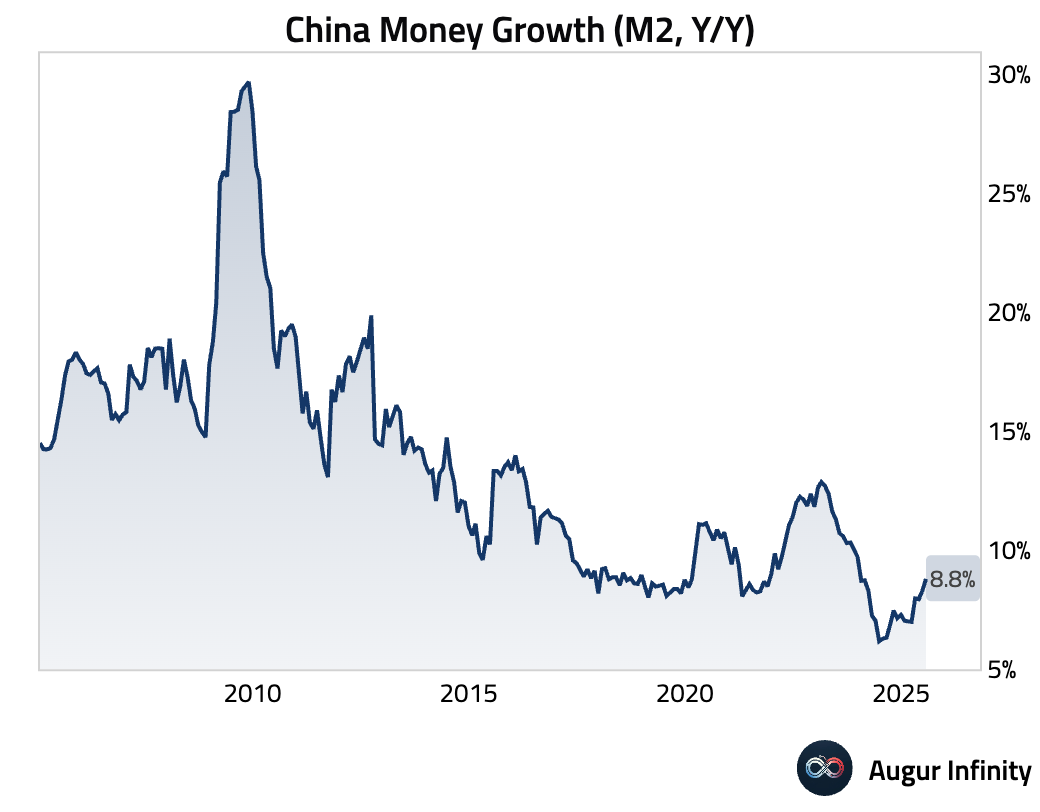
- Despite weak credit growth, China's M2 money supply growth accelerated to 8.8% Y/Y in July, beating the 8.2% consensus. The rise was attributed to a low base effect from the previous year and rapid fiscal spending, as proceeds from high government bond issuance were quickly deployed into the economy.
- In a bid to shore up demand, China announced a 1-percentage-point interest subsidy for new consumer loans and some service-sector business loans. The piecemeal measure is estimated to have a maximum fiscal cost of RMB 80 billion over 12 months. The program's impact is expected to be limited by restrictions, such as the ineligibility of credit card loans and caps on subsidized loan amounts, reinforcing the view that policymakers are avoiding large-scale, broad-based stimulus.
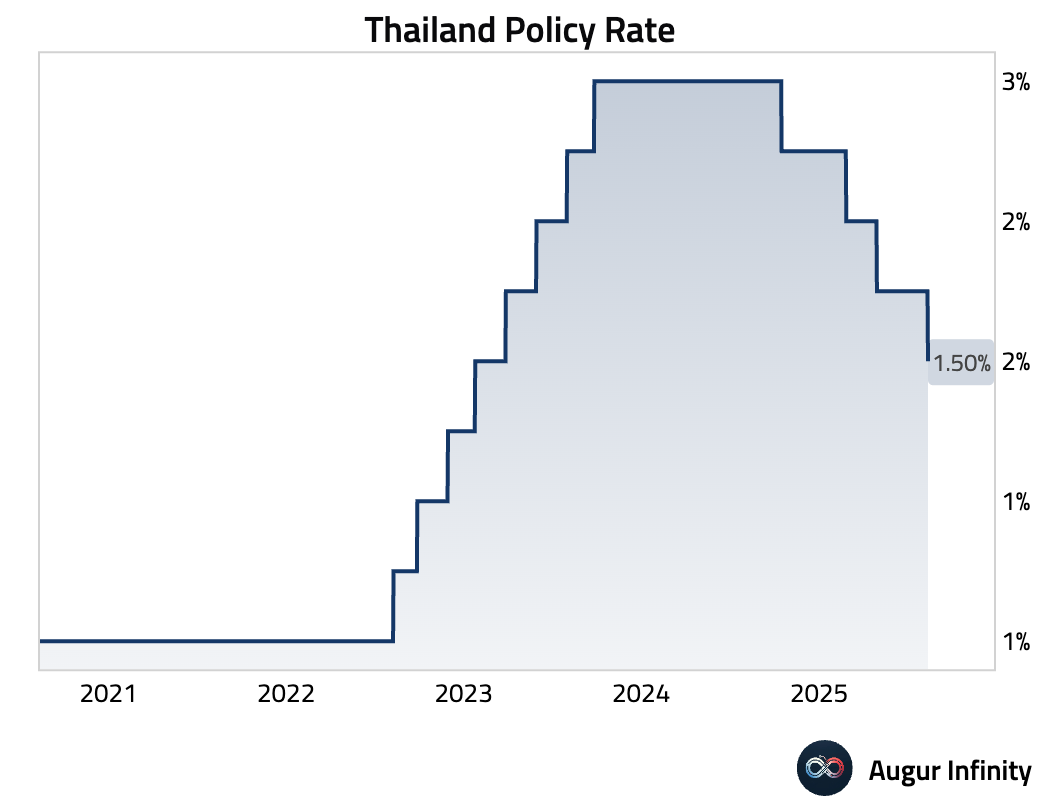
- The Bank of Thailand's monetary policy committee unanimously voted to cut its benchmark interest rate by 25 basis points to 1.50%. The surprise move was aimed at easing financial conditions for vulnerable groups like SMEs. The central bank also adopted more dovish forward guidance, signaling openness to further easing.
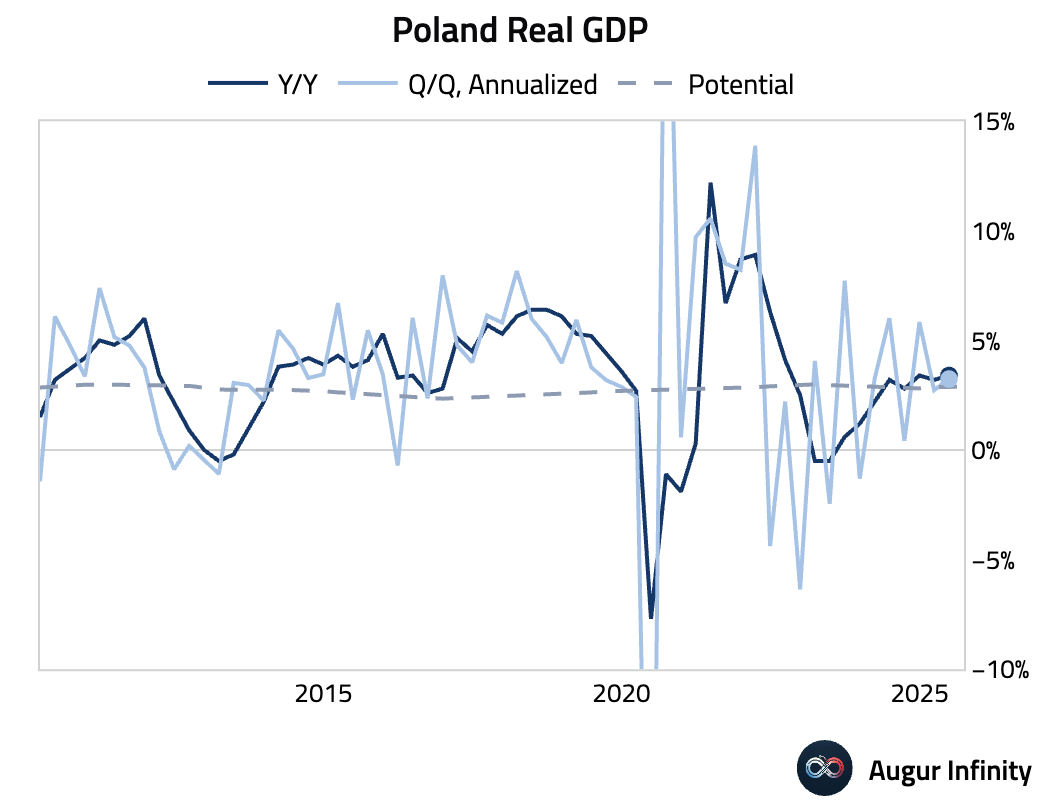
- Poland's preliminary Q2 GDP grew a robust 0.8% Q/Q, with the annual growth rate accelerating to 3.4% Y/Y from 3.2%.
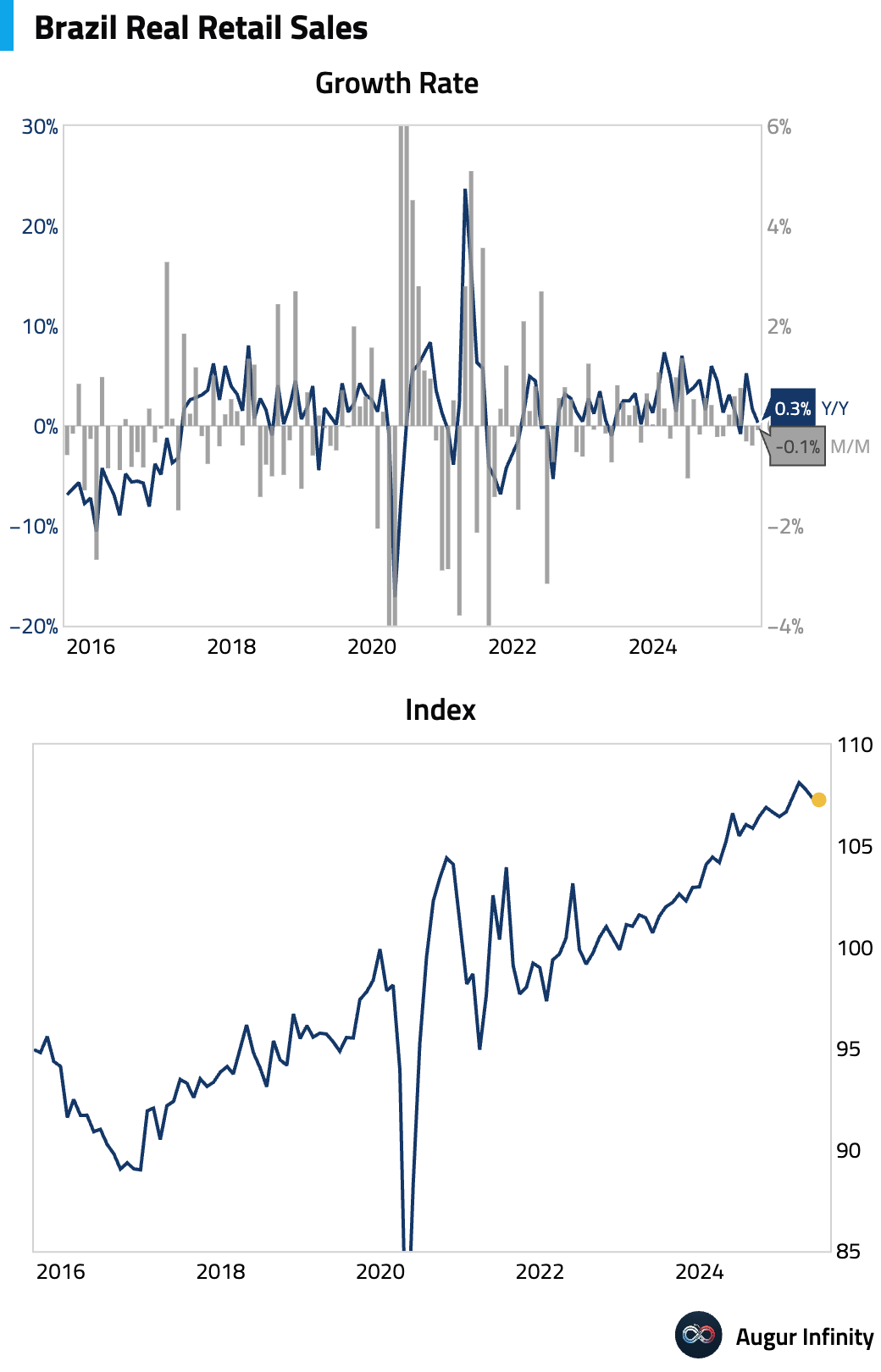
- Brazilian retail sales unexpectedly fell 0.1% M/M in June, missing the consensus forecast for a 0.7% gain. The miss was driven by declines in income-sensitive sectors, while credit-sensitive categories like autos and construction materials also posted sharp drops.
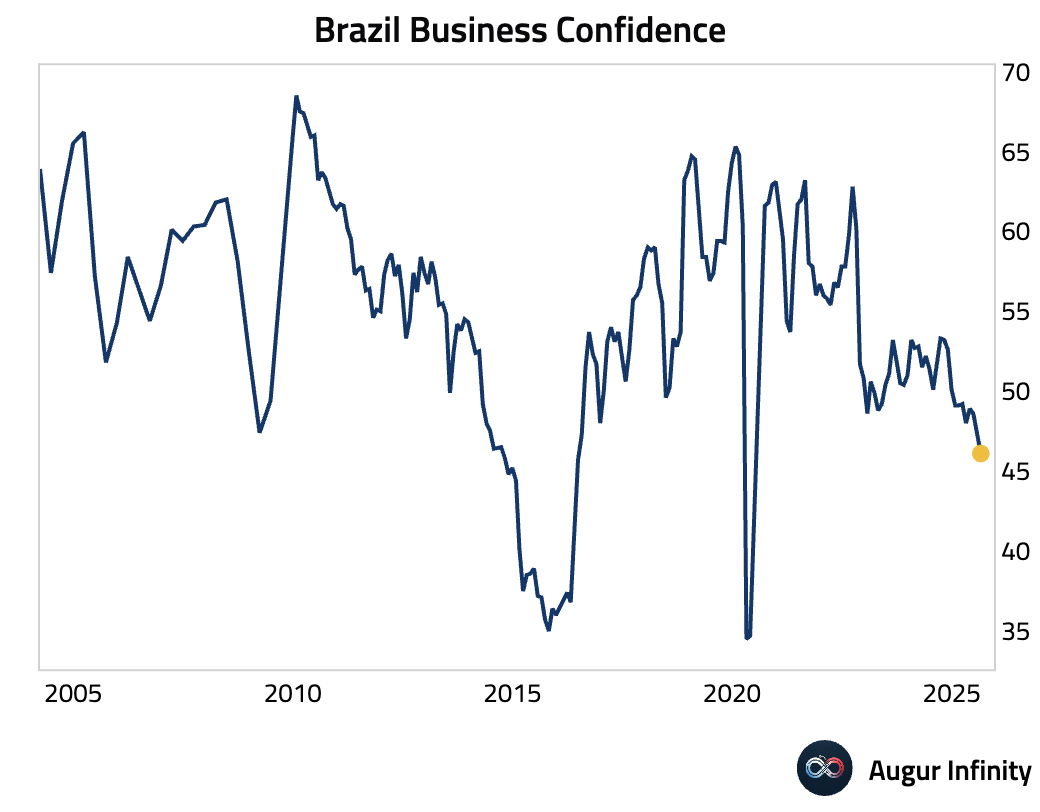
- Brazilian business confidence fell to 46.1 in August from 47.3, marking its lowest reading since the pandemic trough in June 2020.
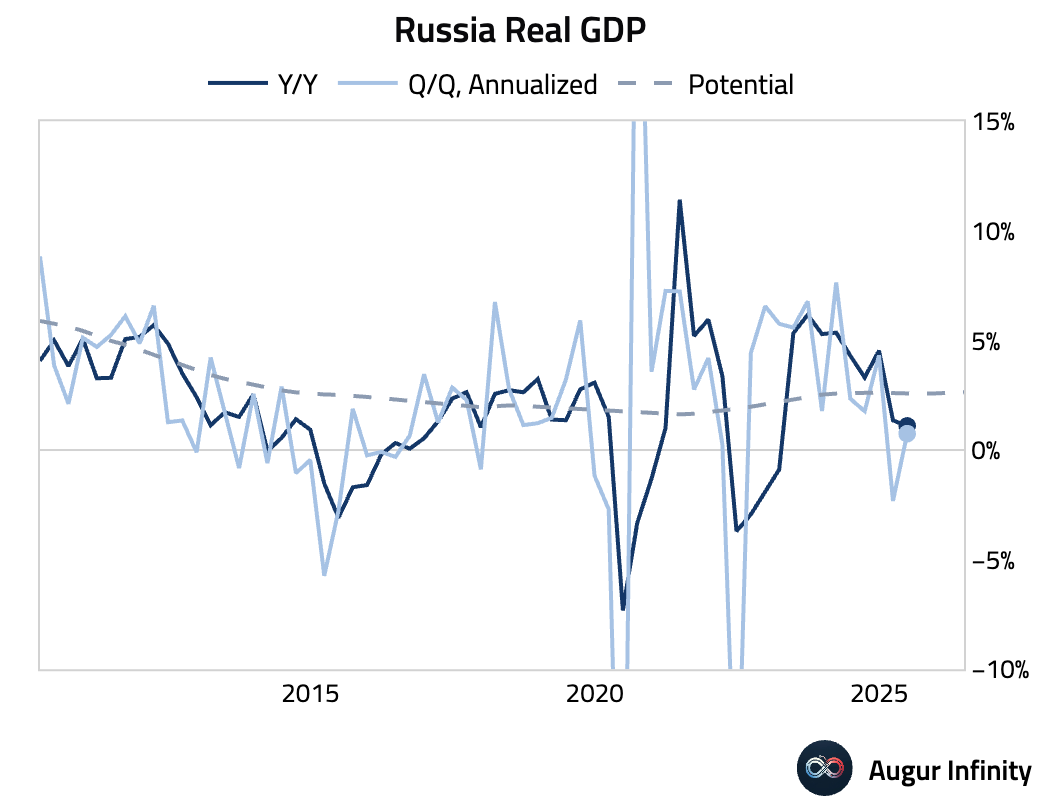
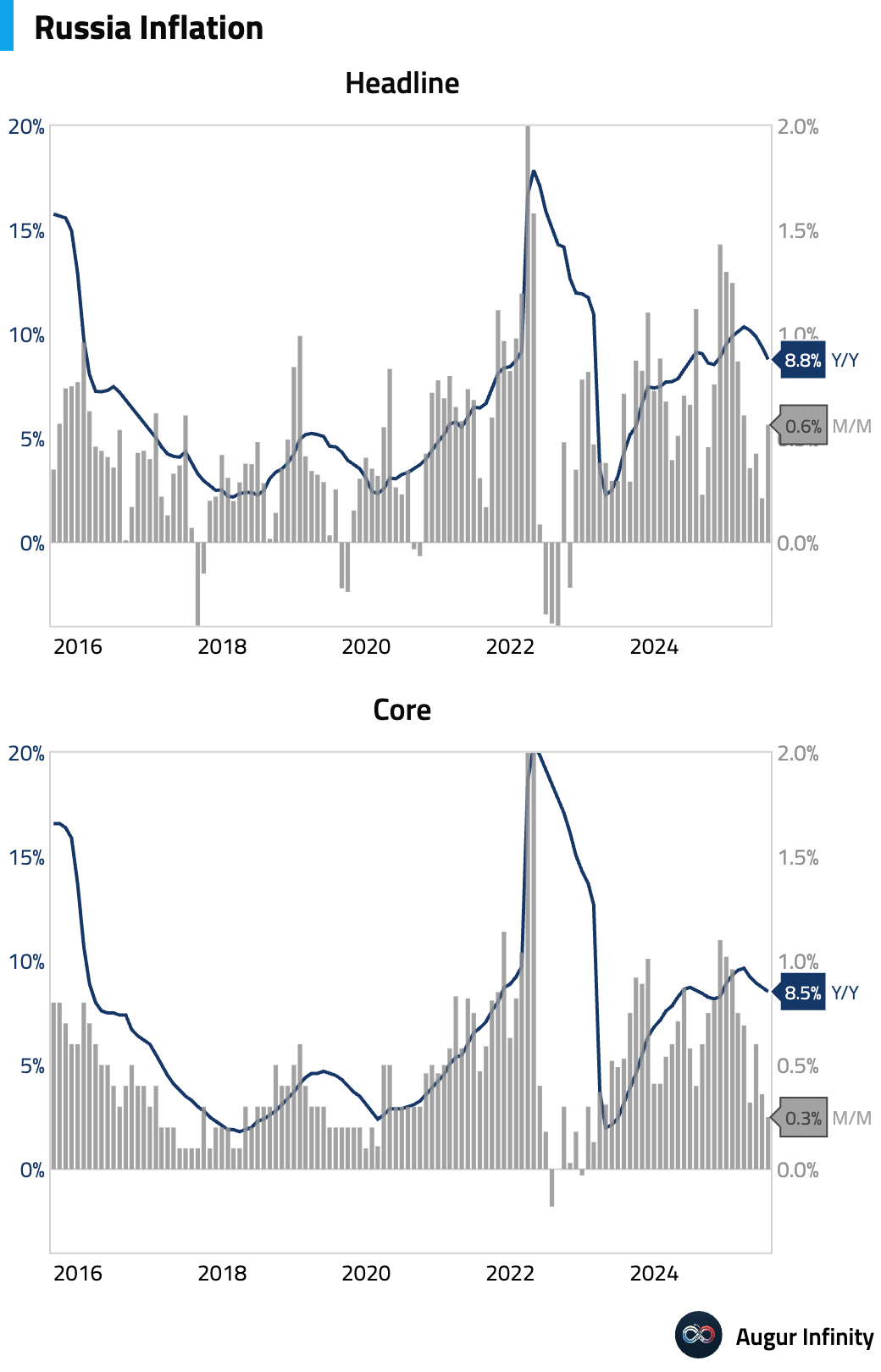
- Russia's preliminary GDP growth slowed to 1.1% Y/Y in Q2 from 1.4% in the prior quarter.
- Russian inflation accelerated to 0.6% M/M in July from 0.2% in June. However, the annual inflation rate eased to 8.8% from 9.4%, aided by base effects.
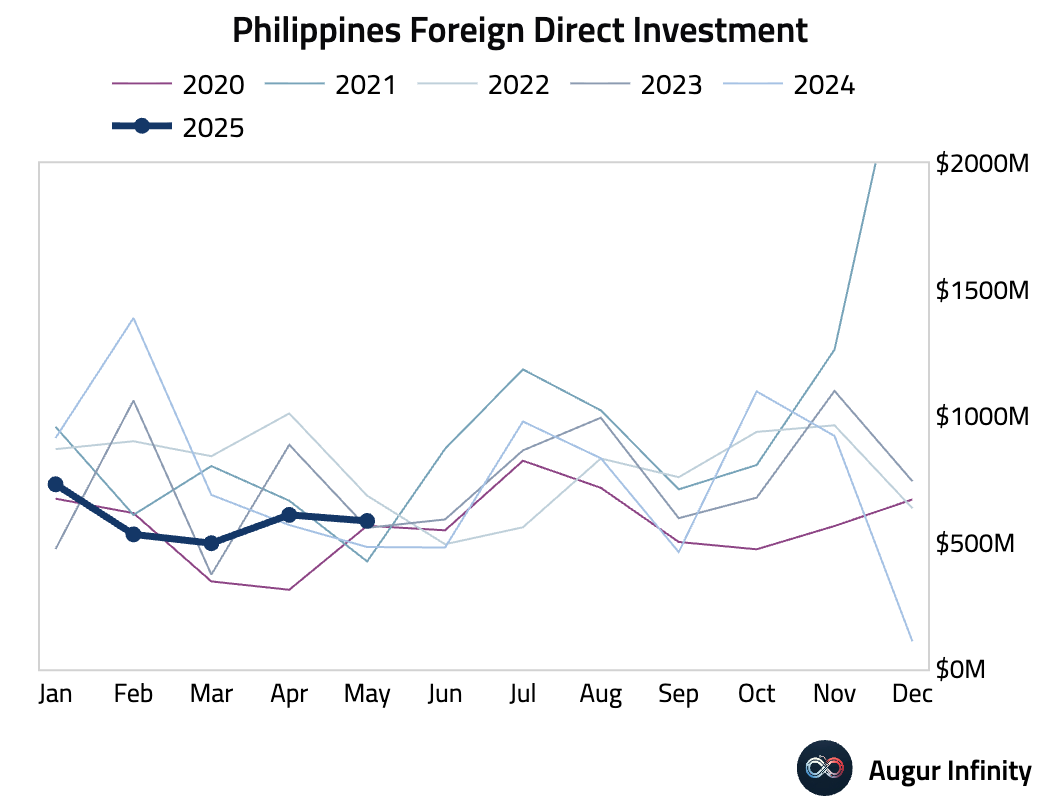
- Philippine foreign direct investment was recorded at $600 million in June, unchanged from the revised May figure.
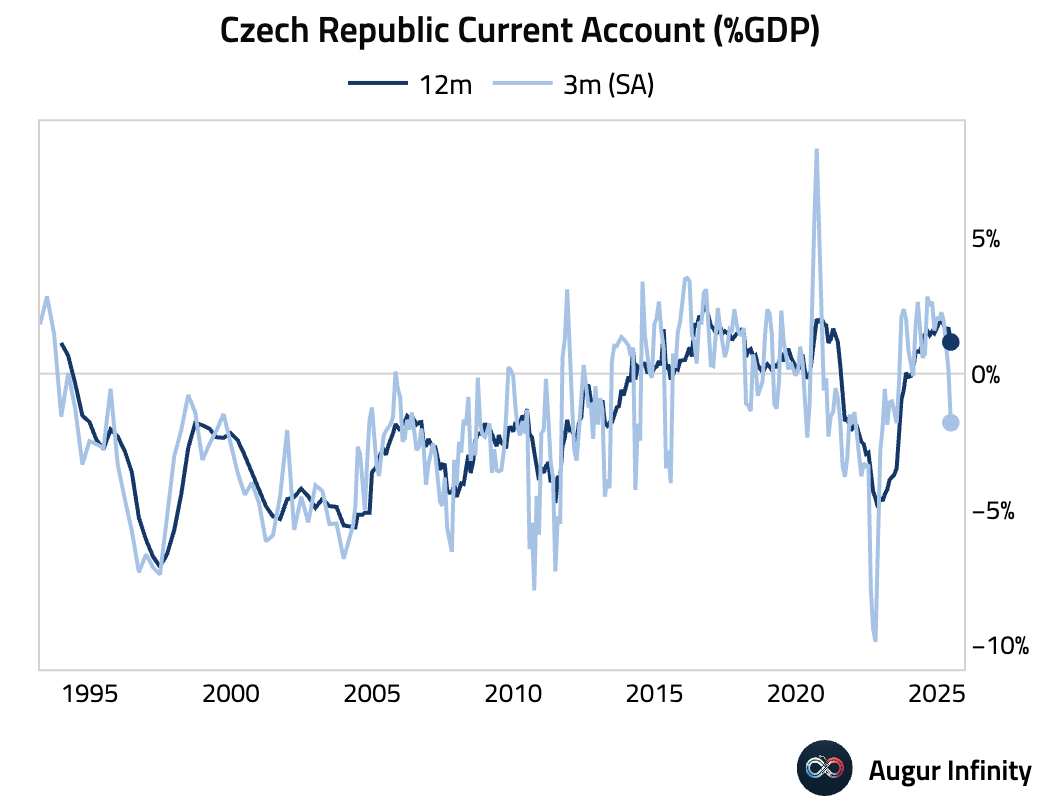
- The Czech Republic's current account deficit widened sharply to CZK 68.79 billion in June, a significant deterioration from the CZK 5.83 billion deficit in May and much larger than the CZK 22.95 billion deficit expected. This is the largest deficit since September 2022.
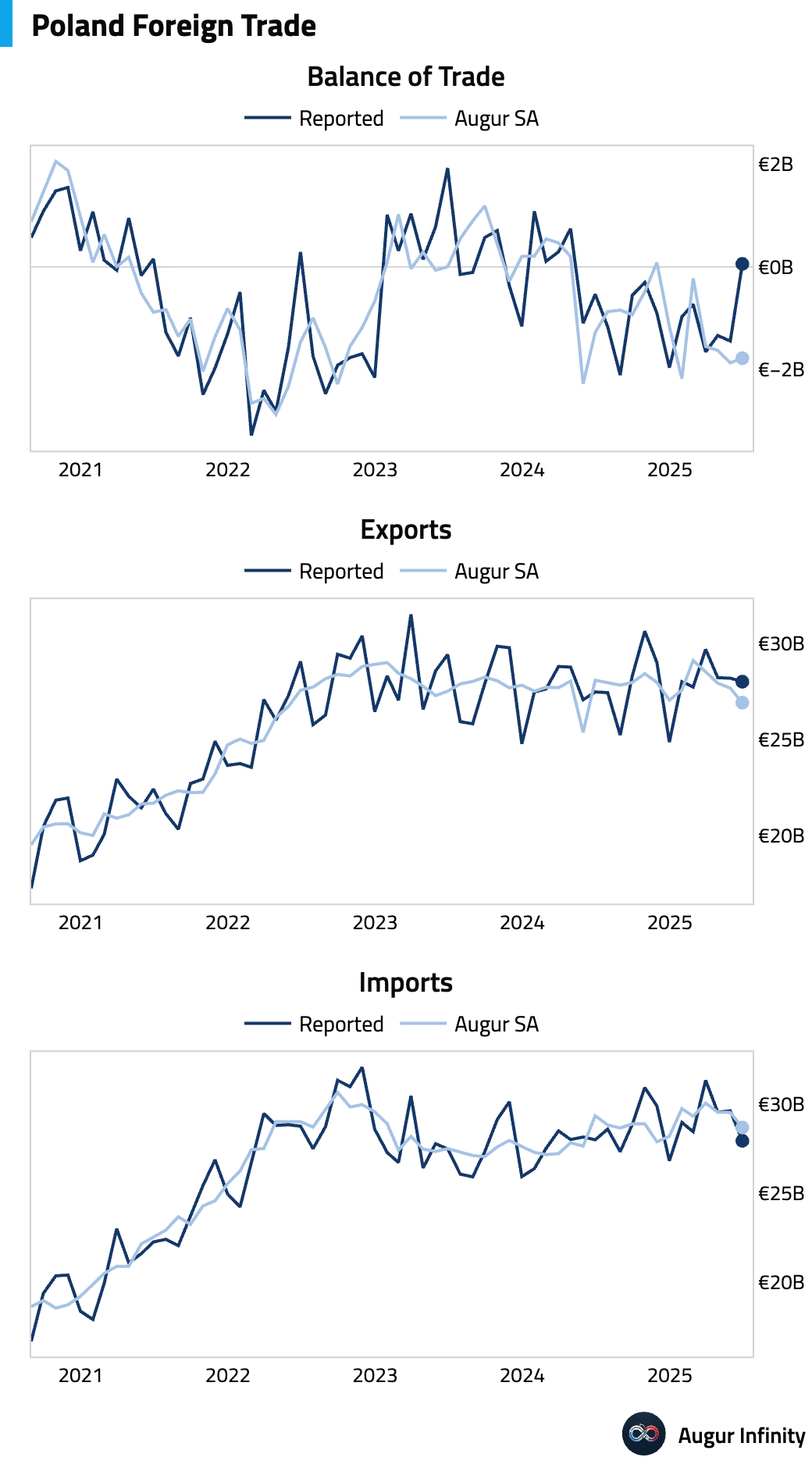
- Poland's balance of trade swung to a surplus of €59 million in June from a deficit of €1.45 billion in May. On a seasonally-adjusted basis, however, trade balance was roughly unchanged.
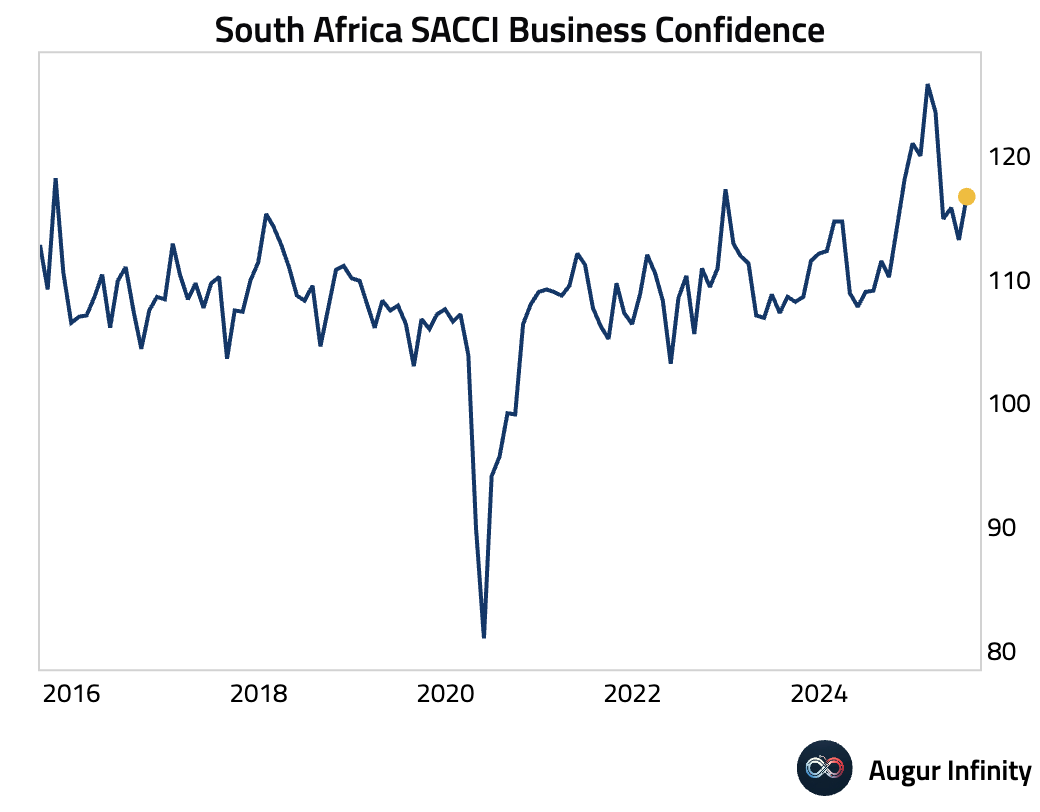
- South African business confidence, as measured by SACCI, rebounded to 116.7 in July from 113.2.
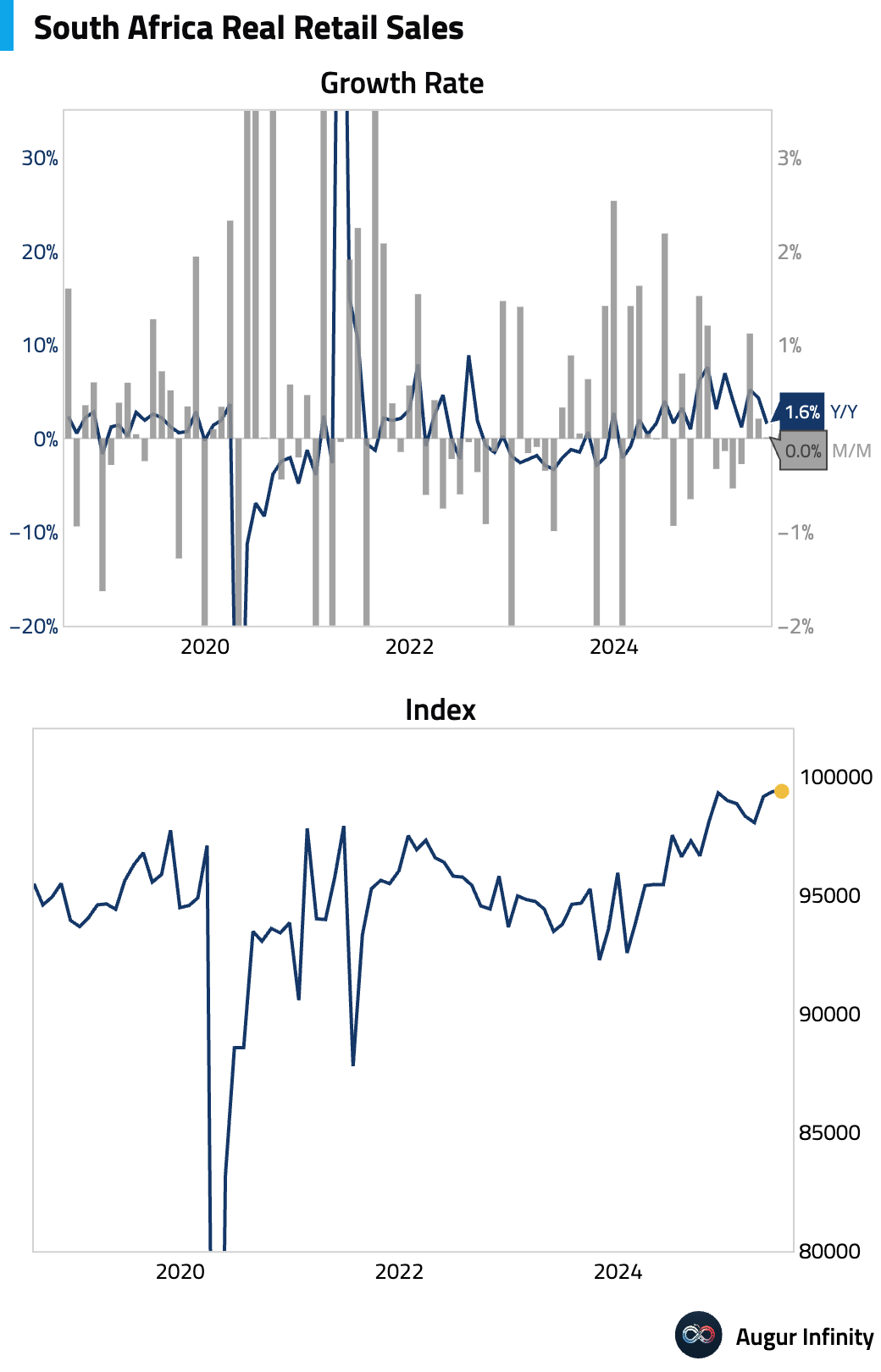
- South African retail sales were flat in June (0.0% M/M), while year-over-year growth slowed to 1.6% from 4.3% in May.
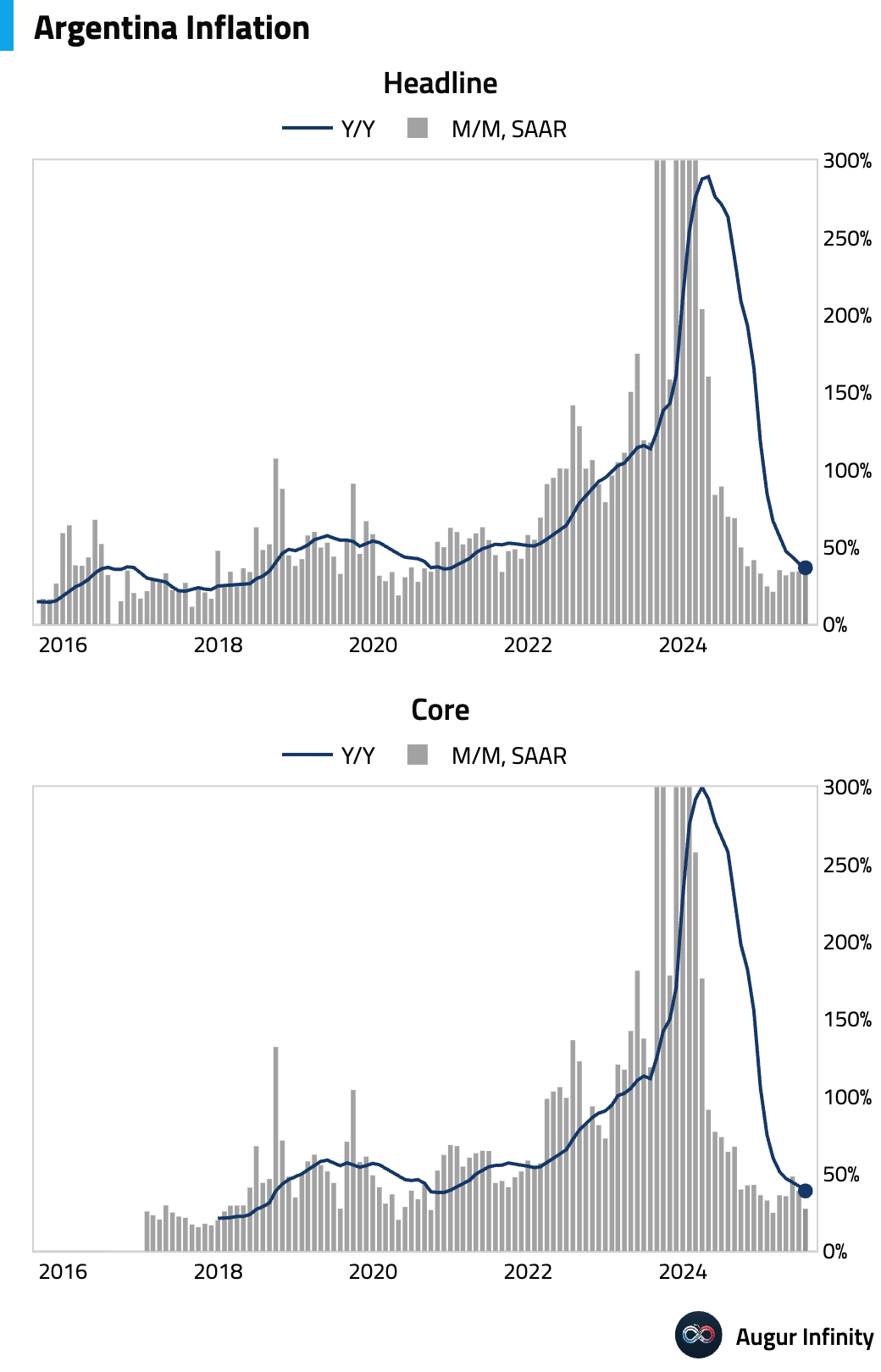
- Argentina's monthly inflation rate came in at 1.9% in July, slightly above the 1.8% consensus and accelerating from 1.6% in June. Year-over-year inflation eased to 36.6%.
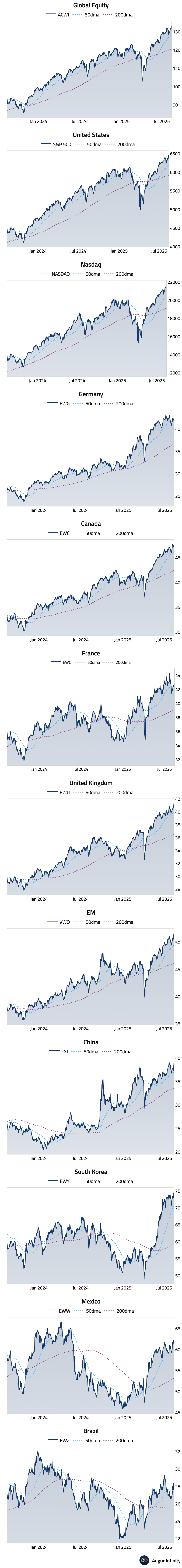
- Global equity markets rallied, driven by dovish sentiment following comments from the US Treasury Secretary. US markets advanced, with the S&P 500 rising 0.32% and the Nasdaq climbing 0.14%. The rally was broad-based, with Chinese equities surging 2.7% and Emerging Markets gaining 1.1%. In Europe, UK equities rose 0.8%, marking a ninth consecutive day of gains. Latin American markets diverged, with Brazil and Mexico declining 0.9% and 0.7%, respectively.
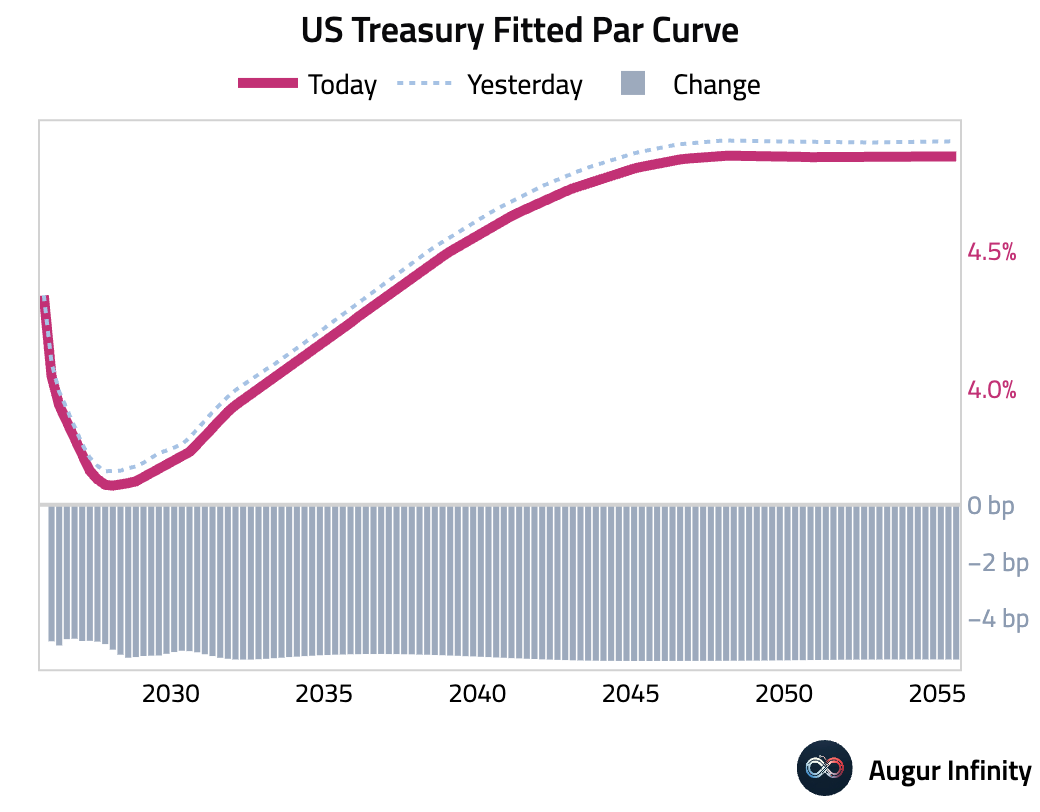
- US Treasury yields fell across the curve as markets increased bets on a near-term Federal Reserve rate cut. Yields on the 2-year and 5-year notes declined for a third straight day, falling by 5.1 bps and 5.7 bps, respectively. The 10-year yield dropped 5.6 bps and the 30-year yield eased by 5.8 bps.
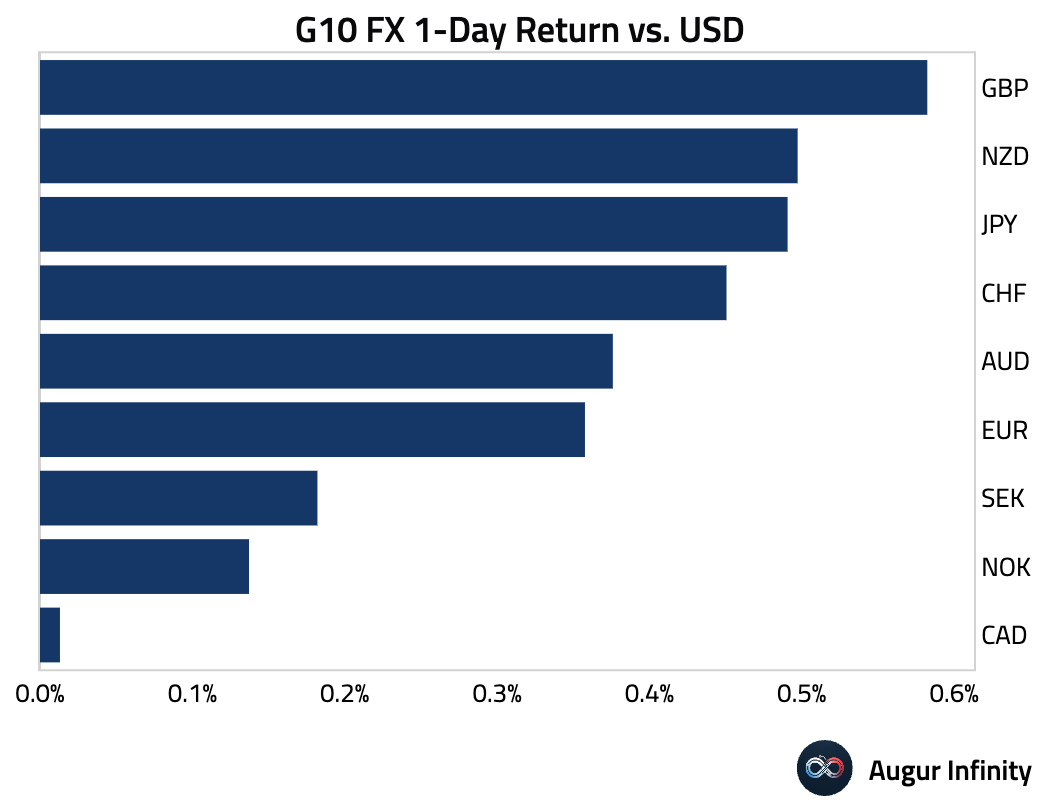
- The US dollar weakened against all G10 peers amid growing expectations for Fed easing. The British pound was the day's top performer, strengthening by 0.6%. The Japanese yen, New Zealand dollar, and Swiss franc all rose by 0.5%. The Norwegian krone gained for a third consecutive day, adding 0.1%.
Asia-Pacific
China
Emerging Markets ex China
Global Markets
Equities
Fixed Income
FX
Disclaimer
Augur Digest is an automatically generated newsletter edited by humans. It may contain inaccuracies and is not investment advice. Augur Labs LLC will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your reliance on the information contained in the newsletter.

